Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
State exterior angle theorem.
Solution
Exterior angle theorem states that, if a side of a triangle is produced, the exterior angle so formed is equal to the sum of the two interior opposite angles.
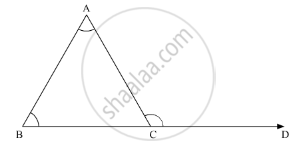
Thus, in ΔABC
∠ACD = ∠A +∠B
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Can a triangle have two acute angles?Justify your answer in case.
If the bisector of the exterior vertical angle of a triangle be parallel to the base. Show that the triangle is isosce
Is the following statement true and false :
A triangle can have two obtuse angles.
Calculate the unknown marked angles of the following figure :
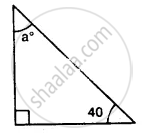
Find the value of the angle in the given figure:
In the given figure, show that: ∠a = ∠b + ∠c
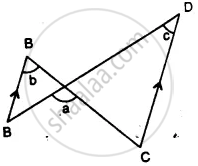
(i) If ∠b = 60° and ∠c = 50° ; find ∠a.
(ii) If ∠a = 100° and ∠b = 55° : find ∠c.
(iii) If ∠a = 108° and ∠c = 48° ; find ∠b.
One angle of a right-angled triangle is 70°. Find the other acute angle.
Find, giving a reason, the unknown marked angles, in a triangle drawn below:

The length of the sides of the triangle is given. Say what types of triangles they are 3.4 cm, 3.4 cm, 5 cm.
In figure, points lying in the interior of the triangle PQR are ______, that in the exterior are ______ and that on the triangle itself are ______.