Advertisements
Chapters
2: Exponents of Real Numbers
3: Rationalisation
4: Algebraic Identities
5: Factorisation of Algebraic Expressions
6: Factorisation of Polynomials
7: Linear Equations in Two Variables
8: Co-ordinate Geometry
9: Introduction to Euclid’s Geometry
10: Lines and Angles
▶ 11: Triangle and its Angles
12: Congruent Triangles
13: Quadrilaterals
14: Areas of Parallelograms and Triangles
15: Circles
16: Constructions
17: Heron’s Formula
18: Surface Areas and Volume of a Cuboid and Cube
19: Surface Areas and Volume of a Circular Cylinder
20: Surface Areas and Volume of A Right Circular Cone
21: Surface Areas and Volume of a Sphere
22: Tabular Representation of Statistical Data
23: Graphical Representation of Statistical Data
24: Measures of Central Tendency
25: Probability
![RD Sharma solutions for Mathematics [English] Class 9 chapter 11 - Triangle and its Angles RD Sharma solutions for Mathematics [English] Class 9 chapter 11 - Triangle and its Angles - Shaalaa.com](/images/8193647912-mathematics-english-class-9_6:1a030933ece146238cec338f12706a07.jpg)
Advertisements
Solutions for Chapter 11: Triangle and its Angles
Below listed, you can find solutions for Chapter 11 of CBSE RD Sharma for Mathematics [English] Class 9.
RD Sharma solutions for Mathematics [English] Class 9 11 Triangle and its Angles Exercise 11.1 [Page 10]
In a ΔABC, if ∠A = 55°, ∠B = 40°, find ∠C.
If the angles of a triangle are in the ratio 1: 2 : 3, determine three angles.
The angles of a triangle are (x − 40)°, (x − 20)° and `(1/2x-10)^@.` find the value of x
Two angles of a triangle are equal and the third angle is greater than each of those angles
by 30°. Determine all the angles of the triangle.
If one angle of a triangle is equal to the sum of the other two, show that the triangle is a
right triangle.
Can a triangle have two right angles? Justify your answer in case.
Can a triangle have two obtuse angles? Justify your answer in case.
Can a triangle have two acute angles?Justify your answer in case.
Can a triangle have All angles more than 60°? Justify your answer in case.
Can a triangle have All angles less than 60° Justify your answer in case.
Can a triangle have All angles equal to 60°? Justify your answer in case.
The angles of a triangle are arranged in ascending order of magnitude. If the difference
between two consecutive angles is 10°, find the three angles.
ABC is a triangle in which ∠A — 72°, the internal bisectors of angles B and C meet in O.
Find the magnitude of ∠BOC.
The bisectors of base angles of a triangle cannot enclose a right angle in any case.
If the bisectors of the base angles of a triangle enclose an angle of 135°, prove that the triangle is a right triangle.
In a ΔABC, ∠ABC = ∠ACB and the bisectors of ∠ABC and ∠ACB intersect at O such that ∠BOC = 120°. Show that ∠A = ∠B = ∠C = 60°.
If each angle of a triangle is less than the sum of the other two, show that the triangle is acute angled.
RD Sharma solutions for Mathematics [English] Class 9 11 Triangle and its Angles Exercise 11.2 [Pages 19 - 22]
The exterior angles, obtained on producing the base of a triangle both way are 104° and 136°. Find all the angles of the triangle.
In the given figure, the sides BC, CA and AB of a Δ ABC have been produced to D, E and F respectively. If ∠ACD = 105° and ∠EAF = 45°, find all the angles of the Δ ABC.
Compute the value of x in the following figure:
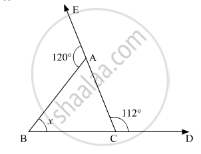
Compute the value of x in the following figure:
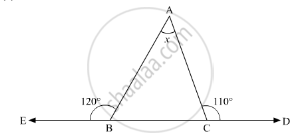
Compute the value of x in the following figure:
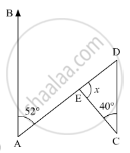
In the given figure, AC ⊥ CE and ∠A : ∠B : ∠C = 3 : 2 : 1, find the value of ∠ECD.
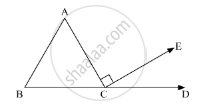
In the given figure, AB || DE. Find ∠ACD.

Is the following statement true and false :
Sum of the three angles of a triangle is 180 .
True
False
Is the following statement true and false :
A triangle can have two right angles.
True
False
Is the following statement true and false :
All the angles of a triangle can be less than 60°
True
False
Is the following statement true and false :
All the angles of a triangle can be greater than 60°.
True
False
Is the following statement true and false :
All the angles of a triangle can be equal to 60°.
True
False
Is the following statement true and false :
A triangle can have two obtuse angles.
True
False
Is the following statement true and false :
A triangle can have at most one obtuse angles.
Ture
False
Is the following statement true and false :
If one angle of a triangle is obtuse, then it cannot be a right angled triangle.
Ture
False
Is the following statement true and false :
An exterior angle of a triangle is less than either of its interior opposite angles.
Ture
False
Is the following statement true and false :
An exterior angle of a triangle is equal to the sum of the two interior opposite angles.
Ture
False
Is the following statement true and false :
An exterior angle of a triangle is greater than the opposite interior angles.
Ture
False
Fill in the blank to make the following statement true:
Sum of the angles of a triangle is ....
Fill in the blank to make the following statement true:
An exterior angle of a triangle is equal to the two ....... opposite angles.
Fill in the blank to make the following statement true:
An exterior angle of a triangle is always ......... than either of the interior opposite angles.
Fill in the blank to make the following statement true:
A triangle cannot have more than ...... right angles.
Fill in the blank to make the following statement true:
A triangles cannot have more than ......obtuse angles.
In a Δ ABC, the internal bisectors of ∠B and ∠C meet at P and the external bisectors of ∠B and ∠C meet at Q, Prove that ∠BPC + ∠BQC = 180°.
In the given figure, compute the value of x.
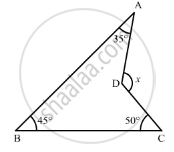
In the given figure, AB divides ∠DAC in the ratio 1 : 3 and AB = DB. Determine the value of x.
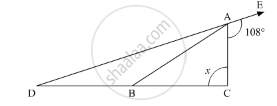
ABC is a triangle. The bisector of the exterior angle at B and the bisector of ∠C intersect each other at D. Prove that ∠D = \[\frac{1}{2}\] ∠A.
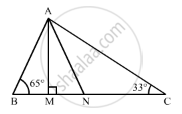
In the given figure, AM ⊥ BC and AN is the bisector of ∠A. If ∠B = 65° and ∠C = 33°, find ∠MAN.
In a Δ ABC, AD bisects ∠A and ∠C > ∠B. Prove that ∠ADB > ∠ADC.
In Δ ABC, BD⊥ AC and CE ⊥ AB. If BD and CE intersect at O, prove that ∠BOC = 180° − A.
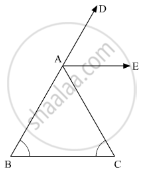
In the given figure, AE bisects ∠CAD and ∠B= ∠C. Prove that AE || BC.
RD Sharma solutions for Mathematics [English] Class 9 11 Triangle and its Angles Exercise 11.3 [Pages 23 - 24]
Define a triangle.
Write the sum of the angles of an obtuse triangle.
In Δ ABC, if u∠B = 60°, ∠C = 80° and the bisectors of angles ∠ABC and ∠ACB meet at a point O, then find the measure of ∠BOC.
If the angles of a triangle are in the ratio 2 : 1 : 3, then find the measure of smallest angle.
State exterior angle theorem.
The sum of two angles of a triangle is equal to its third angle. Determine the measure of the third angle.
In the given figure, if AB || CD, EF || BC, ∠BAC = 65° and ∠DHF = 35°, find ∠AGH.
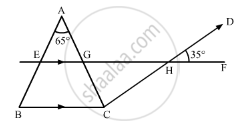
In the given figure, if AB || DE and BD || FG such that ∠FGH = 125° and ∠B = 55°, find x and y.
If the angles A, B and C of ΔABC satisfy the relation B − A = C − B, then find the measure of ∠B.
In ΔABC, if bisectors of ∠ABC and ∠ACB intersect at O at angle of 120°, then find the measure of ∠A.
If the side BC of ΔABC is produced on both sides, then write the difference between the sum of the exterior angles so formed and ∠A.
In a triangle ABC, if AB = AC and AB is produced to D such that BD = BC, find ∠ACD: ∠ADC.
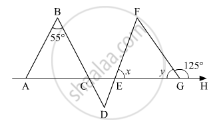
In the given figure, side BC of ΔABC is produced to point D such that bisectors of ∠ABC and ∠ACD meet at a point E. If ∠BAC = 68°, find ∠BEC.
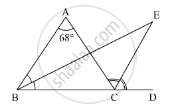
RD Sharma solutions for Mathematics [English] Class 9 11 Triangle and its Angles Exercise 11.4 [Pages 25 - 29]
Mark the correct alternative in each of the following:
If all the three angles of a triangle are equal, then each one of them is equal to
90°
45°
60°
30°
If two acute angles of a right triangle are equal, then each acute is equal to
30°
45°
60°
90°
An exterior angle of a triangle is equal to 100° and two interior opposite angles are equal. Each of these angles is equal to
75°
80°
80°
40°
50°
If one angle of a triangle is equal to the sum of the other two angles, then the triangle is
an isosceles triangle
an obtuse triangle
an equilateral triangle
a right triangle
Side BC of a triangle ABC has been produced to a point D such that ∠ACD = 120°. If ∠B = \[\frac{1}{2}\]∠A is equal to
80°
75°
60°
90°
In ΔABC, ∠B = ∠C and ray AX bisects the exterior angle ∠DAC. If ∠DAX = 70°, then ∠ACB =
35°
90°
70°
55°
In a triangle, an exterior angle at a vertex is 95° and its one of the interior opposite angle is 55°, then the measure of the other interior angle is
55°
85°
40°
9.0°
If the sides of a triangle are produced in order, then the sum of the three exterior angles so formed is
90°
180°
270°
360°
In ΔABC, if ∠A = 100°, AD bisects ∠A and AD ⊥ BC. Then, ∠B =
50°
90°
40°
100°
An exterior angle of a triangle is 108° and its interior opposite angles are in the ratio 4 : 5. The angles of the triangle are
48°, 60°, 72°
50°, 60°, 70°
52°, 56°, 72°
42°, 60°, 76°
In a ΔABC, if ∠A = 60°, ∠B = 80° and the bisectors of ∠B and ∠C meet at O, then ∠BOC =
60°
120°
150°
30°
Line segments AB and CD intersect at O such that AC || DB. If ∠CAB = 45° and ∠CDB = 55°, then ∠BOD =
100°
80°
90°
135°
In the given figure, if EC || AB, ∠ECD = 70° and ∠BDO = 20°, then ∠OBD is
20°
50°
60°
70°
In the given figure, x + y =

270
230
210
190°
If the measures of angles of a triangle are in the ratio of 3 : 4 : 5, what is the measure of the smallest angle of the triangle?
25°
30°
45°
60°
In the given figure, if AB ⊥ BC. then x =
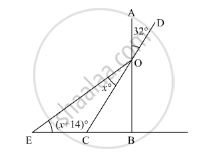
18
22
25
32
In the given figure, what is z in terms of x and y?
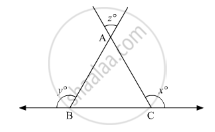
x + y + 180
x + y − 180
180° − (x + y)
x + y + 360°
In the given figure, for which value of x is l1 || l2?
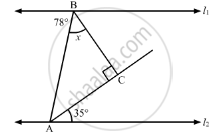
37
43
45
47
In the given figure, what is y in terms of x?

- \[\frac{3}{2}x\]
- \[\frac{4}{3}x\]
- x
\[\frac{3}{4}x\]
In the given figure, what is the value of x?
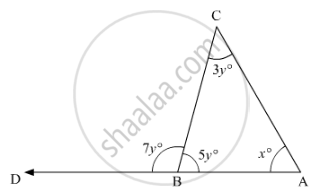
35
45
50
60
In the given figure, the value of x is ______.
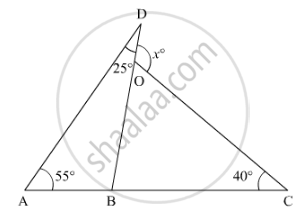
65°
80°
95°
120°
In the given figure, if BP || CQ and AC = BC, then the measure of x is
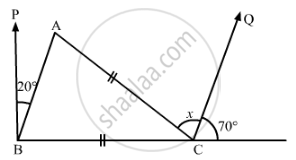
20°
25°
30°
35°
In the given figure, AB and CD are parallel lines and transversal EF intersects them at Pand Q respectively. If ∠APR = 25°, ∠RQC = 30° and ∠CQF = 65°, then

x = 55°, y = 40°
x = 50°, y = 45°
x = 60°, y = 35°
x = 35°, y = 60°
The base BC of triangle ABC is produced both ways and the measure of exterior angles formed are 94° and 126°. Then, ∠BAC =
94°
54°
40°
44°
If the bisectors of the acute angles of a right triangle meet at O, then the angle at Obetween the two bisectors is
45°
95°
135°
90°
The bisects of exterior angle at B and C of ΔABC meet at O. If ∠A = x°, then ∠BOC =
- \[90^\circ + \frac{x^\circ }{2}\]
\[90^\circ - \frac{x^\circ }{2}\]
\[180^\circ + \frac{x^\circ }{2}\]
\[180^\circ - \frac{x^\circ }{2}\]
In a ΔABC, ∠A = 50° and BC is produced to a point D. If the bisectors of ∠ABC and ∠ACDmeet at E, then ∠E =
25°
50°
100°
75°
The side BC of ΔABC is produced to a point D. The bisector of ∠A meets side BC in L. If ∠ABC = 30° and ∠ACD = 115°, then ∠ALC = ______.
85°
- \[72\frac{1}{2}^\circ\]
145°
none of these
In the given figure, if l1 || l2, the value of x is
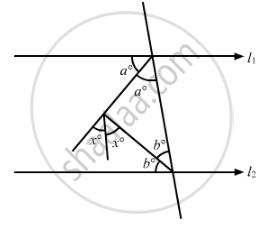
\[22\frac{1}{2}\]
30
45
60
In ΔRST (See figure), what is the value of x?
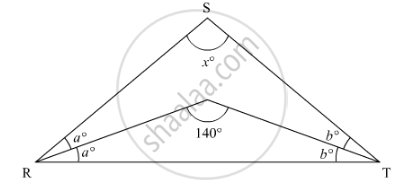
40°
90°
80°
100°
Solutions for 11: Triangle and its Angles
![RD Sharma solutions for Mathematics [English] Class 9 chapter 11 - Triangle and its Angles RD Sharma solutions for Mathematics [English] Class 9 chapter 11 - Triangle and its Angles - Shaalaa.com](/images/8193647912-mathematics-english-class-9_6:1a030933ece146238cec338f12706a07.jpg)
RD Sharma solutions for Mathematics [English] Class 9 chapter 11 - Triangle and its Angles
Shaalaa.com has the CBSE Mathematics Mathematics [English] Class 9 CBSE solutions in a manner that help students grasp basic concepts better and faster. The detailed, step-by-step solutions will help you understand the concepts better and clarify any confusion. RD Sharma solutions for Mathematics Mathematics [English] Class 9 CBSE 11 (Triangle and its Angles) include all questions with answers and detailed explanations. This will clear students' doubts about questions and improve their application skills while preparing for board exams.
Further, we at Shaalaa.com provide such solutions so students can prepare for written exams. RD Sharma textbook solutions can be a core help for self-study and provide excellent self-help guidance for students.
Concepts covered in Mathematics [English] Class 9 chapter 11 Triangle and its Angles are Concept of Triangles, Properties of a Triangle, Some More Criteria for Congruence of Triangles, Inequalities in a Triangle, Criteria for Congruence of Triangles, Congruence of Triangles.
Using RD Sharma Mathematics [English] Class 9 solutions Triangle and its Angles exercise by students is an easy way to prepare for the exams, as they involve solutions arranged chapter-wise and also page-wise. The questions involved in RD Sharma Solutions are essential questions that can be asked in the final exam. Maximum CBSE Mathematics [English] Class 9 students prefer RD Sharma Textbook Solutions to score more in exams.
Get the free view of Chapter 11, Triangle and its Angles Mathematics [English] Class 9 additional questions for Mathematics Mathematics [English] Class 9 CBSE, and you can use Shaalaa.com to keep it handy for your exam preparation.
