Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
In ΔABC, if ∠A = 100°, AD bisects ∠A and AD ⊥ BC. Then, ∠B =
Options
50°
90°
40°
100°
Solution
In the given ΔABC, ∠A= 100°, AD bisects ∠Aand AD ⊥ BC.
Here, we need to find ∠B.
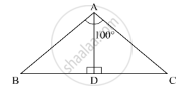
As, AD bisects∠A,
We get,
∠BAD = ∠DAC
100 = 2∠BAD
∠BAD = 50°
Now, according to angle sum property of the triangle
In ΔABD
∠A + ∠B + ∠D = 180°
50° + ∠B + 90° = 180°
140° + ∠B = 180°
∠B = 180° - 140°
= 40°
Hence, ∠B = 40°
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
If the base of an isosceles triangle is produced on both sides, prove that the exterior angles so formed are equal to each other.
In a ΔPQR, if PQ = QR and L, M and N are the mid-points of the sides PQ, QR and RP
respectively. Prove that LN = MN.
Fill the blank in the following so that the following statement is true.
If altitudes CE and BF of a triangle ABC are equal, then AB = ....
In ΔABC, if ∠A = 40° and ∠B = 60°. Determine the longest and shortest sides of the triangle.
Fill in the blank to make the following statement true.
If two sides of a triangle are unequal, then the larger side has .... angle opposite to it.
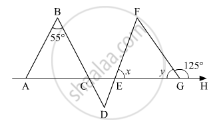
In the given figure, if AB || DE and BD || FG such that ∠FGH = 125° and ∠B = 55°, find x and y.
If the angles A, B and C of ΔABC satisfy the relation B − A = C − B, then find the measure of ∠B.
Which of the following correctly describes the given triangle?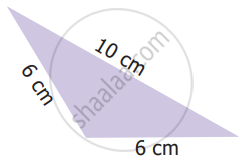
Two sides of a triangle are of lengths 5 cm and 1.5 cm. The length of the third side of the triangle cannot be ______.
Bisectors of the angles B and C of an isosceles triangle ABC with AB = AC intersect each other at O. Show that external angle adjacent to ∠ABC is equal to ∠BOC
