Advertisements
Chapters
2: Exponents of Real Numbers
3: Rationalisation
4: Algebraic Identities
5: Factorisation of Algebraic Expressions
6: Factorisation of Polynomials
7: Linear Equations in Two Variables
8: Co-ordinate Geometry
9: Introduction to Euclid’s Geometry
▶ 10: Lines and Angles
11: Triangle and its Angles
12: Congruent Triangles
13: Quadrilaterals
14: Areas of Parallelograms and Triangles
15: Circles
16: Constructions
17: Heron’s Formula
18: Surface Areas and Volume of a Cuboid and Cube
19: Surface Areas and Volume of a Circular Cylinder
20: Surface Areas and Volume of A Right Circular Cone
21: Surface Areas and Volume of a Sphere
22: Tabular Representation of Statistical Data
23: Graphical Representation of Statistical Data
24: Measures of Central Tendency
25: Probability
![RD Sharma solutions for Mathematics [English] Class 9 chapter 10 - Lines and Angles RD Sharma solutions for Mathematics [English] Class 9 chapter 10 - Lines and Angles - Shaalaa.com](/images/8193647912-mathematics-english-class-9_6:1a030933ece146238cec338f12706a07.jpg)
Advertisements
Solutions for Chapter 10: Lines and Angles
Below listed, you can find solutions for Chapter 10 of CBSE RD Sharma for Mathematics [English] Class 9.
RD Sharma solutions for Mathematics [English] Class 9 10 Lines and Angles Exercise 10.1 [Page 7]
Write the complement of the following angle.
20°
Write the complement of the following angles .
35°
Write the complement of the following angles.
90°
Write the complement of the following angles.
77°
Write the complement of the following angles .
30°
Write the supplement of the following angles .
54°
Write the supplement of the following angles.
132°
Write the supplement of the following angles .
138°
If an angle is 28° less than its complement, find its measure.
If an angle is 30° more than one half of its complement, find the measure of the angle.
Two supplementary angles are in the ratio 4 : 5. Find the angles.
Two supplementary angles differ by 48°. Find the angles.
An angle is equal to 8 times its complement. Determine its measure.
If the angles (2x −10)° and (x − 5)° are complementary angles, find x.
If an angle differs from its complement by 10°, find the angle .
If the supplement of an angle is two-third of itself. Determine the angle and its supplement.
An angle is 14° more than its complementary angle. What is its measure?
The measure of an angle is twice the measure of its supplementary ang Find its measure.
If the complement of an angle is equal to the supplement of the thrice of it. Find the measure of the angle.
If the supplement of an angle is three times its complement, find the angle.
RD Sharma solutions for Mathematics [English] Class 9 10 Lines and Angles Exercise 10.2 [Pages 14 - 17]
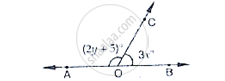
In the below Fig, OA and OB are opposite rays :
If x = 25°, what is the value of y?
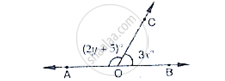
In the below Fig, OA and OB are opposite rays.
If y = 35°, what is the value of x?
In the below fig, write all pairs of adjacent angles and all the linear pairs .

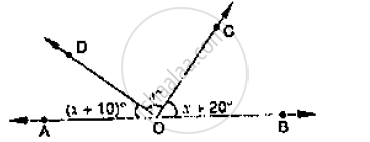
In the given below Fig, find x. Further find ∠BOC, ∠COD and ∠AOD .
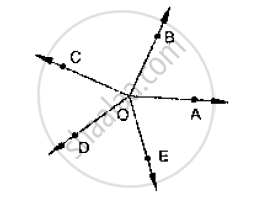
In the given below fig, rays OA, OB, OC, OP and 0E have the common end point O. Show
that ∠AOB + ∠BOC + ∠COD + ∠DOE + ∠EOA = 360°.
In the below Fig, ∠AOC and ∠BOC form a linear pair. if a − 2b = 30°, find a and b.
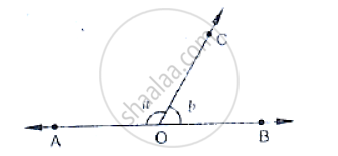
How many pairs of adjacent angles are formed when two lines intersect in a point?
How many pairs of adjacent angles, in all, can you name in below fig.?
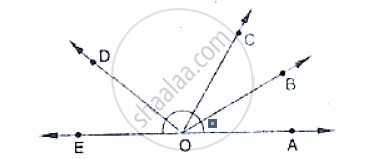
In below fig, determine the value of x.

In the below fig, AOC is a line, find x.
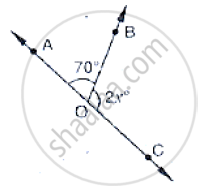
In the below fig, POS is a line, find x.
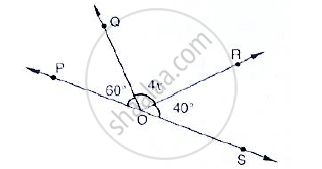
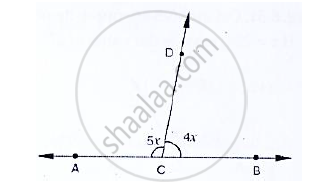
In the below fig, ACB is a line such that ∠DCA = 5x and ∠DCB = 4x. Find the value of x.
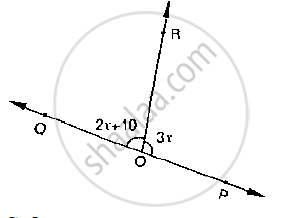
Given ∠POR = 3x and ∠QOR = 2x + 10, find the value of x for which POQ will be a line.
(Below fig).
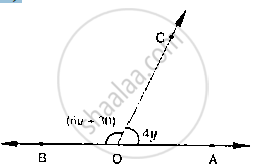
What value of y would make AOB a line in below fig, if ∠AOC = 4y and ∠BOC = (6y +
30)
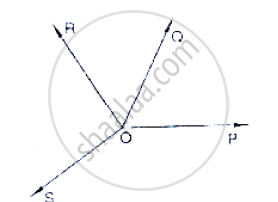
In below fig, OP, OQ, OR and OS arc four rays. Prove that:
∠POQ + ∠QOR + ∠SOR + ∠POS = 360°
In below fig, ray OS stand on a line POQ. Ray OR and ray OT are angle bisectors of ∠POS
and ∠SOQ respectively. If ∠POS = x, find ∠ROT.
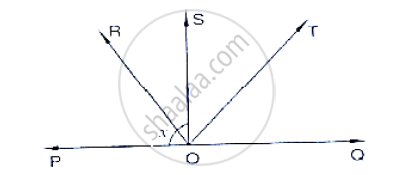
In the below fig, lines PQ and RS intersect each other at point O. If ∠POR: ∠ROQ − 5 : 7,
find all the angles.

In Fig. 8.42, a is greater than b by one third of a right-angle. Find the values of a and b.
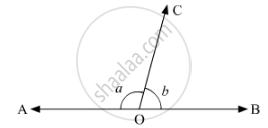
If below fig, ∠AOF and ∠FOG form a linear pair.
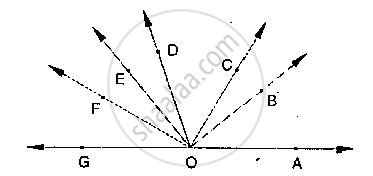
∠EOB = ∠FOC = 90° and ∠DOC = ∠FOG = ∠AOB = 30°
(i) Find the measures of ∠FOE, ∠COB and ∠DOE.
(ii) Name all the right angles.
(iii) Name three pairs of adjacent complementary angles.
(iv) Name three pairs of adjacent supplementary angles.
(v) Name three pairs of adjacent angles.
In the below fig, POQ is a line. Ray OR is perpendicular to line OS is another ray lying
between rays OP and OR. Prove that ∠ROS = 1 (∠QOS − ∠POS).

RD Sharma solutions for Mathematics [English] Class 9 10 Lines and Angles Exercise 10.3 [Pages 22 - 23]
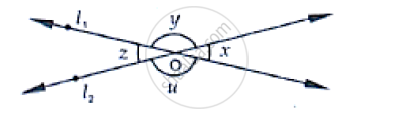
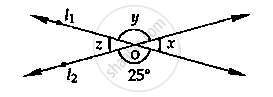
In the below fig, lines �1 and �2 intersect at O, forming angles as shown in the figure. If x = 45, Find the values of x, y, z and u.
In the below fig, three coplanar lines intersect at a point O, forming angles as shown in the figure. Find the values of x, y, z and u.

In the given fig, find the values of x, y and z.
In the below fig, find the value of x.

If one of the four angles formed by two intersecting lines is a right angle, then show that
each of the four angles is a right angle.
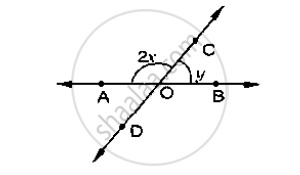
In the below fig, rays AB and CD intersect at O.
Determine y when x = 60°
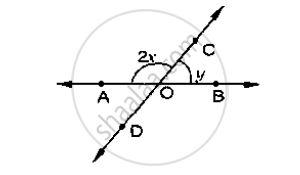
In the below fig, rays AB and CD intersect at O
Determine x when y =40
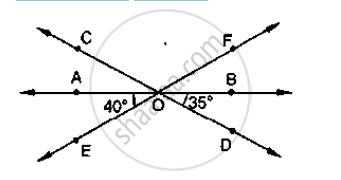
In the below fig, lines AB, CD and EF intersect at O. Find the measures of ∠AOC, ∠COF,
∠DOE and ∠BOF.
AB, CD and EF are three concurrent lines passing through the point O such that OF bisects
∠BOD. If ∠BOF = 35°, find ∠BOC and ∠AOD.
In below figure, lines AB and CD intersect at O. If ∠AOC + ∠BOE = 70° and ∠BOD =
40°, find ∠BOE and reflex ∠COE.
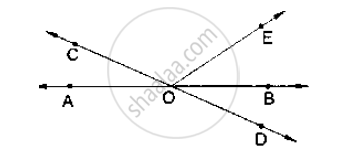
statement are true and false
Angles forming a linear pair are supplementary.
statement are true and false
If two adjacent angles are equal, and then each angle measures 90°.
statement are true and false
Angles forming a linear pair can both the acute angles.
statement are true and false
If angles forming a linear pair are equal, then each of these angles is of measure 90°.
Fill in the blank so as to make the following statement true:
If one angle of a linear pair is acute, then its other angle will be _____
Fill in the blank so as to make the following statement true:
A ray stands on a line, then the sum of the two adjacent angles so formed is ______
Fill in the blank so as to make the following statement true:
If the sum of two adjacent angles is 180°, then the ______ arms of the two angles are
opposite rays
Prove that the bisectors of a pair of vertically opposite angles are in the same straight line.
If two straight lines intersect each other, prove that the ray opposite to the bisector of one of the angles thus formed bisects the vertically opposite angle.
RD Sharma solutions for Mathematics [English] Class 9 10 Lines and Angles Exercise 10.4 [Pages 46 - 49]
In below fig, AB CD and ∠1 and ∠2 are in the ratio 3 : 2. Determine all angles from 1 to 8.
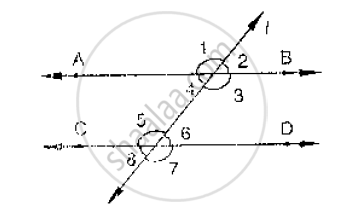
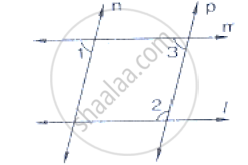
In the below fig, l, m and n are parallel lines intersected by transversal p at X, Y and Z
respectively. Find ∠1, ∠2 and ∠3.

If below fig, if AB || CD and CD || EF, find ∠ACE.
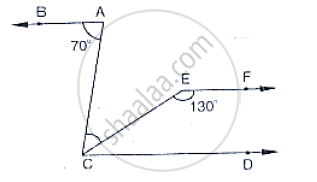
In the below fig, state which lines are parallel and why?
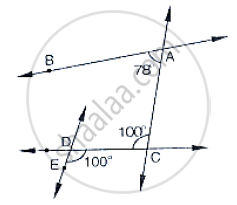
In the below fig, if l || m, n || p and ∠1 = 85°, find `∠`2.
If two straight lines are perpendicular to the same line, prove that they are parallel to each
other.
Two unequal angles of a parallelogram are in the ratio 2 : 3. Find all its angles in degrees .
If each of the two lines is perpendicular to the same line, what kind of lines are they to each
other?
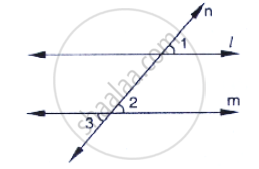
In the below fig, `∠`1 = 60° and `∠`2 = `(2/3)^(rd)`of a right angle. Prove that l || m.
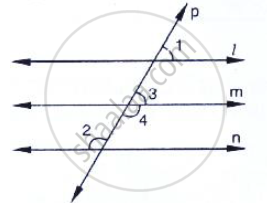
In the below fig, if l || m || n and `∠`1 = 60°, find `∠`2.
Prove that the straight lines perpendicular to the same straight line are parallel to one
another.
The opposite sides of a quadrilateral are parallel. If one angle of the quadrilateral is 60°,
find the other angles.
Two lines AB and CD intersect at O. If `∠`AOC + `∠`COB + `∠`BOD = 270°, find the
measures of `∠`AOC, `∠`COB, `∠`BOD and `∠`DOA.
In the below fig, p is a transversal to lines m and n,`∠`2 = 120° and `a∠`5 = 60°. Prove that m || n.
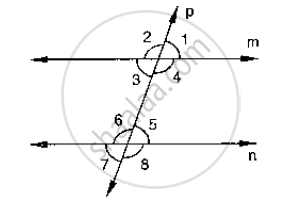
In the below fig, transversal 𝑙 intersects two lines m and n, `∠`4 = 110° and `∠`7 = 65°. Is m || n?
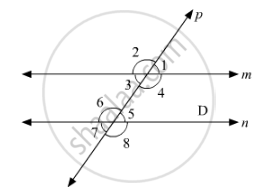
Which pair of lines in the below fig, is parallel? Given reasons.

If l, m, n are three lines such that l || m and n ⊥ l, prove that n ⊥ m.
Which of the following statement are true and false ? Give reason.
If two lines are intersected by a transversal, then corresponding angles are equal.
Which of the following statement are true and false ? Give reason.
If two parallel lines are intersected by a transversal, then alternate interior angles are equal.
Which of the following statement are true and false ? Give reason.
Two lines perpendicular to the same line are perpendicular to each other.
Which of the following statement are true and false ? Give reason.
Two lines parallel to the same line are parallel to each other.
Which of the following statement are true and false ? Give reason.
If two parallel lines are intersected by a transversal, then the interior angles on the same side of the transversal are equal.
Fill in the blank in the following to make the statement true:
If two parallel lines are intersected by a transversal, then each pair of corresponding
angles are _______
Fill in the blank in the following to make the statement true:
If two parallel lines are intersected by a transversal, then interior angles on the same
side of the transversal are _______
Fill in the blank in the following to make the statement true:
Two lines perpendicular to the same line are _______ to each other.
Fill in the blank in the following to make the statement true:
Two lines parallel to the same line are _______ to each other.
Fill in the blank in the following to make the statement true:
If a transversal intersects a pair of lines in such a way that a pair of alternate angles
are equal, then the lines are _______
Fill in the blank :
If a transversal intersects a pair of lines in such a way that the sum of interior angles
on the same side of transversal is 180°, then the lines are _______.
In the below fig, AB || CD || EF and GH || KL. Find `∠`HKL
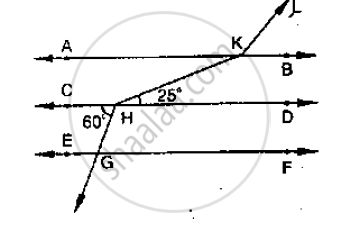
In the below fig, show that AB || EF.
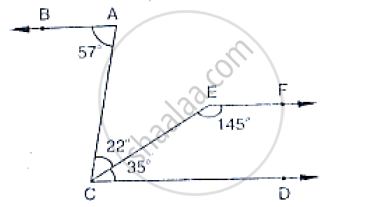
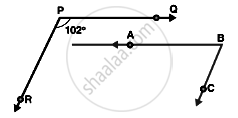
In the below, PQ || AB and PR || BC. If `∠`QPR = 102°, determine `∠`ABC. Give reasons.
Prove that if the two arms of an angle are perpendicular to the two arms of another angle, then the angles are either equal or supplementary
In the below fig, lines AB and CD are parallel and P is any point as shown in the figure.
Show that` ∠`ABP +` ∠`CDP = ∠DPB.
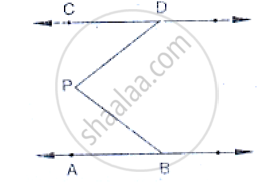
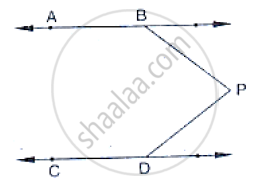
In the below fig, AB || CD and P is any point shown in the figure. Prove that:
`∠`ABP+`∠`BPD+`∠`CDP = 36O°
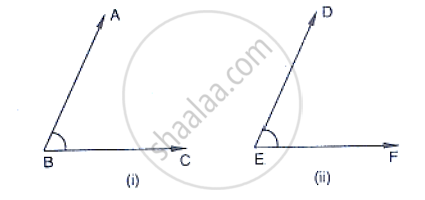
In the below fig, arms BA and BC of `∠`ABC are respectively parallel to arms ED and EF of
`∠`DEF. Prove that `∠`ABC = ∠DEF.
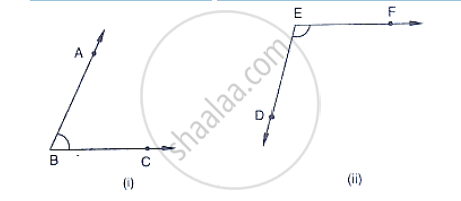
In the below fig, arms BA and BC of ∠ABC are respectively parallel to arms ED and EF of
∠DEF. Prove that ∠ABC + ∠DEF = 180°.
RD Sharma solutions for Mathematics [English] Class 9 10 Lines and Angles Exercise 10.5 [Page 50]
Define complementary angles.
Define supplementary angles.
Define adjacent angles.
The complement of an acute angle is ..............
The supplement of an acute angle is .................
The supplement of a right angle is ..............
Write the complement of an angle of measure x°.
Write the supplement of an angle of measure 2y°.
If a wheel has six spokes equally spaced, then find the measure of the angle between two adjacent spokes.
An angle is equal to its supplement. Determine its measure.
An angle is equal to five times its complement. Determine its measure.
How many pairs of adjacent angles are formed when two lines intersect in a point?
RD Sharma solutions for Mathematics [English] Class 9 10 Lines and Angles Exercise 10.6 [Pages 51 - 57]
One angle is equal to three times its supplement. The measure of the angle is
130°
135°
90°
120°
Two straight line AB and CD intersect one another at the point O. If ∠AOC + ∠COB + ∠BOD = 274°, then ∠AOD =
86°
90°
94°
137°
Two straight lines AB and CD cut each other at O. If ∠BOD = 63°, then ∠BOC =
63°
117°
17°
153°
Consider the following statements:
When two straight lines intersect:
(i) adjacent angles are complementary
(ii) adjacent angles are supplementary
(iii) opposite angles are equal
(iv) opposite angles are supplementary
Of these statements
(i) and (ii) are correct
(ii) and (iii) are correct
(i) and (iv) are correct
(ii) and (iv) are correct
Given ∠POR = 3x and ∠QOR = 2x + 10°. If POQ is a straight line, then the value of x is
30°
34°
36°
none of these
In the given figure, AOB is a straight line. If ∠AOC + ∠BOD = 85°, then ∠COD =
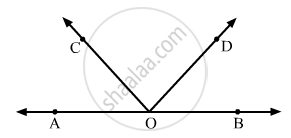
85°
90°
95°
100°
In the given figure, the value of y is
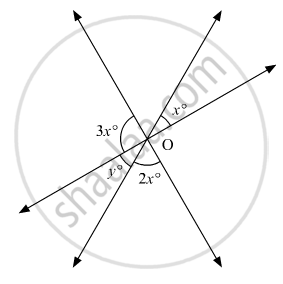
20°
30°
45°
60°
In the given figure, the value of x is ______.

12
15
20
30
In the given figure, which of the following statements must be true?
(i) a + b = d + c
(ii) a + c + e = 180°
(iii) b + f = c + e
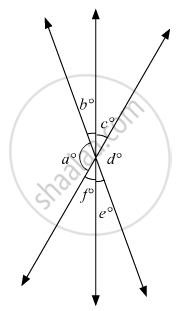
(i) only
(ii) only
(iii) only
(ii) and (iii) only
If two interior angles on the same side of a transversal intersecting two parallel lines are in the ratio 2:3, then the measure of the larger angle is
54°
120°
108°
136°
In the given figure, if AB || CD, then the value of x is

20°
30°
45°
60°
Two lines AB and CD intersect at O. If ∠AOC + ∠COB + ∠BOD = 270°, then ∠AOC =
70°
80°
90°
180°
In the given figure, PQ || RS, ∠AEF = 95°, ∠BHS = 110° and ∠ABC = x°. Then the value of x is

15°
25°
70°
35°
In the given figure, if l1 || l2, what is the value of x?

80°
85°
90°
95°
In the given figure, if l1 || l2, what is x + y in terms of w and z?
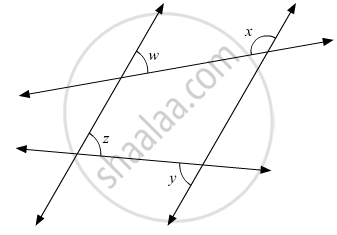
180° − w + z
180° + w − z
180° - w − z
180° + w + z
In the given figure, if l1 || l2, what is the value of y?
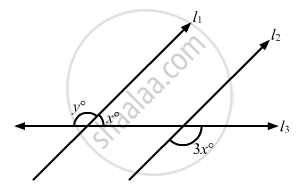
100°
120°
135°
150°
In the given figure, if l1 || l2 and l3 || l4, what is y in terms of x?

90 + x
90 + 2x
`90 + x/2`
90 − 2x
In the given figure, if l || m, what is the value of x?
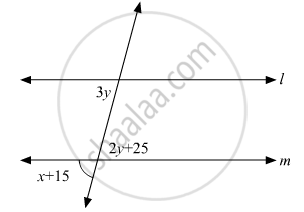
60°
50°
45°
30°
In the given figure, if AB || HF and DE || FG, then the measure of ∠FDE is
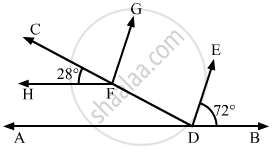
108°
80°
100°
90°
In the given figure, if lines l and m are parallel, then x =
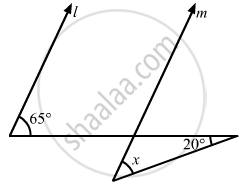
20°
45°
65°
85°
In the given figure, if AB || CD, then x =

100°
105°
110°
115°
In the given figure, if lines l and m are parallel lines, then x =
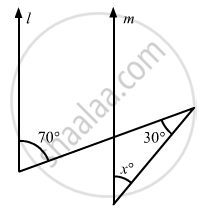
70°
100°
40°
30°
In the given figure, if l || m, then x =

105°
65°
40°
25°
In the given figure, if lines l and m are parallel, then the value of x is

35°
55°
65°
75°
Two complementary angles are such that two times the measure of one is equal to three times the measure of the other. The measure of the smaller angle is
45°
30°
36°
none of these
In the given figure, if \[\frac{y}{x} = 5\] and \[\frac{z}{x} = 4\] then the value of x isc
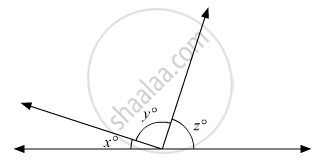
8°
18°
12°
15°
In the given figure, AB || CD || EF and GH || KL. The measure of ∠HKL is

85°
135°
145°
215°
AB and CD are two parallel lines. PQ cuts AB and CD at E and F respectively. EL is the bisector of ∠FEB. If ∠LEB = 35°, then ∠CFQ will be
55°
70°
110°
130°
In the given figure, If line segment AB is parallel to the line segment CD, what is the value of y?

12
15
18
20
In the given figure, if CP || DQ, then the measure of x is
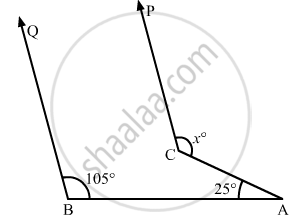
130°
105°
175°
125°
Solutions for 10: Lines and Angles
![RD Sharma solutions for Mathematics [English] Class 9 chapter 10 - Lines and Angles RD Sharma solutions for Mathematics [English] Class 9 chapter 10 - Lines and Angles - Shaalaa.com](/images/8193647912-mathematics-english-class-9_6:1a030933ece146238cec338f12706a07.jpg)
RD Sharma solutions for Mathematics [English] Class 9 chapter 10 - Lines and Angles
Shaalaa.com has the CBSE Mathematics Mathematics [English] Class 9 CBSE solutions in a manner that help students grasp basic concepts better and faster. The detailed, step-by-step solutions will help you understand the concepts better and clarify any confusion. RD Sharma solutions for Mathematics Mathematics [English] Class 9 CBSE 10 (Lines and Angles) include all questions with answers and detailed explanations. This will clear students' doubts about questions and improve their application skills while preparing for board exams.
Further, we at Shaalaa.com provide such solutions so students can prepare for written exams. RD Sharma textbook solutions can be a core help for self-study and provide excellent self-help guidance for students.
Concepts covered in Mathematics [English] Class 9 chapter 10 Lines and Angles are Intersecting Lines and Non-intersecting Lines, Introduction to Lines and Angles, Basic Terms and Definitions, Introduction to Parallel Lines, Pairs of Angles, Parallel Lines and a Transversal, Angle Sum Property of a Triangle.
Using RD Sharma Mathematics [English] Class 9 solutions Lines and Angles exercise by students is an easy way to prepare for the exams, as they involve solutions arranged chapter-wise and also page-wise. The questions involved in RD Sharma Solutions are essential questions that can be asked in the final exam. Maximum CBSE Mathematics [English] Class 9 students prefer RD Sharma Textbook Solutions to score more in exams.
Get the free view of Chapter 10, Lines and Angles Mathematics [English] Class 9 additional questions for Mathematics Mathematics [English] Class 9 CBSE, and you can use Shaalaa.com to keep it handy for your exam preparation.
