Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
In the given figure, if AB ⊥ BC. then x =
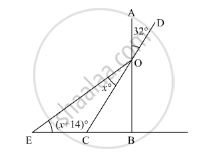
Options
18
22
25
32
Solution
In the given figure, AB ⊥ BC
We need to find the value of x.
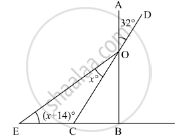
Now, since AB and CD are straight lines intersecting at point O, using the property, “vertically opposite angles are equal”, we get,
∠BOC = ∠AOD
∠BOC = 32°
Further, applying angle sum property of the triangle
In ΔBOC
∠BOC + ∠OBC + ∠BCO = 180°
32° + 90° + ∠BCO = 180°
∠BCO = 180° -122°
∠BCO = 58°
Then, using the property, “an exterior angle of the triangle is equal to the sum of the two opposite interior angles”, we get,
In ΔEOC
∠BCO = ∠OEC +∠EOC
58° = (x + 14)° + x
58° = 2x + 14°
2x = 58° - 14°
Further solving for x, we get,
2x = 44°
`x = (44° )/2`
x = 22°
Thus x = 22°
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Show that the angles of an equilateral triangle are 60° each.
Find the measure of each exterior angle of an equilateral triangle.
Which of the following statements are true (T) and which are false (F):
The measure of each angle of an equilateral triangle is 60°
Which of the following statements are true (T) and which are false (F):
The bisectors of two equal angles of a triangle are equal
Which of the following statements are true (T) and which are false (F):
The two altitudes corresponding to two equal sides of a triangle need not be equal.
Fill in the blank to make the following statement true.
In a right triangle the hypotenuse is the .... side.
If the angles of a triangle are in the ratio 2 : 1 : 3, then find the measure of smallest angle.
In the given figure, x + y =

Is it possible to construct a triangle with lengths of its sides as 9 cm, 7 cm and 17 cm? Give reason for your answer.
Show that in a quadrilateral ABCD, AB + BC + CD + DA < 2(BD + AC)
