Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Find, giving a reason, the unknown marked angles, in a triangle drawn below:

Solution
We know that,
Exterior angle of a triangle is always equal to the sum of its two interior opposite angles (property)
110° = 2x + 3x
5x – 110°
x = `110^circ/5`
x = 22°
∴ 2x = 2 x 22 = 44°
3x = 3 x 22 = 66°
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
In a ΔABC, ∠ABC = ∠ACB and the bisectors of ∠ABC and ∠ACB intersect at O such that ∠BOC = 120°. Show that ∠A = ∠B = ∠C = 60°.
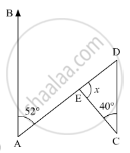
Compute the value of x in the following figure:
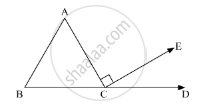
In the given figure, AC ⊥ CE and ∠A : ∠B : ∠C = 3 : 2 : 1, find the value of ∠ECD.
Is the following statement true and false :
Sum of the three angles of a triangle is 180 .
Fill in the blank to make the following statement true:
An exterior angle of a triangle is always ......... than either of the interior opposite angles.
If the side BC of ΔABC is produced on both sides, then write the difference between the sum of the exterior angles so formed and ∠A.
In a ∆ABC, AB = AC. The value of x is ________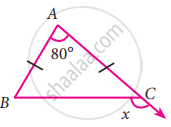
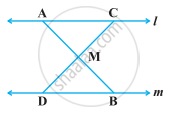
In the following figure, l || m and M is the mid-point of a line segment AB. Show that M is also the mid-point of any line segment CD, having its end points on l and m, respectively.
Can we have two acute angles whose sum is a straight angle? Why or why not?
Can we have two acute angles whose sum is a reflex angle? Why or why not?
