Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The sides of triangle is given below. Determine it is right triangle or not.
a = 1.6 cm, b = 3.8 cm and c = 4 cm
उत्तर
In order to prove that the given sides of a certain triangle forms a right angled triangle we have to prove that square of the larger side is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides.
Here, the larger side is c = 4 cm.
Hence, we have to prove that a2 + b2 = c2..
Let solve the left hand side of the above equation.
a2 + b2 = (1.6)2 + (3.8)2
= 2.56 + 14.44
= 17
Now we will solve the right hand side of the equation,
c2 = 42 = 16
Here we can observe that left hand side is not equal to the right hand side.
Therefore, the given sides of a certain triangle do not form a right angled triangle.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
The sides of triangle is given below. Determine it is right triangle or not.
a = 9 cm, b = l6 cm and c = 18 cm
Using Pythagoras theorem determine the length of AD in terms of b and c shown in Figure.
In a ΔABC, AB = BC = CA = 2a and AD ⊥ BC. Prove that
(i) AD = a`sqrt3`
(ii) Area (ΔABC) = `sqrt3` a2
In right-angled triangle ABC in which ∠C = 90°, if D is the mid-point of BC, prove that AB2 = 4AD2 − 3AC2.
In a right ∆ABC right-angled at C, if D is the mid-point of BC, prove that BC2 = 4(AD2 − AC2).
If D, E, F are the respectively the midpoints of sides BC, CA and AB of ΔABC. Find the ratio of the areas of ΔDEF and ΔABC.
A man goes 12m due south and then 35m due west. How far is he from the starting point.
Find the side and perimeter of a square whose diagonal is `13sqrt2` cm.
From given figure, In ∆ABC, AB ⊥ BC, AB = BC, AC = `5sqrt(2)` , then what is the height of ∆ABC?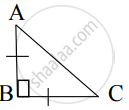
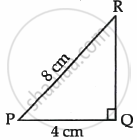
In the given figure, ΔPQR is a right triangle right angled at Q. If PQ = 4 cm and PR = 8 cm, then P is ______.