Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
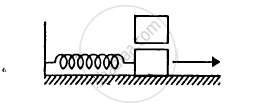
The spring shown in figure is unstretched when a man starts pulling on the cord. The mass of the block is M. If the man exerts a constant force F, find (a) the amplitude and the time period of the motion of the block, (b) the energy stored in the spring when the block passes through the equilibrium position and (c) the kinetic energy of the block at this position.
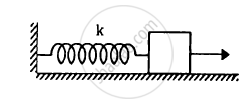
उत्तर
(a) We know-
f = kx
\[\Rightarrow x = \frac{F}{k}\]
\[\text { Acceleration }= \frac{F}{m}\]
Using the relation of time period of S.H.M.,
\[\text { Time period }, T = 2\pi\sqrt{\frac{\text { Displacement } }{\text { Acceleration }}}\]
\[ = 2\pi\sqrt{\frac{\left( \frac{F}{k} \right)}{\left( \frac{F}{m} \right)}} = 2\pi\sqrt{\frac{m}{k}}\]
Amplitude = Maximum displacement \[= \frac{F}{k}\]
When the block passes through the equilibrium position, the energy contained by the spring is given by,
\[E = \frac{1}{2}k x^2 = \frac{1}{2}k \left( \frac{F}{k} \right)^2 = \frac{1}{2}\left( \frac{F^2}{k} \right)\]
(b) At the mean position, potential energy is zero.
Kinetic energy is given by,
\[\frac{1}{2}k x^2 = \frac{1}{2}\frac{F^2}{k}\]
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A particle having mass 10 g oscillates according to the equation x = (2.0 cm) sin [(100 s−1)t + π/6]. Find (a) the amplitude, the time period and the spring constant. (c) the position, the velocity and the acceleration at t = 0.
The equation of motion of a particle started at t = 0 is given by x = 5 sin (20t + π/3), where x is in centimetre and t in second. When does the particle
(a) first come to rest
(b) first have zero acceleration
(c) first have maximum speed?
Consider a particle moving in simple harmonic motion according to the equation x = 2.0 cos (50 πt + tan−1 0.75) where x is in centimetre and t in second. The motion is started at t = 0. (a) When does the particle come to rest for the first time? (b) When does he acceleration have its maximum magnitude for the first time? (c) When does the particle come to rest for the second time ?
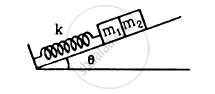
The block of mass m1 shown in figure is fastened to the spring and the block of mass m2 is placed against it. (a) Find the compression of the spring in the equilibrium position. (b) The blocks are pushed a further distance (2/k) (m1 + m2)g sin θ against the spring and released. Find the position where the two blocks separate. (c) What is the common speed of blocks at the time of separation?
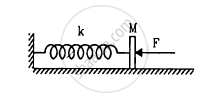
In following figure k = 100 N/m M = 1 kg and F = 10 N.
- Find the compression of the spring in the equilibrium position.
- A sharp blow by some external agent imparts a speed of 2 m/s to the block towards left. Find the sum of the potential energy of the spring and the kinetic energy of the block at this instant.
- Find the time period of the resulting simple harmonic motion.
- Find the amplitude.
- Write the potential energy of the spring when the block is at the left extreme.
- Write the potential energy of the spring when the block is at the right extreme.
The answer of b, e and f are different. Explain why this does not violate the principle of conservation of energy.
Repeat the previous exercise if the angle between each pair of springs is 120° initially.
Find the elastic potential energy stored in each spring shown in figure, when the block is in equilibrium. Also find the time period of vertical oscillation of the block.
Solve the previous problem if the pulley has a moment of inertia I about its axis and the string does not slip over it.
A rectangle plate of sides a and b is suspended from a ceiling by two parallel string of length L each in Figure . The separation between the string is d. The plate is displaced slightly in its plane keeping the strings tight. Show that it will execute simple harmonic motion. Find the time period.

A 1 kg block is executing simple harmonic motion of amplitude 0.1 m on a smooth horizontal surface under the restoring force of a spring of spring constant 100 N/m. A block of mass 3 kg is gently placed on it at the instant it passes through the mean position. Assuming that the two blocks move together, find the frequency and the amplitude of the motion.
Discuss in detail the energy in simple harmonic motion.
If a body is executing simple harmonic motion and its current displacements is `sqrt3/2` times the amplitude from its mean position, then the ratio between potential energy and kinetic energy is:
A body is executing simple harmonic motion with frequency ‘n’, the frequency of its potential energy is ______.
A body is executing simple harmonic motion with frequency ‘n’, the frequency of its potential energy is ______.
A body is executing simple harmonic motion with frequency ‘n’, the frequency of its potential energy is ______.
Displacement versus time curve for a particle executing S.H.M. is shown in figure. Identify the points marked at which (i) velocity of the oscillator is zero, (ii) speed of the oscillator is maximum.

Draw a graph to show the variation of P.E., K.E. and total energy of a simple harmonic oscillator with displacement.
Find the displacement of a simple harmonic oscillator at which its P.E. is half of the maximum energy of the oscillator.
A body of mass m is attached to one end of a massless spring which is suspended vertically from a fixed point. The mass is held in hand so that the spring is neither stretched nor compressed. Suddenly the support of the hand is removed. The lowest position attained by the mass during oscillation is 4 cm below the point, where it was held in hand.
What is the amplitude of oscillation?
