Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The work function of a metal is 2.5 × 10−19 J. (a) Find the threshold frequency for photoelectric emission. (b) If the metal is exposed to a light beam of frequency 6.0 × 1014 Hz, what will be the stopping potential?
(Use h = 6.63 × 10-34J-s = 4.14 × 10-15 eV-s, c = 3 × 108 m/s and me = 9.1 × 10-31kg)
उत्तर
Given :-
Work function of a metal, W0 = 2.5 × 10−19 J
Frequency of light beam, v = 6.0 × 1014 Hz
(a) Work function of a metal,
W0 = hv0,
where h = Planck's constant
v0 = threshold frequency
`therefore "v"_0 = W_0/h`
`⇒ v_0 = (2.5 xx 10^-19)/(6.63 xx 10^-34)`
`= 3.77 xx 10^14 "Hz"`
`= 3.8 xx 10^14 "Hz"`
(b) Einstein's photoelectric equation :-
`eV_0 = hv - W_0`,
where
v = frequency of light
V0 = Stopping potential
e = charge on electron
`therefore V_0 = (hv - W_0)/e`
`= (6.63 xx 10^-34 xx 6 xx 10^14 - 2.5 xx 10^-19)/(1.6 xx 10^-19)`
`= (3.97 xx 10^-19 - 2.5 xx 10^-19)/(1.6 xx 10^-19) = 0.91 V`
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
(a) Estimate the speed with which electrons emitted from a heated emitter of an evacuated tube impinge on the collector maintained at a potential difference of 500 V with respect to the emitter. Ignore the small initial speeds of the electrons. The specific charge of the electron, i.e., its e/m is given to be 1.76 × 1011 C kg−1.
(b) Use the same formula you employ in (a) to obtain electron speed for an collector potential of 10 MV. Do you see what is wrong? In what way is the formula to be modified?
Use the same formula you employ in (a) to obtain electron speed for an collector potential of 10 MV. Do you see what is wrong? In what way is the formula to be modified?
Ultraviolet light of wavelength 2271 Å from a 100 W mercury source irradiates a photo-cell made of molybdenum metal. If the stopping potential is −1.3 V, estimate the work function of the metal. How would the photo-cell respond to a high intensity (∼105 W m−2) red light of wavelength 6328 Å produced by a He-Ne laser?
A mercury lamp is a convenient source for studying frequency dependence of photoelectric emission, since it gives a number of spectral lines ranging from the UV to the red end of the visible spectrum. In our experiment with rubidium photo-cell, the following lines from a mercury source were used:
λ1 = 3650 Å, λ2 = 4047 Å, λ3 = 4358 Å, λ4 = 5461 Å, λ5 = 6907 Å,
The stopping voltages, respectively, were measured to be:
V01 = 1.28 V, V02 = 0.95 V, V03 = 0.74 V, V04 = 0.16 V, V05 = 0 V
Determine the value of Planck’s constant h, the threshold frequency and work function for the material.
[Note: You will notice that to get h from the data, you will need to know e (which you can take to be 1.6 × 10−19 C). Experiments of this kind on Na, Li, K, etc. were performed by Millikan, who, using his own value of e (from the oil-drop experiment) confirmed Einstein’s photoelectric equation and at the same time gave an independent estimate of the value of h.]
A hot body is placed in a closed room maintained at a lower temperature. Is the number of photons in the room increasing?
In an experiment on photoelectric effect, a photon is incident on an electron from one direction and the photoelectron is emitted almost in the opposite direction. Does this violate the principle of conservation of momentum?
The threshold wavelength of a metal is λ0. Light of wavelength slightly less than λ0 is incident on an insulated plate made of this metal. It is found that photoelectrons are emitted for some time and after that the emission stops. Explain.
When stopping potential is applied in an experiment on photoelectric effect, no photoelectric is observed. This means that
When the intensity of a light source in increased,
(a) the number of photons emitted by the source in unit time increases
(b) the total energy of the photons emitted per unit time increases
(c) more energetic photons are emitted
(d) faster photons are emitted
In which of the following situations, the heavier of the two particles has smaller de Broglie wavelength? The two particles
(a) move with the same speed
(b) move with the same linear momentum
(c) move with the same kinetic energy
(d) have fallen through the same height
Calculate the number of photons emitted per second by a 10 W sodium vapour lamp. Assume that 60% of the consumed energy is converted into light. Wavelength of sodium light = 590 nm
(Use h = 6.63 × 10-34J-s = 4.14 × 10-15 eV-s, c = 3 × 108 m/s and me = 9.1 × 10-31kg)
A parallel beam of monochromatic light of wavelength 663 nm is incident on a totally reflecting plane mirror. The angle of incidence is 60° and the number of photons striking the mirror per second is 1.0 × 1019. Calculate the force exerted by the light beam on the mirror.
(Use h = 6.63 × 10-34J-s = 4.14 × 10-15 eV-s, c = 3 × 108 m/s and me = 9.1 × 10-31kg)
A beam of white light is incident normally on a plane surface absorbing 70% of the light and reflecting the rest. If the incident beam carries 10 W of power, find the force exerted by it on the surface.
(Use h = 6.63 × 10-34J-s = 4.14 × 10-15 eV-s, c = 3 × 108 m/s and me = 9.1 × 10-31kg)
Show that it is not possible for a photon to be completely absorbed by a free electron.
Answer the following question.
Plot a graph of photocurrent versus anode potential for radiation of frequency ν and intensities I1 and I2 (I1 < I2).
Define the term: stopping potential in the photoelectric effect.
Two monochromatic beams A and B of equal intensity I, hit a screen. The number of photons hitting the screen by beam A is twice that by beam B. Then what inference can you make about their frequencies?
Why it is the frequency and not the intensity of the light source that determines whether the emission of photoelectrons will occur or not? Explain.
Read the following paragraph and answer the questions.
| The figure shows the variation of photoelectric current measured in a photocell circuit as a function of the potential difference between the plates of the photocell when light beams A, B, C and D of different wavelengths are incident on the photocell. Examine the given figure and answer the following questions: |
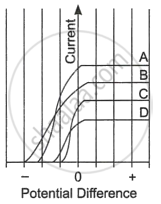
- Which light beam has the highest frequency and why?
- Which light beam has the longest wavelength and why?
- Which light beam ejects photoelectrons with maximum momentum and why?
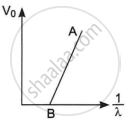
The figure shows a plot of stopping potential (V0) versus `1/lambda`, where λ is the wavelength of the radiation causing photoelectric emission from a surface. The slope of the line is equal to ______.