Science (English Medium)
Academic Year: 2011-2012
Date: मार्च 2012
Advertisements
When electrons drift in a metal from lower to higher potential, does it mean that all the free electrons of the metal are moving in the same direction?
Chapter: [0.03] Current Electricity
The horizontal component of the earth’s magnetic field at a place is B and angle of dip is 60°. What is the value of vertical component of earth’s magnetic field at equator?
Chapter: [0.05] Magnetism and Matter
Show on a graph, the variation of resistivity with temperature for a typical semiconductor.
Chapter: [0.14] Semiconductor Electronics - Materials, Devices and Simple Circuits
Why should electrostatic field be zero inside a conductor?
Chapter: [0.02] Electrostatic Potential and Capacitance
Name of physical quantity which remains same for microwaves of wavelength 1 mm and UV radiations of 1600 Å in vacuum.
Chapter: [0.08] Electromagnetic Waves
Under what condition does a biconvex lens of glass having a certain refractive index act as a plane glass sheet when immersed in a liquid?
Chapter:
Predict the directions of induced currents in metal rings 1 and 2 lying in the same plane where current I in the wire is increasing steadily.
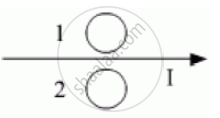
Chapter: [0.06] Electromagnetic Induction
State de Broglie hypothesis
Chapter: [0.11] Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter
A ray of light, incident on an equilateral prism `(μ_g = sqrt3)`moves parallel to the base line of the prism inside it. Find the angle of incidence for this ray.
Chapter: [0.09] Ray Optics and Optical Instruments
Distinguish between ‘Analog and Digital signals’.
Chapter: [0.15] Communication Systems
Mention the function of any two of the following used
(i) Transducer
(ii) Repeater
(iii) Transmitter
(iv) Bandpass Filter
Chapter: [0.15] Communication Systems
A cell of emf E and internal resistance r is connected to two external resistance R1 and R2 and a perfect ammeter. The current in the circuit is measured in four different situations:
(i) without any external resistance in the circuit
(ii) with resistance R1 only
(iii) with R1 and R2 in series combination
(iv) with R1 and R2 in parallel combination
The currents measured in the four cases are 0.42 A, 1.05 A, 1.4 A and 4.2 A, but not necessarily in the order. Identify the currents corresponding to the four cases mentioned above.
Chapter: [0.03] Current Electricity
The susceptibility of a magnetic material is − 2.6 × 10−5. Identify the type of magnetic material and state its two properties.
Chapter: [0.05] Magnetism and Matter
Two identical circular wires P and Q each of radius R and carrying current ‘I’ are kept in perpendicular planes such that they have a common centre as shown in the figure. Find the magnitude and direction of the net magnetic field at the common centre of the two coils.
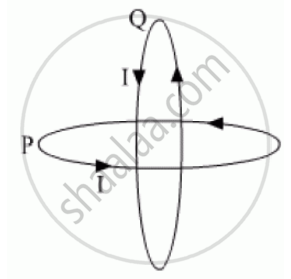
Chapter: [0.04] Moving Charges and Magnetism
When an ideal capacitor is charged by a dc battery, no current flows. However, when an ac source is used, the current flows continuously. How does one explain this, based on the concept of displacement current?
Chapter: [0.08] Electromagnetic Waves
Draw a plot showing the variation of (i) electric field (E) and (ii) electric potential (V) with distance r due to a point charge Q.
Chapter: [0.02] Electrostatic Potential and Capacitance
Advertisements
Define self-inductance of a coil. Show that magnetic energy required to build up the current I in a coil of self inductance L is given by `1/2 LI^2`
Chapter: [0.06] Electromagnetic Induction
The current in the forward bias is known to be more (~mA) than the current in the reverse bias (~μA). What is the reason, then, to operate the photodiode in reverse bias?
Chapter: [0.14] Semiconductor Electronics - Materials, Devices and Simple Circuits
A metallic rod of ‘L’ length is rotated with angular frequency of ‘ω’ with one end hinged at the centre and the other end at the circumference of a circular metallic ring of radius L, about an axis passing through the centre and perpendicular to the plane of the ring. A constant and uniform magnetic field B parallel to the axis is presents everywhere. Deduce the expression for the emf between the centre and the metallic ring.
Chapter: [0.06] Electromagnetic Induction
The figure shows a series LCR circuit with L = 10.0 H, C = 40 μF, R = 60 Ω connected to a variable frequency 240 V source, calculate
(i) the angular frequency of the source which drives the circuit at resonance,
(ii) the current at the resonating frequency,
(iii) the rms potential drop across the inductor at resonance.
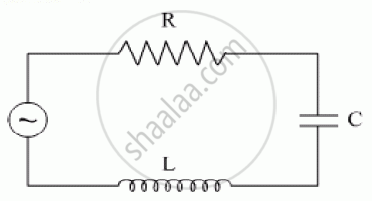
Chapter: [0.07] Alternating Current
A rectangular loop of wire of size 4 cm × 10 cm carries a steady current of 2 A. A straight long wire carrying 5 A current is kept near the loop as shown. If the loop and the wire are coplanar, find
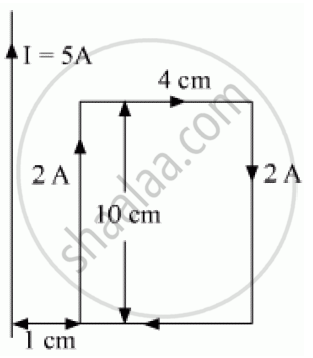
(i) the torque acting on the loop and
(ii) the magnitude and direction of the force on the loop due to the current carrying wire.
Chapter: [0.04] Moving Charges and Magnetism
Using Bohr’s second postulate of quantization of orbital angular momentum show that the circumference of the electron in the nth orbital state in hydrogen atom is n times the de Broglie wavelength associated with it.
Chapter: [0.12] Atoms
The electron in hydrogen atom is initially in the third excited state. What is the maximum number of spectral lines which can be emitted when it finally moves to the ground state?
Chapter: [0.12] Atoms
In the figure a long uniform potentiometer wire AB is having a constant potential gradient along its length. The null points for the two primary cells of emfs ε1 and ε2 connected in the manner shown are obtained at a distance of 120 cm and 300 cm from the end A. Find (i) ε1/ ε2 and (ii) position of null point for the cell ε1.
How is the sensitivity of a potentiometer increased?
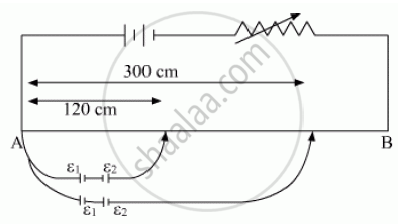
Chapter: [0.03] Current Electricity
Using Kirchhoff’s rules determine the value of unknown resistance R in the circuit so that no current flows through 4 Ω resistance. Also find the potential difference between A and D.
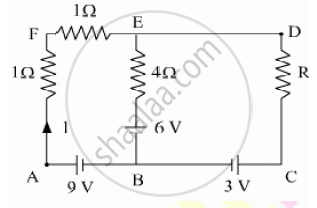
Chapter: [0.03] Current Electricity
What characteristic property of nuclear force explains the constancy of binding energy per nucleon (BE/A) in the range of mass number ‘A’ lying 30 < A < 170?
Chapter: [0.13] Nuclei
Show that the density of nucleus over a wide range of nuclei is constant-independent of mass number A.
Chapter: [0.13] Nuclei
Write any two factors which justify the need for modulating a signal ?
Chapter: [0.15] Communication Systems
Draw a diagram showing an amplitude modulated wave by superposing a modulating signal over a sinusoidal carrier wave.
Chapter: [0.15] Communication Systems
Write Einstein’s photoelectric equation?
Chapter: [0.11] Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter
State clearly how photoelectric equation is obtained using the photon pictu.re of electromagnetic radiation.
Chapter: [0.11] Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter
Write the three salient features observed in photoelectric effect which can be explained using this equation.
Chapter: [0.11] Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter
Advertisements
Why are coherent sources necessary to produce a sustained interference pattern?
Chapter: [0.1] Wave Optics
In Young’s double slit experiment using monochromatic light of wavelength λ, the intensity of light at a point on the screen where path difference is λ, is K units. Find out the intensity of light at a point where path difference is λ/3.
Chapter: [0.1] Wave Optics
Use Huygens’s principle to explain the formation of diffraction pattern due to a single slit illuminated by a monochromatic source of light.
Chapter: [0.1] Wave Optics
When the width of the slit is made double the original width, how would this affect the size and intensity of the central diffraction band?
Chapter: [0.1] Wave Optics
Explain the principle of a device that can build up high voltages of the order of a few million volts.
Chapter: [0.02] Electrostatic Potential and Capacitance
Draw a schematic diagram and explain the working of Van de Graff generator device.
Chapter: [0.02] Electrostatic Potential and Capacitance
Is there any restriction on the upper limit of the high voltage set up in Van de Graff generator machine? Explain.
Chapter: [0.02] Electrostatic Potential and Capacitance
Define Electric Flux. Write its SI unit.
Chapter: [0.01] Electric Charges and Fields
Using Gauss’s law, prove that the electric field at a point due to a uniformly charged infinite plane sheet is independent of the distance from it.
Chapter: [0.01] Electric Charges and Fields
How is the field directed if (i) the sheet is positively charged, (ii) negatively charged?
Chapter: [0.01] Electric Charges and Fields
Define magnifying power of a telescope. Write its expression.
Chapter: [0.09] Ray Optics and Optical Instruments
A small telescope has an objective lens of focal length 150 cm and an eye piece of focal length 5 cm. If this telescope is used to view a 100 m high tower 3 km away, find the height of the final image when it is formed 25 cm away from the eye piece.
Chapter: [0.09] Ray Optics and Optical Instruments
How is the working of a telescope different from that of a microscope?
Chapter: [0.09] Ray Optics and Optical Instruments
The focal lengths of the objective and eyepiece of a microscope are 1.25 cm and 5 cm respectively. Find the position of the object relative to the objective in order to obtain an angular magnification of 30 in normal adjustment.
Chapter: [0.09] Ray Optics and Optical Instruments
Draw a simple circuit of a CE transistor amplifier. Explain its working ?
Chapter: [0.14] Semiconductor Electronics - Materials, Devices and Simple Circuits
Show that the voltage gain, AV, of the amplifier is given by `A_v = (beta_(ac) R_1)/r_i`where βac is the current gain, RL is the load resistance and ri is the input resistance of the transistor. What is the significance of the negative sign in the expression for the voltage gain?
Chapter: [0.14] Semiconductor Electronics - Materials, Devices and Simple Circuits
Draw the circuit diagram of a full wave rectifier using p-n junction diode.
Explain its working and show the output, input waveforms.
Chapter: [0.14] Semiconductor Electronics - Materials, Devices and Simple Circuits
Show the output waveforms (Y) for the following inputs A and B of (i) OR gate (ii) NAND gate ?
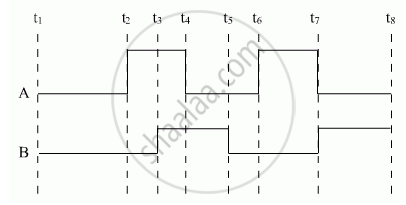
Chapter: [0.14] Semiconductor Electronics - Materials, Devices and Simple Circuits
Other Solutions
Submit Question Paper
Help us maintain new question papers on Shaalaa.com, so we can continue to help studentsonly jpg, png and pdf files
CBSE previous year question papers Class 12 Physics with solutions 2011 - 2012
Previous year Question paper for CBSE Class 12 Physics-2012 is solved by experts. Solved question papers gives you the chance to check yourself after your mock test.
By referring the question paper Solutions for Physics, you can scale your preparation level and work on your weak areas. It will also help the candidates in developing the time-management skills. Practice makes perfect, and there is no better way to practice than to attempt previous year question paper solutions of CBSE Class 12.
How CBSE Class 12 Question Paper solutions Help Students ?
• Question paper solutions for Physics will helps students to prepare for exam.
• Question paper with answer will boost students confidence in exam time and also give you an idea About the important questions and topics to be prepared for the board exam.
• For finding solution of question papers no need to refer so multiple sources like textbook or guides.
