Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
A 5 m long ladder is placed leaning towards a vertical wall such that it reaches the wall at a point 4 m high. If the foot of the ladder is moved 1.6 m towards the wall, then find the distance by which the top of the ladder would slide upwards on the wall.
Solution
Let AC be the ladder of length 5 m and BC = 4 m be the height of the wall, which ladder is placed.
If the foot of the ladder is moved 1.6 m towards the wall i.e, AD = 1.6 m,
Then the ladder is slide upward i.e., CE = x m.
In right angled ∆ABC,
AC2 = AB2 + BC2 ...[By pythagoras theorem]
⇒ (5)2 = (AB)2 + (4)2
⇒ AB2 = 25 – 16 = 9
⇒ AB = 3 m
Now, DB = AB – AD
= 3 – 1.6
= 1.4 m
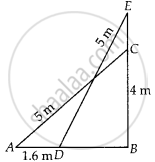
In right angled ∆EBD,
ED2 = EB2 + BD2 ...[By pythagoras theorem]
⇒ (5)2 = (EB)2 + (14)2 ...[BD = 1.4]
⇒ 25 = (EB)2 + 1.96
⇒ (EB)2 = 25 – 1.96 = 23.04
⇒ EB = `sqrt(23.04)` = 4.8
Now, EC = EB – BC
= 4.8 – 4
= 0.8
Hence, the top of the ladder would slide upwards on the wall at distance is 0.8 m.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Side of a triangle is given, determine it is a right triangle.
`(2a – 1) cm, 2\sqrt { 2a } cm, and (2a + 1) cm`
Sides of triangle are given below. Determine it is a right triangle or not? In case of a right triangle, write the length of its hypotenuse. 50 cm, 80 cm, 100 cm
Two poles of heights 6 m and 11 m stand on a plane ground. If the distance between the feet of the poles is 12 m, find the distance between their tops.
D and E are points on the sides CA and CB respectively of a triangle ABC right angled at C. Prove that AE2 + BD2 = AB2 + DE2
Find the perimeter of the rectangle whose length is 40 cm and a diagonal is 41 cm.
In the given figure, ∆ABC is an equilateral triangle of side 3 units. Find the coordinates of the other two vertices ?
ABC is a triangle, right-angled at B. M is a point on BC.
Prove that: AM2 + BC2 = AC2 + BM2
Find the Pythagorean triplet from among the following set of numbers.
9, 40, 41
In figure, PQR is a right triangle right angled at Q and QS ⊥ PR. If PQ = 6 cm and PS = 4 cm, find QS, RS and QR.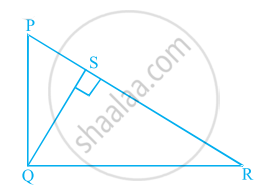
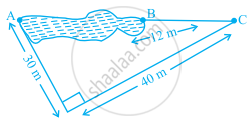
Points A and B are on the opposite edges of a pond as shown in figure. To find the distance between the two points, the surveyor makes a right-angled triangle as shown. Find the distance AB.