Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
A conductor has three segments; two straights of length L and a semicircular with radius R. It carries a current I What is the magnetic field B at point P?
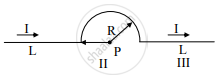
Options
`(mu_0 I)/(4piR)`
`mu_0/(4pi)I/R^2`
`(mu_0I)/(4R)`
`(mu_0I)/(4pi)`
Solution
`(mu_0I)/(4R)`
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
(a) Write the expression for the magnetic force acting on a charged particle moving with velocity v in the presence of magnetic field B.
Use this law to find magnetic field due to straight infinite current carrying wire.
Deduce the expression for the magnetic field at a point on the axis of a current carrying circular loop of radius ‘R’ distant ‘x’ from the centre. Hence, write the magnetic field at the centre of a loop.
The electric current flowing in a wire in the direction from B to A is decreasing. Find out the direction of the induced current in the metallic loop kept above the wire as shown.
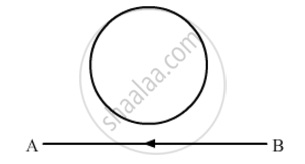
Magnetic lines of force always cross each other
A steady current (I1) flows through a long straight wire. Another wire carrying steady current (I2) in the same direction is kept close and parallel to the first wire. Show with the help of a diagram how the magnetic field due to the current I1 exerts a magnetic force on the second wire. Write the expression for this force.
A straight wire carrying an electric current is placed along the axis of a uniformly charged ring. Will there be a magnetic force on the wire if the ring starts rotating about the wire? If yes, in which direction?
Two wires carrying equal currents i each, are placed perpendicular to each other, just avoiding a contact. If one wire is held fixed and the other is free to move under magnetic forces, what kind of motion will result?
A straight horizontal wire of mass 10 mg and length 1.0 m carries a current of 2.0 A. What minimum magnetic field B should be applied in the region, so that the magnetic force on the wire may balance its weight?
If a particle of charge 1012 coulomb moving along the `hat"x" -` direction with a velocity 102 m/s experiences a force of 1 o-s newton in `hat"y" -` direction due to magnetic field, then the minimum magnetic field is ____________.
A magnetic field set up using Helmholtz coils is uniform in a small region and has a magnitude of 0.75 T. In the same region, a uniform electrostatic field is maintained in a direction normal to the common axis of the coils. A narrow beam of (single species) charged particles all accelerated through 15 kV enters this region in a direction perpendicular to both the axis of the coils and the electrostatic field. If the beam remains undeflected when the electrostatic field is 9.0 × 10–5 V m–1, make a simple guess as to what the beam contains. Why is the answer not unique?
In SI system, permeability has the units ______.
Lorentz Force generally refers to ______.
- If v is parallel to B, then path of particle is spiral.
- If v is perpendicular to B, then path of particle is a circle.
- If v has a component along B, then path of particle is helical.
- If v is along B, then path of particle is a circle.
The correct plot of the magnitude of magnetic field `vec"B"` vs distance r from centre of the wire is, if the radius of wire is R.
Which one of the following is a correct statement about magnetic forces?
What is the magnetic induction of the field at the point O in a current I carrying wire that has the shape shown in the figure? The radius of the curved part of the wire is R, the linear parts are assumed to be very long.

The phenomenon in which a magnetic field is produced in the space near a conductor carrying current is called ______
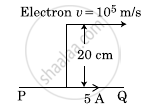
An infinitely long straight conductor carries a current of 5 A as shown. An electron is moving with a speed of 105 m/s parallel to the conductor. The perpendicular distance between the electron and the conductor is 20 cm at an instant. Calculate the magnitude of the force experienced by the electron at that instant.
An electron enters with a velocity v = v0i into a cubical region (faces parallel to coordinate planes) in which there are uniform electric and magnetic fields. The orbit of the electron is found to spiral down inside the cube in plane parallel to the x-y plane. Suggest a configuration of fields E and B that can lead to it.
Two long current-carrying conductors are placed parallel to each other at a distance of 8 cm between them. The magnitude of the magnetic field produced at the mid-point between the two conductors due to the current flowing in them is 300µT. The equal current flowing in the two conductors is ______.
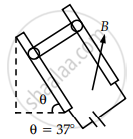
Two conducting rails are connected to a source of emf and form an incline as shown in figure. A bar of mass 50 g slides without friction down the incline through a vertical magnetic field B. If the length of the bar is 50 cm and a current of 2.5 A is provided by battery. Value of B for which the bar slide at a constant velocity ______ × 10-1 Tesla. 2 [g = 10 m/s2]
Write the expression for the Lorentz force on a particle of charge q moving with a velocity `vecv` in a magnetic field `vecB`. When is the magnitude of this force maximum? Show that no work is done by this force on the particle during its motion from point `vecr_1` to point `vecr_2`.
State the expression for the Lorentz force on a charge due to an electric field as well as a magnetic field. Hence discuss the magnetic force on a charged particle which is (i) moving parallel to the magnetic field and (ii) stationary.
What is the relation between Tesla and Gauss?
