Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
A point source of light is placed in front of a plane mirror.
Options
All the reflected rays meet at a point when produced backward.
Only the reflected rays close to the normal meet at a point when produced backward.
Only the reflected rays making a small angle with the mirror meet at a point when produced backward.
Light of different colours make different images.
Solution
All the reflected rays meet at a point when produced backward.
Here, the angle of reflection is equal to the angle of incidence. Therefore, all rays get reflected to converge at a single point to form the point image of the point source.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Use the mirror equation to show that a convex mirror always produces a virtual image independent of the location of the object.
Using mirror formula, explain why does a convex mirror always produce a virtual image.
An object is kept on the principal axis of a concave mirror of focal length 10 cm. at a distance of 15
cm from its pole. The image formed by the mirror is:
(a) Virtual and magnified
(b) Virtual and diminished
(c) Real and magnified
(d) Real and diminished
Use the mirror equation to show that an object placed between f and 2f of a concave mirror forms an image beyond 2f.
Define the term 'limit of resolution'?
Use the mirror equation to show a convex mirror always produces a virtual image independent of the location of the object ?
following Figure shows two rays A and B being reflected by a mirror and going as A' and B'. The mirror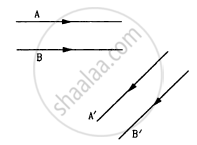
The rays of different colours fail to converge at a point after going through a converging lens. This defect is called
A light ray falling at an angle of 45° with the surface of a clean slab of ice of thickness 1.00 m is refracted into it at an angle of 30°. Calculate the time taken by the light rays to cross the slab. Speed of light in vacuum = 3 × 108 m s−1.
A small object is placed at the centre of the bottom of a cylindrical vessel of radius 3 cm and height 4 cm filled completely with water. Consider the ray leaving the vessel through a corner. Suppose this ray and the ray along the axis of the vessel are used to trace the image. Find the apparent depth of the image and the ratio of real depth to the apparent depth under the assumptions taken. Refractive index of water = 1.33.
A light ray is incident at an angle of 45° with the normal to a √2 cm thick plate (μ = 2.0). Find the shift in the path of the light as it emerges out from the plate.
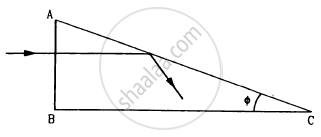
A light ray is incident normally on the face AB of a right-angled prism ABC (μ = 1.50) as shown in figure. What is the largest angle ϕ for which the light ray is totally reflected at the surface AC?
A light ray, going through a prism with the angle of prism 60°, is found to deviate by 30°. What limit on the refractive index can be put from these data?
For paraxial rays, show that the focal length of a spherical mirror is one-half of its radius of curvature.
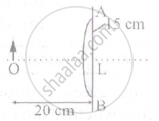
A point object is placed at a distance of 20 cm from a thin plano-convex lens of focal length 15 cm, if the plane surface is silvered. The image will form at:
The focal length f is related to the radius of curvature r of the spherical convex mirror by ______.
When a clock is viewed in a mirror, the needles exhibit a time which appears to be 8:20. Then the actual time will be:
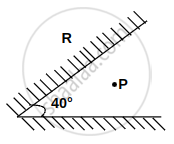
Two plane mirrors are inclined at an angle of 40°. The possible number of images of an object placed at point P would be?