Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Solve the following problem.
A projectile is thrown at an angle of 30° to the horizontal. What should be the range of initial velocity (u) so that its range will be between 40m and 50 m? Assume g = 10 m s-2.
Solution
Given: 40 ≤ R ≤ 50, θ = 30°, g = 10 m/s2
To find: Range of initial velocity (u)
Formula: R = `("u"^2 sin (2theta))/"g"`
Calculation: From formula,
The range of initial velocity,
`40 <= ("u"^2 sin (2theta))/"g" <= 50`
∴ `"40g"/(sin (2theta)) <= "u"^2 <= "50g"/(sin(2theta))`
∴ `sqrt(("40g")/(sin (2theta))) <= "u" <= sqrt(("50g")/(sin(2theta))`
∴ `sqrt((40 xx 10)/(sin (60))) <= "u" <= sqrt((50 xx 10)/(sin (60)))`
∴ 21.49 m/s ≤ u ≤ 24.03 m/s
The range of initial velocity should be between 21.49 m/s ≤ u ≤ 24.03 m/s.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
In U. C. M (Uniform Circular Motion), prove the relation `vec v = vec w xx vec r`, where symbols have their usual meanings.
A vehicle is moving on a circular track whose surface is inclined towards the horizon at an angle of 10°. The maximum velocity with which it can move safely is 36 km / hr. Calculate the length of the circular track. [π = 3.142]
Explain the meaning of uniform circular motion. Give one example of such motion.
Is it possible to have an accelerated motion with a constant speed? Name such type of motion.
Give an example of motion in which speed remains uniform, but the velocity changes.
A piece of stone tied at the end of a thread is whirled in a horizontal circle with uniform speed by hand. Answer the following questions:
- Is the velocity of stone uniform or variable?
- Is the acceleration of stone uniform or variable?
- What is the direction of acceleration of stone at any instant?
- Which force provides the centripetal force required for circular motion?
- Name the force and its direction which acts on the hand.
Which of the following quantity remains constant in a uniform circular motion?
A uniform metre rule of mass 100g is balanced on a fulcrum at mark 40cm by suspending an unknown mass m at the mark 20cm.
To which side the rule will tilt if the mass m is moved to the mark 10cm ?
Name the force required for uniform circular motion. State its direction.
Is it possible to have an accelerated motion with a constant speed? Explain.
Answer the following question.
Define angular velocity.
Solve the following problem.
A car moves in a circle at a constant speed of 50 m/s and completes one revolution in 40 s. Determine the magnitude of the acceleration of the car.
Solve the following problem.
A particle moves in a circle with a constant speed of 15 m/s. The radius of the circle is 2 m. Determine the centripetal acceleration of the particle.
Is the uniform circular motion accelerated? Give reasons for your answer.
A small sphere is attached to a cord and rotates in a vertical circle about a point O. If the average speed of the sphere is increased, the cord is most likely to break at the orientation when the mass is at ____________.
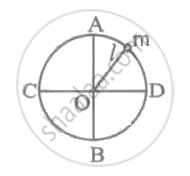
A particle is moving in uniform circular motion with speed 'V' and radius 'R'. The angular acceleration of the particle is ______.
Select the WRONG statement.
A ball of mass 'm' is attached to the free end of an inextensible string of length 'l'. Let 'T' be the tension in the string. The ball is moving in horizontal circular path about the vertical axis. The angular velocity of the ball at any particular instant will be ______.
A stone of mass 3 kg attached at one end of a 2m long string is whirled in horizontal circle. The string makes an angle of 45° with the vertical then the centripetal force acting on the string is ______.
(g = 10 m/s2 , tan 45° = 1)
A particle is given an initial speed u inside a smooth spherical shell of radius R = 1 m that it is just able to complete the circle. Acceleration of the particle when its velocity is vertical is ______.
A wet open umbrella is held upright and is rotated about the handle at a uniform rate of 21 revolutions in 44 s. If the rim of the umbrella is a circle of 1 metre in diameter and the height of the rim above the floor is 1.5 m, the drops of water spun off the rim and hit the floor at a horizontal ______ m from the umbrella.
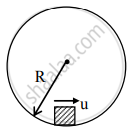
A rod PQ of mass M and length L is hinged at end P. The rod is kept horizontal by a massless string tied to point Q as shown in figure. When string is cut, the initial angular acceleration of the rod is ______.
A particle moves along a circle of radius r with constant tangential acceleration. If the velocity of the particle is v at the end of second revolution, after the revolution has started, then the tangential acceleration is ______.
A horizontal circular platform of mass M is rotating at angular velocity ω about a vertical axis passing through its centre. A boy of mass m is standing at the edge of the platform. If the boy comes to the centre of the platform, then the new angular velocity becomes ______.
A wheel is rotating at 900 rpm about its axis. When the power is cut off it comes to rest in 1 min. The angular retardation (assumed to be uniform (in rad s-1) is ______.
Two bodies of masses 10 kg and 5 kg moving in concentric orbits of radii R and r such that their periods are the same. Then the ratio between their centripetal accelerations is ______.
Explain the meaning of uniform circular motion.
