Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Answer the following question.
Define angular velocity.
Solution
Angular velocity of a particle is the rate of change of angular displacement.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
A particle rotates in U.C.M. with tangential velocity V along a horizontal circle of diameter ‘D' . Total angular displacement of the particle in time 't' is..........
A stone tied to the end of a string 80 cm long is whirled in a horizontal circle with a constant speed. If the stone makes 14 revolutions in 25 s, what is the magnitude and direction of acceleration of the stone?
How does uniform circular motion differ from uniform linear motion?
A piece of stone tied at the end of a thread is whirled in a horizontal circle with uniform speed by hand. Answer the following questions:
- Is the velocity of stone uniform or variable?
- Is the acceleration of stone uniform or variable?
- What is the direction of acceleration of stone at any instant?
- Which force provides the centripetal force required for circular motion?
- Name the force and its direction which acts on the hand.
A uniform linear motion is unaccelerated, while a uniform circular motion is an accelerated motion.
In a uniform circular motion, the speed continuously changes because of the direction of motion changes.
Which of the following quantity remains constant in uniform circular motion:
Name the force required for uniform circular motion. State its direction.
Define Uniform circular motion.
Answer the following question.
Show that the centripetal force on a particle undergoing uniform circular motion is -mrω2.
Which one of the following is most likely not a case of uniform circular motion?
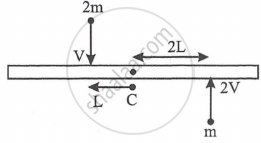
A uniform rod of length '6L' and mass '8 m' is pivoted at its centre 'C'. Two masses 'm' and ' 2m' with speed 2v, v as shown strikes the rod and stick to the rod. Initially the rod is at rest. Due to impact, if it rotates with angular velocity 'w1' then 'w' will be ________.
A particle goes round a circular path with uniform speed v. After describing half the circle, what is the change in its centripetal acceleration?
A particle performs uniform circular motion in a horizontal plane. The radius of the circle is 8 cm. The centripetal force acting on the particle is 15 N. Its kinetic energy is ____________.
A particle is moving in uniform circular motion with speed 'V' and radius 'R'. The angular acceleration of the particle is ______.
Consider a simple pendulum of length 4 m. Its bob performs a circular motion in horizontal plane with its string making an angle 60° with the vertical. The Period of rotation of the bob is ____________.(Take g = 10 m/s2)
A body of mass ·m' is moving along a circle of radius 'r' with linear speed 'v'. Now, to change the linear speed to `V/2` and to move it along the circle of radius '4r', required change in the centripetal force of the body is ______.
A stone of mass 3 kg attached at one end of a 2m long string is whirled in horizontal circle. The string makes an angle of 45° with the vertical then the centripetal force acting on the string is ______.
(g = 10 m/s2 , tan 45° = 1)
A cyclist is riding with a speed of 43.2 km/h. As he approaches a circular turn on the road of radius 60 m, he applies brakes and reduces his speed at constant rate of 1.8 ms-2. The magnitude of the net acceleration of the cyclist is ______.
The given graph represents motion with ______ speed.
A small bead of mass m can move on a smooth circular wire (radius R) under the action of a force F = `"Km"/"r"^2` directed (r = position of bead r from P and K = constant) towards a point P within the circle at a distance R/2 from the centre. The minimum velocity should be ______ m/s of bead at the point of the wire nearest the centre of force (P) so that bead will complete the circle. (Take `"k"/(3"R")` = 8 unit)

A wheel rotating at the same angular speed undergoes constant angular retardation. After the revolution, angular velocity reduces to half its initial value. It will make ______ revolution before stopping.
A particle is performing a uniform circular motion along a circle of radius R. In half the period of revolution, its displacement and distance covered are respectively.
The acceleration of a point on the rim of a flywheel 1 m in diameter, if it makes 1200 rpm is ______.
A wheel is Subjected to uniform angular acceleration about its axis. Initially. its angular velocity is zero. In the first 2 s, it rotates through an angle θ1, in the next 2 s, it rotates through an angle θ2. The ratio of `theta_2/theta_1` is ______.
The kinetic energy K of a particle moving along a circle of radius R depends on the distance covered s as K = as2, where a is a constant. The force acting on the particle is ______.
