Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Solve the following problem.
A car moves in a circle at a constant speed of 50 m/s and completes one revolution in 40 s. Determine the magnitude of the acceleration of the car.
Solution 1
Given: v = 50 m/s, t = 40 s, s = 2πr
To find: acceleration (a)
Formulae:
i. v = `"s"/"t"`
ii. a = `"v"^2/"r"`
Calculation: From formula (i),
`50 = (2pi"r")/40`
∴ r = `(50 xx 40)/(2pi)`
∴ r = `1000/pi` cm
From formula (ii),
a = `"v"^2/"r" = 50^2/(1000//pi)`
a = `(5pi)/2 = 7.85 "m"//"s"^2`
The magnitude of acceleration of the car is 7.85 m/s2.
Solution 2
Given: v = 50 m/s, t = 40 s,
To find: acceleration (a)
Formula: a = rω2 = vω
Calculation: From formula,
a = vω
`= "v"(("2"pi)/"t")`
`= 50((2 xx 3.142)/40)`
`= 5/2 xx 3.142`
∴ a = 7.85 m/s2
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
A particle rotates in U.C.M. with tangential velocity V along a horizontal circle of diameter ‘D' . Total angular displacement of the particle in time 't' is..........
A stone tied to the end of a string 80 cm long is whirled in a horizontal circle with a constant speed. If the stone makes 14 revolutions in 25 s, what is the magnitude and direction of acceleration of the stone?
Why is the motion of a body moving with a constant speed around a circular path said to be accelerated?
Explain the meaning of uniform circular motion. Give one example of such motion.
A uniform circular motion is an accelerated motion. Explain it. State whether the acceleration is uniform or variable? Name the force responsible to cause this acceleration. What is the direction of force at any instant? Draw a diagram in support of your answer.
State True or False
The earth moves around the sun with a uniform.
A uniform linear motion is unaccelerated, while a uniform circular motion is an accelerated motion.
Which of the following quantity remains constant in uniform circular motion:
A uniform metre rule of mass 100g is balanced on a fulcrum at mark 40cm by suspending an unknown mass m at the mark 20cm.
To which side the rule will tilt if the mass m is moved to the mark 10cm ?
Define Uniform circular motion.
Is it possible to have an accelerated motion with a constant speed? Explain.
Solve the following problem.
A projectile is thrown at an angle of 30° to the horizontal. What should be the range of initial velocity (u) so that its range will be between 40m and 50 m? Assume g = 10 m s-2.
Which one of the following is most likely not a case of uniform circular motion?
Is the uniform circular motion accelerated? Give reasons for your answer.
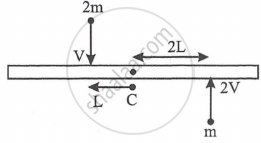
A uniform rod of length '6L' and mass '8 m' is pivoted at its centre 'C'. Two masses 'm' and ' 2m' with speed 2v, v as shown strikes the rod and stick to the rod. Initially the rod is at rest. Due to impact, if it rotates with angular velocity 'w1' then 'w' will be ________.
A particle is perfonning uniform circular motion. If 'θ', 'ω', 'α' and ' a' are its angular displacement, angular velocity, angular acceleration, and centripetal acceleration respectively, then which of the following is 'WRONG'?
A ball of mass 'm' is attached to the free end of an inextensible string of length 'l'. Let 'T' be the tension in the string. The ball is moving in horizontal circular path about the vertical axis. The angular velocity of the ball at any particular instant will be ______.
A stone of mass 3 kg attached at one end of a 2m long string is whirled in horizontal circle. The string makes an angle of 45° with the vertical then the centripetal force acting on the string is ______.
(g = 10 m/s2 , tan 45° = 1)
Statement A: Uniform circular motion is a case of accelerated motion
Statement B: In the third equation of motion we do not have the term time
Define uniform circular motion and give an example of it. Why is it called accelerated motion?
A cyclist starts from centre O of a circular park of radius 1 km and moves along the path OPRQO as shown figure. If he maintains constant speed of 10 ms–1, what is his acceleration at point R in magnitude and direction?

Earth also moves in circular orbit around sun once every year with on orbital radius of 1.5 × 1011 m. What is the acceleration of earth (or any object on the surface of the earth) towards the centre of the sun? How does this acceleration compare with g = 9.8 m/s2?
A small bead of mass m can move on a smooth circular wire (radius R) under the action of a force F = `"Km"/"r"^2` directed (r = position of bead r from P and K = constant) towards a point P within the circle at a distance R/2 from the centre. The minimum velocity should be ______ m/s of bead at the point of the wire nearest the centre of force (P) so that bead will complete the circle. (Take `"k"/(3"R")` = 8 unit)

A particle moves along a circle of radius r with constant tangential acceleration. If the velocity of the particle is v at the end of second revolution, after the revolution has started, then the tangential acceleration is ______.
The acceleration of a point on the rim of a flywheel 1 m in diameter, if it makes 1200 rpm is ______.
A body of mass m is moving in circle of radius r with a constant speed v. The work done by the centripetal force in moving the body over half the circumference of the circle is ______.
