Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
An ideal gas is pumped into a rigid container having diathermic walls so that the temperature remains constant. In a certain time interval, the pressure in the container is doubled. Is the internal energy of the contents of the container also doubled in the interval ?
Solution
An ideal gas is continuously being pumped into the container. Therefore, the number of moles, n are continuously increasing. In a certain interval,
Pressure, P2 = 2P1
n2 = 2n1
Thus, internal energy, U = nCvT will double as the number of moles get doubled.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
A force F is applied on a block of mass M. The block is displaced through a distance d in the direction of the force. What is the work done by the force on the block? Does the internal energy change because of this work?
When we rub our hands they become warm. Have we supplied heat to the hands?
When a tyre bursts, the air coming out is cooler than the surrounding air. Explain.
Consider the process on a system shown in figure. During the process, the work done by the system ______________ .
Consider the following two statements.
(A) If heat is added to a system, its temperature must increase.
(B) If positive work is done by a system in a thermodynamic process, its volume must increase.
A gas is contained in a metallic cylinder fitted with a piston. The piston is suddenly moved in to compress the gas and is maintained at this position. As time passes the pressure of the gas in the cylinder ______________ .
The pressure p and volume V of an ideal gas both increase in a process.
(a) Such a process is not possible.
(b) The work done by the system is positive.
(c) The temperature of the system must increase.
(d) Heat supplied to the gas is equal to the change in internal energy.
In a process on a system, the initial pressure and volume are equal to the final pressure and volume.
(a) The initial temperature must be equal to the final temperature.
(b) The initial internal energy must be equal to the final internal energy.
(c) The net heat given to the system in the process must be zero.
(d) The net work done by the system in the process must be zero.
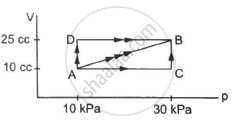
Figure shows three paths through which a gas can be taken from the state A to the state B. Calculate the work done by the gas in each of the three paths.
Explain given cases related to energy transfer between the system and surrounding –
- energy transferred (Q) > 0
- energy transferred (Q) < 0
- energy transferred (Q) = 0
A thermodynamic system goes from states
(i) P, V to 2P, V (ii) P, V to P, 2V
The work done in the two cases is ____________.
8 m3 of a gas is heated at the pressure 105 N/m2 until its volume increases by 10%. Then, the external work done by the gas is ____________.
Which of the following represents isothermal process?
Two cylinders A and B of equal capacity are connected to each other via a stopcock. A contains a gas at standard temperature and pressure. B is completely evacuated. The entire system is thermally insulated. The stopcock is suddenly opened. Answer the following:
What is the change in internal energy of the gas?
A person of mass 60 kg wants to lose 5kg by going up and down a 10 m high stairs. Assume he burns twice as much fat while going up than coming down. If 1 kg of fat is burnt on expending 7000 kilo calories, how many times must he go up and down to reduce his weight by 5 kg?
If a gas is compressed adiabatically:
The internal energy of one mole of argon is ______.
The internal energy of one mole of argon at 300 K is ______. (R = 8.314 J/mol.K)
