Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Answer in brief.
Derive the expression for PV work.
Solution
Pressure-volume work
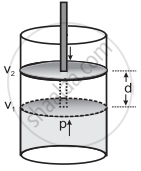
- Consider a certain amount of gas at constant pressure P is enclosed in a cylinder fitted with a frictionless, rigid movable piston of area A. Let the volume of the gas be V1 at temperature T. This is shown in the adjacent diagram.
- On expansion, the force exerted by a gas is equal to area of the piston multiplied by pressure with which the gas pushes against piston. This pressure is equal in magnitude and opposite in sign to the external atmospheric pressure that opposes the movement and has its value - Pext.
Thus,
f = - Pext × A .....(1)
where, Pext is the external atmospheric pressure. - If the piston moves out a distance d, then the amount of work done is equal to the force multiplied by distance.
W = f × d .....(2)
Substituting equation (1) in (2) gives
W = - Pext × A × d .....(3) - The product of area of the piston and distance it moves is the volume change (ΔV) in the system.
ΔV = A × d .....(4)
Combining equation (3) and (4), we get
W = - Pext ΔV
W = - Pext (V2 - V1)
Where V2 is the final volume of the gas.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Answer the following in one or two sentences.
Comment on the statement:
no work is involved in an expansion of gas in a vacuum.
Answer the following question.
One mole of an ideal gas is compressed from 500 cm3 against a constant pressure of 1.2 × 105 Pa. The work involved in the process is 36.0 J. Calculate the final volume.
Answer the following question.
Calculate the work done during the synthesis of NH3 in which volume changes from 8.0 dm3 to 4.0 dm3 at a constant external pressure of 43 bar. In what direction the work-energy flows?
The value of 1dm3 bar is ______.
The work done in the dm3 bar when 200 mL of ethylene gas and 150 mL of HCl gas were allowed to react at 1 bar pressure is ______.
Three moles of an ideal gas are expanded isothermally from 15 dm3 to 20 dm3 at a constant external pressure of 1.2 bar, calculate the amount of work in Joules.
Work done when 2 mole of an ideal gas is compressed from a volume of 5m3 to 2.5m3 at 300 K, under a pressure of 100 kpa is ______.
If, 2 moles of an ideal gas at 546 K has volume of 44.8 L, then what will be it's pressure?
Three moles of an ideal gas are expanded isothermally from a volume of 300 cm3 to 2.5 L at 300 K against a pressure of 1.9 atm. The work done in joules is ____________.
10 bar dm3 is approximately equal to ____________.
3 moles of an ideal gas is compressed from 50 dm3 to 30 dm3 against a constant external pressure of 3.039 × 105 N m−2. The work done in calories is ____________.
(1 J = 0.239 cal)
If 200 mL of ethylene gas and 200 mL of HCl gas are allowed to react at 2 atmosphere pressure as per given reaction,
\[\ce{C2H_{4(g)} + HCl_{(g)} -> C2H5Cl_{(g)}}\]
Calculate pressure volume work in Joule.
Calculate the work done during compression of 2 mol of an ideal gas from a volume of 1m3 to 10 dm3 300K against a pressure of 100 KP a.
Two moles of an ideal gas are allowed to expand from a volume of 10 dm3 to 2 m3 at 300 K against a pressure of 101.325 KPa. Calculate the work done.
Calculate the work done during the expansion of 2 moles of an ideal gas from 10 dm3 to 20 dm3 at 298 K in a vacuum.
Write the sign convention of work done during expansion of gas.
