Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
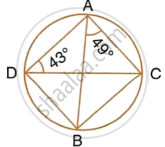
Calculate:
- ∠CDB,
- ∠ABC,
- ∠ACB.
Solution

Here,
∠CDB = ∠BAC = 49°
∠ABC =∠ADC = 43°
(Angle subtend by the same chord on the circle are equal)
By angle – sum property of a triangle,
∠ACB = 180° – 49° – 43° = 88°
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
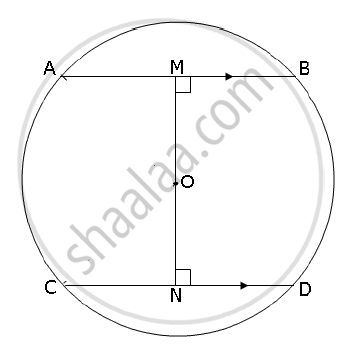
In the figure given below AB and CD are two parallel chords and O is the centre. If the radius of the circle is 15 cm, find the distance MN between the two chords of length 24 cm and 18 cm respectively.
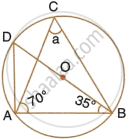
In the following figure, O is the centre of the circle. Find the value of a, b, c and d.
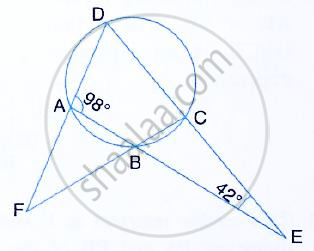
The sides AB and DC of a cyclic quadrilateral ABCD are produced to meet at E; the sides DA and CB are produced to meet at F. If ∠BEC = 42° and ∠BAD = 98°; Calculate :
(i) ∠AFB (ii) ∠ADC
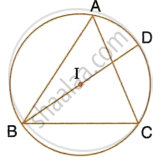
In the given figure, I is the incentre of ΔABC. BI when produced meets the circumcircle of ΔABC at D. ∠BAC = 55° and ∠ACB = 65°; calculate:
- ∠DCA,
- ∠DAC,
- ∠DCI,
- ∠AIC.
The line joining the midpoints of two chords of a circle passes through its center.
Prove that the chords are parallel.
The length of the common chord of two intersecting circles is 30 cm. If the diameters of these two circles are 50 cm and 34 cm, calculate the distance between their centers.
Given two equal chords AB and CD of a circle with center O, intersecting each other at point P.
Prove that:
(i) AP = CP
(ii) BP = DP
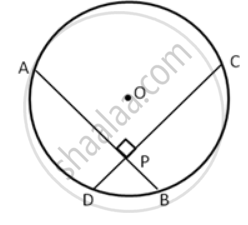
If two chords of a circle are equally inclined to the diameter through their point of intersection, prove that the chords are equal.
AB and CD are two chords of a circle such that AB = 6 cm, CD = 12 cm and AB || CD. If the distance between AB and CD is 3 cm, find the radius of the circle.
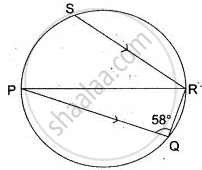
In the adjoining figure, PQ is the diameter, chord SR is parallel to PQ. Give ∠ PQR = 58°.
Calculate:
(i) ∠ RPQ,
(ii) ∠ STP ( T is a point on the minor arc)