Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Can you add two vectors representing physical quantities having different dimensions? Can you multiply two vectors representing physical quantities having different dimensions?
Solution
No, we cannot add two vectors representing physical quantities of different dimensions. However, we can multiply two vectors representing physical quantities with different dimensions.
Example: Torque,
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
India has had a long and unbroken tradition of great scholarship — in mathematics, astronomy, linguistics, logic and ethics. Yet, in parallel with this, several superstitious and obscurantistic attitudes and practices flourished in our society and unfortunately continue even today — among many educated people too. How will you use your knowledge of science to develop strategies to counter these attitudes ?
If two quantities have same dimensions, do they represent same physical content?
A unitless quantity
\[\int\frac{dx}{\sqrt{2ax - x^2}} = a^n \sin^{- 1} \left[ \frac{x}{a} - 1 \right]\]
The value of n is
Find the dimensions of frequency .
Find the dimensions of the coefficient of linear expansion α and
The height of mercury column in a barometer in a Calcutta laboratory was recorded to be 75 cm. Calculate this pressure in SI and CGS units using the following data : Specific gravity of mercury = \[13 \cdot 6\] , Density of \[\text{ water} = {10}^3 kg/ m^3 , g = 9 \cdot 8 m/ s^2\] at Calcutta. Pressure
= hpg in usual symbols.
Test if the following equation is dimensionally correct:
\[V = \frac{\pi P r^4 t}{8 \eta l}\]
where v = frequency, P = pressure, η = coefficient of viscosity.
Can a vector have zero component along a line and still have nonzero magnitude?
If \[\vec{A} \times \vec{B} = 0\] can you say that
(a) \[\vec{A} = \vec{B} ,\]
(b) \[\vec{A} \neq \vec{B}\] ?
A vector is not changed if
Which of the sets given below may represent the magnitudes of three vectors adding to zero?
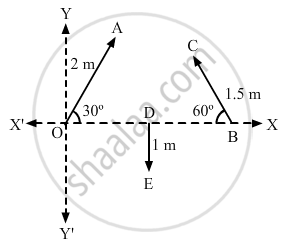
Refer to figure (2 − E1). Find (a) the magnitude, (b) x and y component and (c) the angle with the X-axis of the resultant of \[\overrightarrow{OA}, \overrightarrow{BC} \text { and } \overrightarrow{DE}\].
Suppose \[\vec{a}\] is a vector of magnitude 4.5 units due north. What is the vector (a) \[3 \vec{a}\], (b) \[- 4 \vec{a}\] ?
Let \[\vec{a} = 2 \vec{i} + 3 \vec{j} + 4 \vec{k} \text { and } \vec{b} = 3 \vec{i} + 4 \vec{j} + 5 \vec{k}\] Find the angle between them.
Prove that \[\vec{A} . \left( \vec{A} \times \vec{B} \right) = 0\].
Give an example for which \[\vec{A} \cdot \vec{B} = \vec{C} \cdot \vec{B} \text{ but } \vec{A} \neq \vec{C}\].
Draw a graph from the following data. Draw tangents at x = 2, 4, 6 and 8. Find the slopes of these tangents. Verify that the curve draw is y = 2x2 and the slope of tangent is \[\tan \theta = \frac{dy}{dx} = 4x\]
\[\begin{array}x & 1 & 2 & 3 & 4 & 5 & 6 & 7 & 8 & 9 & 10 \\ y & 2 & 8 & 18 & 32 & 50 & 72 & 98 & 128 & 162 & 200\end{array}\]
