Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Check the injectivity and surjectivity of the following function:
f: N → N given by f(x) = x3
Solution
f: N → N given by,
f(x) = x3
It is seen that for x, y ∈N, f(x) = f(y)
⇒ x3 = y3
⇒ x = y.
∴ f is injective.
Now, 2 ∈ N. But there does not exist any element x in domain N such that f(x) = x3 = 2.
∴ f is not surjective
Hence, function f is injective but not surjective.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Following the case, state whether the function is one-one, onto, or bijective. Justify your answer.
f: R → R defined by f(x) = 1 + x2
If the function `f(x) = sqrt(2x - 3)` is invertible then find its inverse. Hence prove that `(fof^(-1))(x) = x`
Which of the following functions from A to B are one-one and onto?
f1 = {(1, 3), (2, 5), (3, 7)} ; A = {1, 2, 3}, B = {3, 5, 7}
Classify the following function as injection, surjection or bijection :
f : R → R, defined by f(x) = |x|
Classify the following function as injection, surjection or bijection :
f : Z → Z, defined by f(x) = x2 + x
Classify the following function as injection, surjection or bijection :
f : R → R, defined by f(x) = 3 − 4x
Find fog and gof if : f(x) = c, c ∈ R, g(x) = sin `x^2`
Let f(x) = x2 + x + 1 and g(x) = sin x. Show that fog ≠ gof.
Consider f : R+ → [−5, ∞) given by f(x) = 9x2 + 6x − 5. Show that f is invertible with `f^-1 (x) = (sqrt (x +6)-1)/3 .`
Consider the function f : R+ → [-9 , ∞ ]given by f(x) = 5x2 + 6x - 9. Prove that f is invertible with f -1 (y) = `(sqrt(54 + 5y) -3)/5` [CBSE 2015]
If A = {1, 2, 3, 4} and B = {a, b, c, d}, define any four bijections from A to B. Also give their inverse functions.
If f : A → A, g : A → A are two bijections, then prove that fog is an injection ?
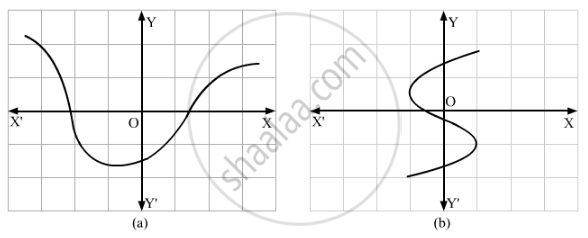
Which one of the following graphs represents a function?
Let C denote the set of all complex numbers. A function f : C → C is defined by f(x) = x3. Write f−1(1).
If f : R → R be defined by f(x) = (3 − x3)1/3, then find fof (x).
Let A = {1, 2, 3}, B = {4, 5, 6, 7} and let f = {(1, 4), (2, 5), (3, 6)} be a function from A to B. State whether f is one-one or not.
\[f : R \to R \text{given by} f\left( x \right) = x + \sqrt{x^2} \text{ is }\]
Which of the following functions from
to itself are bijections?
Let
\[A = \left\{ x : - 1 \leq x \leq 1 \right\} \text{and} f : A \to \text{A such that f}\left( x \right) = x|x|\]
Let
\[f : R \to R\] be a function defined by
The function
The inverse of the function
\[f : R \to \left\{ x \in R : x < 1 \right\}\] given by
\[f\left( x \right) = \frac{e^x - e^{- x}}{e^x + e^{- x}}\] is
Mark the correct alternative in the following question:
If the set A contains 5 elements and the set B contains 6 elements, then the number of one-one and onto mappings from A to B is
If A = {a, b, c, d} and f = {a, b), (b, d), (c, a), (d, c)}, show that f is one-one from A onto A. Find f–1
Let f: R → R be defined by f(x) = 3x – 4. Then f–1(x) is given by ______.
The domain of the function f: R → R defined by f(x) = `sqrt(x^2 - 3x + 2)` is ______
Let A be a finite set. Then, each injective function from A into itself is not surjective.
Let X = {1, 2, 3}and Y = {4, 5}. Find whether the following subset of X ×Y are function from X to Y or not
f = {(1, 4), (1, 5), (2, 4), (3, 5)}
Let f: R → R be given by f(x) = tan x. Then f–1(1) is ______.
Let f : R → R be defind by f(x) = `1/"x" AA "x" in "R".` Then f is ____________.
Let A = R – {3}, B = R – {1}. Let f : A → B be defined by `"f"("x") = ("x" - 2)/("x" - 3)` Then, ____________.
Let R be a relation on the set L of lines defined by l1 R l2 if l1 is perpendicular to l2, then relation R is ____________.
A general election of Lok Sabha is a gigantic exercise. About 911 million people were eligible to vote and voter turnout was about 67%, the highest ever

Let I be the set of all citizens of India who were eligible to exercise their voting right in the general election held in 2019. A relation ‘R’ is defined on I as follows:
R = {(V1, V2) ∶ V1, V2 ∈ I and both use their voting right in the general election - 2019}
- Mr. ’X’ and his wife ‘W’ both exercised their voting right in the general election-2019, Which of the following is true?
Let the function f: R → R be defined by f(x) = 4x – 1, ∀ x ∈ R then 'f' is
The domain of the function `cos^-1((2sin^-1(1/(4x^2-1)))/π)` is ______.
Let f: R→R be defined as f(x) = 2x – 1 and g: R – {1}→R be defined as g(x) = `(x - 1/2)/(x - 1)`. Then the composition function f (g(x)) is ______.
Find the domain of sin–1 (x2 – 4).
