Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Which one of the following graphs represents a function?
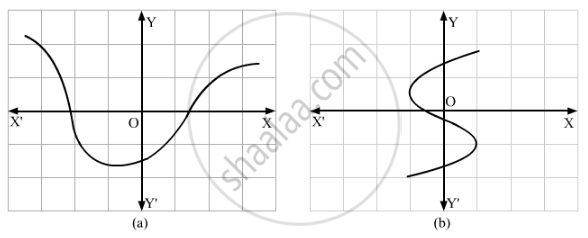
Solution
In graph (b), 0 has more than one image, whereas every value of x in graph (a) has a unique image.
Thus, graph (a) represents a function.
So, the answer is (a).
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Show that the Signum Function f: R → R, given by `f(x) = {(1, if x > 0), (0, if x = 0), (-1, if x < 0):}` is neither one-one nor onto
Given examples of two functions f: N → N and g: N → N such that gof is onto but f is not onto.
(Hint: Consider f(x) = x + 1 and `g(x) = {(x-1, ifx >1),(1, if x = 1):}`
Let f: R → R be the Signum Function defined as
f(x) = `{(1,x>0), (0, x =0),(-1, x< 0):}`
and g: R → R be the Greatest Integer Function given by g(x) = [x], where [x] is greatest integer less than or equal to x. Then does fog and gof coincide in (0, 1]?
Give an example of a function which is neither one-one nor onto ?
Which of the following functions from A to B are one-one and onto?
f2 = {(2, a), (3, b), (4, c)} ; A = {2, 3, 4}, B = {a, b, c}
Classify the following function as injection, surjection or bijection : f : N → N given by f(x) = x2
Classify the following function as injection, surjection or bijection :
f : R → R, defined by f(x) = sin2x + cos2x
Classify the following function as injection, surjection or bijection :
f : R → R, defined by f(x) = 5x3 + 4
Classify the following function as injection, surjection or bijection :
f : R → R, defined by f(x) = 3 − 4x
Set of ordered pair of a function? If so, examine whether the mapping is injective or surjective :{(x, y) : x is a person, y is the mother of x}
Let A = {1, 2, 3}. Write all one-one from A to itself.
Find gof and fog when f : R → R and g : R → R is defined by f(x) = 2x + x2 and g(x) = x3
Find fog (2) and gof (1) when : f : R → R ; f(x) = x2 + 8 and g : R → R; g(x) = 3x3 + 1.
Let f : R → R and g : R → R be defined by f(x) = x + 1 and g (x) = x − 1. Show that fog = gof = IR.
Find fog and gof if : f(x) = sin−1 x, g(x) = x2
If f(x) = 2x + 5 and g(x) = x2 + 1 be two real functions, then describe each of the following functions:
(1) fog
(2) gof
(3) fof
(4) f2
Also, show that fof ≠ f2
Let f be a real function given by f (x)=`sqrt (x-2)`
Find each of the following:
(i) fof
(ii) fofof
(iii) (fofof) (38)
(iv) f2
Also, show that fof ≠ `f^2` .
A function f : R → R is defined as f(x) = x3 + 4. Is it a bijection or not? In case it is a bijection, find f−1 (3).
If A = {a, b, c} and B = {−2, −1, 0, 1, 2}, write the total number of one-one functions from A to B.
If f : C → C is defined by f(x) = x4, write f−1 (1).
If f : R → R is defined by f(x) = 10 x − 7, then write f−1 (x).
Let f be an invertible real function. Write ( f-1 of ) (1) + ( f-1 of ) (2) +..... +( f-1 of ) (100 )
If f : {5, 6} → {2, 3} and g : {2, 3} → {5, 6} are given by f = {(5, 2), (6, 3)} and g = {(2, 5), (3, 6)}, then find fog. [NCERT EXEMPLAR]
\[f : R \to R \text{given by} f\left( x \right) = x + \sqrt{x^2} \text{ is }\]
Let f: R → R be the function defined by f(x) = 2x – 3 ∀ x ∈ R. write f–1
Let A = [–1, 1]. Then, discuss whether the following functions defined on A are one-one, onto or bijective:
g(x) = |x|
Let A = {1, 2, 3, ...n} and B = {a, b}. Then the number of surjections from A into B is ______.
If `f : R -> R^+ U {0}` be defined by `f(x) = x^2, x ∈ R`. The mapping is
A function f: x → y is/are called onto (or surjective) if x under f.
Consider a function f: `[0, pi/2] ->` R, given by f(x) = sinx and `g[0, pi/2] ->` R given by g(x) = cosx then f and g are
Let [x] denote the greatest integer ≤ x, where x ∈ R. If the domain of the real valued function f(x) = `sqrt((|[x]| - 2)/(|[x]| - 3)` is (–∞, a) ∪ [b, c) ∪ [4, ∞), a < b < c, then the value of a + b + c is ______.
Let x is a real number such that are functions involved are well defined then the value of `lim_(t→0)[max{(sin^-1 x/3 + cos^-1 x/3)^2, min(x^2 + 4x + 7)}]((sin^-1t)/t)` where [.] is greatest integer function and all other brackets are usual brackets.
Let a and b are two positive integers such that b ≠ 1. Let g(a, b) = Number of lattice points inside the quadrilateral formed by lines x = 0, y = 0, x = b and y = a. f(a, b) = `[a/b] + [(2a)/b] + ... + [((b - 1)a)/b]`, then the value of `[(g(101, 37))/(f(101, 37))]` is ______.
(Note P(x, y) is lattice point if x, y ∈ I)
(where [.] denotes greatest integer function)
For x ∈ R, x ≠ 0, let f0(x) = `1/(1 - x)` and fn+1 (x) = f0(fn(x)), n = 0, 1, 2, .... Then the value of `f_100(3) + f_1(2/3) + f_2(3/2)` is equal to ______.
Write the domain and range (principle value branch) of the following functions:
f(x) = tan–1 x.
