Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Conductivity of 0.00241 M acetic acid is 7.896 × 10−5 S cm−1. Calculate its molar conductivity and if `∧_"m"^0` for acetic acid is 390.5 S cm2 mol−1, what is its dissociation constant?
Solution
`∧_"m"^"c" = (κ xx 1000)/"Molarity"`
= `(7.896 xx 10^-5 xx 1000)/0.00241`
= 32.763 S cm2 mol−1
α = `(∧_"m"^"c")/(∧_"m"^0) = 32.763/390.5` = 0.084
K = `(α^2"c")/(1 - α)`
= `((0.084)^2 xx 0.00241)/(1 - 0.084)`
= `((0.084)^2 xx 0.00241)/(0.916)`
= 1.86 × 10−5
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Define "Molar conductivity".
The conductivity of 0.20 mol L−1 solution of KCl is 2.48 × 10−2 S cm−1. Calculate its molar conductivity and degree of dissociation (α). Given λ0 (K+) = 73.5 S cm2 mol−1 and λ0 (C1−) = 76.5 S cm2 mol−1.
Why does the conductivity of a solution decrease with dilution?
Write mathematical expression of molar conductivity of the given solution at infinite dilution.
Kohlrausch law of independent migration of ions states ____________.
\[\ce{Λ^0_m}_{(NH_4OH)}\] is equal to ______.
Molar conductivity of ionic solution depends on:
(i) temperature.
(ii) distance between electrodes.
(iii) concentration of electrolytes in solution.
(iv) surface area of electrodes.
Solutions of two electrolytes ‘A’ and ‘B’ are diluted. The Λm of ‘B’ increases 1.5 times while that of A increases 25 times. Which of the two is a strong electrolyte? Justify your answer.
Write the cell reaction of a lead storage battery when it is discharged. How does the density of the electrolyte change when the battery is discharged?
Assertion: `"E"_("Ag"^+ //"Ag")` increases with increase in concentration of Ag+ ions.
Reason: `"E"_("Ag"^+ //"Ag")` has a positive value.
Consider figure and answer the question to given below.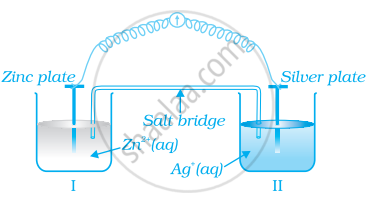
How will the concentration of Zn2+ ions and Ag+ ions be affected after the cell becomes ‘dead’?
The molar conductance of \[\ce{NaCl, HCl}\] and \[\ce{CH3COONa}\] at infinite dilution are 126.45, 426.16 and 91.0 S cm2 mol−1 respectively. The molar conductance of \[\ce{CH3COOH}\] at infinite dilution is. Choose the right option for your answer.
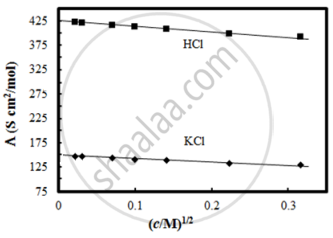
The molar conductivity of CH3COOH at infinite dilution is 390 Scm2/mol. Using the graph and given information, the molar conductivity of CH3COOK will be:
The solubility of Co2[Fe(CN)6] in water at 25°C from the following data:
Conductivity of saturated solution of Co2[Fe(CN)6] = 2.06 × 10−6 ohm−1 cm−1 and that of water = 4.1 × 10−7 ohm−1 cm−1. The ionic molar conductivities of Co2+ and [Fe(CN)6]4− are 86 and 444 ohm−1 cm2 mol−1 respectively, is ______ × 10−6 mol/L.
Which of the following solutions of KCl will have the highest value of molar conductivity?
Which of the following solutions will have the highest conductivity at 298 K?
The resistance of a conductivity cell with a 0.1 M KCl solution is 200 ohm. When the same cell is filled with a 0.02 M NaCl solution, the resistance is 1100 ohm. If the conductivity of 0.1 M KCl solution is 0.0129 ohm-1 cm-1, calculate the cell constant and molar conductivity of 0.02 M NaCl solution.
