Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Consider the situation shown in the figure. Suppose the wire connecting O and C has zero resistance but the circular loop has a resistance Runiformly distributed along its length. The rod OA is made to rotate with a uniform angular speed ω as shown in the figure. Find the current in the rod when ∠ AOC = 90°.
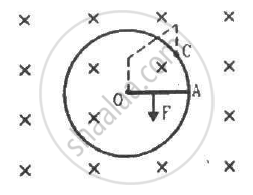
Solution
Calculation of the emf induced in the rotating rod:-
It is given that the angular velocity of the disc is ω and the magnetic field perpendicular to the disc is having magnitude B.
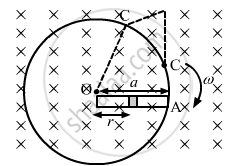
Let us take an element of the rod of thickness dr at a distance r from the centre.
Now,
Linear speed of the element at r from the centre, v = ωr
\[de = Blv\]
\[de = B \times dr \times \omega r\]
\[ \Rightarrow e = \int_0^a \left( B\omega r \right)dr\]
\[= \frac{1}{2}B\omega a^2\]
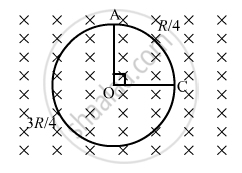
As ∠AOC = 90°, the minor and major segments of AC are in parallel with the rod.
The resistances of the segments are `R/4` and `(3R)/4.`
The equivalent resistance is given by
`R'=(R/4xx(3R/4))/R=(3R)/16`
The motional emf induced in the rod rotating in the clockwise direction is given by
`e=1/2Bomegaa^2`
The current through the rod is given by
\[i = \frac{e}{R'}\]
\[ = \frac{B a^2 \omega}{2R'}\]
\[ = \frac{B a^2 \omega}{2 \times 3R/16}\]
\[ = \frac{B a^2 \omega \times 16}{2 \times 3R} = \frac{8B a^2 \omega}{3R}\]
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
An aircraft of wing span of 50 m flies horizontally in the Earth's magnetic field of 6 x 10-5 T at a speed of 400 m/s. Calculate the emf generated between the tips of the wings of the aircraft.
A cycle wheel of radius 0.6 m is rotated with constant angular velocity of 15 rad/s in a region of magnetic field of 0.2 T which is perpendicular to the plane of the wheel. The e.m.f generated between its center and the rim is, ____________.
A wire of length 50 cm moves with a velocity of 300 m/min, perpendicular to a magnetic field. If the e.m.f. induced in the wire is 2 V, the magnitude of the field in tesla is ______.
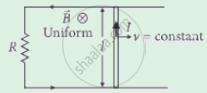
The emf induced across the ends of a conductor due to its motion in a magnetic field is called motional emf. It is produced due to magnetic Lorentz force acting on the free electrons of the conductor. For a circuit shown in the figure, if a conductor of length l moves with velocity v in a magnetic field B perpendicular to both its length and the direction of the magnetic field, then all the induced parameters are possible in the circuit.
Direction of current induced in a wire moving in a magnetic field is found using ______.
The emf induced across the ends of a conductor due to its motion in a magnetic field is called motional emf. It is produced due to magnetic Lorentz force acting on the free electrons of the conductor. For a circuit shown in the figure, if a conductor of length l moves with velocity v in a magnetic field B perpendicular to both its length and the direction of the magnetic field, then all the induced parameters are possible in the circuit.
A 0.1 m long conductor carrying a current of 50 A is held perpendicular to a magnetic field of 1.25 mT. The mechanical power required to move the conductor with a speed of 1 ms-1 is ______.
Motional e.m.f is the induced e.m.f. ______
An e.m.f is produced in a coil, which is not connected to an external voltage source. This can be due to ______.
- the coil being in a time varying magnetic field.
- the coil moving in a time varying magnetic field.
- the coil moving in a constant magnetic field.
- the coil is stationary in external spatially varying magnetic field, which does not change with time.
A circular coil expands radially in a region of magnetic field and no electromotive force is produced in the coil. This can be because ______.
- the magnetic field is constant.
- the magnetic field is in the same plane as the circular coil and it may or may not vary.
- the magnetic field has a perpendicular (to the plane of the coil) component whose magnitude is decreasing suitably.
- there is a constant magnetic field in the perpendicular (to the plane of the coil) direction.
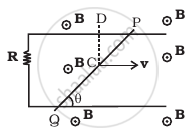
Find the current in the wire for the configuration shown in figure. Wire PQ has negligible resistance. B, the magnetic field is coming out of the paper. θ is a fixed angle made by PQ travelling smoothly over two conducting parallel wires separated by a distance d.
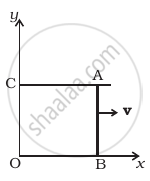
A magnetic field B = Bo sin ( ωt )`hatk` wire AB slides smoothly over two parallel conductors separated by a distance d (Figure). The wires are in the x-y plane. The wire AB (of length d) has resistance R and the parallel wires have negligible resistance. If AB is moving with velocity v, what is the current in the circuit. What is the force needed to keep the wire moving at constant velocity?
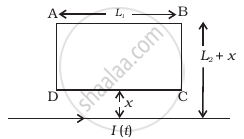
A rectangular loop of wire ABCD is kept close to an infinitely long wire carrying a current I(t) = Io (1 – t/T) for 0 ≤ t ≤ T and I(0) = 0 for t > T (Figure). Find the total charge passing through a given point in the loop, in time T. The resistance of the loop is R.
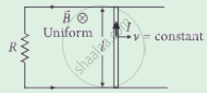
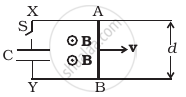
Find the current in the sliding rod AB (resistance = R) for the arrangement shown in figure. B is constant and is out of the paper. Parallel wires have no resistance. v is constant. Switch S is closed at time t = 0.
An aeroplane, with its wings spread 10 m, is flying at a speed of 180 km/h in a horizontal direction. The total intensity of earth's field at that part is 2.5 × 10-4 Wb/m2 and the angle of dip is 60°. The emf induced between the tips of the plane wings will be ______.
A wire 5 m long is supported horizontally at a height of 15 m along an east-west direction. When it is about to hit the ground, calculate the average e.m.f. induced in it. (g = 10 m/s2)
A magnetic flux associated with a coil changes by 0.04 Wb in 0.2 second. The induced emf with coil is ______.
An aircraft of wing span of 60 m flies horizontally in earth’s magnetic field of 6 × 10−5 T at a speed of 500 m/s. Calculate the e.m.f. induced between the tips of the wings of the aircraft.
