Advertisements
Advertisements
Questions
Consider the fission of
In a fission event of
Given:
Solution
In the fission of
It is given that:
Mass of a nucleus
Mass of a nucleus
Mass of a nucleus
Mass of a neutron
Q-value of the above equation,
Where,
m’ = Represents the corresponding atomic masses of the nuclei
But 1 u =
Hence, the Q-value of the fission process is 231.510 MeV.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Is the nucleus formed in the decay of the nucleus
The neutron separation energy is defined as the energy required to remove a neutron from the nucleus. Obtain the neutron separation energies of the nuclei
What is meant by the terms half-life of a radioactive substance and binding energy of a nucleus?
What is the significance of binding energy per nucleon of a nucleus of a radioactive element?
What is the minimum energy which a gamma-ray photon must possess in order to produce electron-positron pair?
Binding energy per nucleon for helium nucleus (2 He) is 7.0 MeV Find value of mass defect for helium nucleus
Calculate mass defect and binding energy per nucleon of
Mass of
Mass of
Mass of
In a nuclear reactor, what is the function of:
(i) The moderator
(ii) The control rods
(iii) The coolant
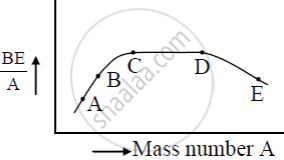
The figure shows the plot of binding energy (BE) per nucleon as a function of mass number A. The letters A, B, C, D, and E represent the positions of typical nuclei on the curve. Point out, giving reasons, the two processes (in terms of A, B, C, D, and E ), one of which can occur due to nuclear fission and the other due to nuclear fusion.
Calculate the binding energy of an alpha particle given its mass to be 4.00151 u.
An electron in hydrogen atom stays in its second orbit for 10−8 s. How many revolutions will it make around the nucleus at that time?
The difference in mass of a nucleus and its constituents is called ______.
A body's centre of mass
Tritium is an isotope of hydrogen whose nucleus Triton contains 2 neutrons and 1 proton. Free neutrons decay into
Nuclei with magic no. of proton Z = 2, 8, 20, 28, 50, 52 and magic no. of neutrons N = 2, 8, 20, 28, 50, 82 and 126 are found to be very stable.
(i) Verify this by calculating the proton separation energy Sp for 120Sn (Z = 50) and 121Sb = (Z = 51).
The proton separation energy for a nuclide is the minimum energy required to separate the least tightly bound proton from a nucleus of that nuclide. It is given by
Given 119In = 118.9058u, 120Sn = 119.902199u, 121Sb = 120.903824u, 1H = 1.0078252u.
(ii) What does the existance of magic number indicate?
State the significance of binding energy per nucleon.
What is binding energy of nucleus?
What is meant by “binding energy per nucleon” of a nucleus?
