Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Construct a rectangle whose one side is 3 cm and a diagonal equal to 5 cm.
Solution
We know that, diagonals of a rectangle and opposite sides are equal.
All the angles of rectangle are right angle.
So, AC = 5 cm
AB = 3 cm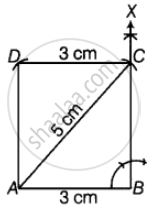
Steps of construction:
Step I: Draw AB = 3 cm.
Step II: Draw a ray BX such that ∠ABX = 90°.
Step III: Draw an arc such that AC = 5 cm.
Step IV: With B as centre, draw an arc of radius 5 cm. With C as centre, draw another arc of radius 3 cm which intersect first arc at a point, suppose D.
Step V: Join CD and AD.
Thus, ABCD is the required rectangle.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
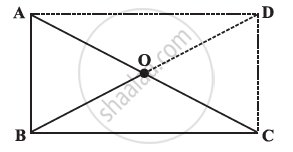
ABC is a right-angled triangle and O is the mid point of the side opposite to the right angle. Explain why O is equidistant from A, B and C. (The dotted lines are drawn additionally to help you)
Fill in the blank in the following, so as to make the statement true:
A rectangle is a parallelogram in which .....
In a rectangle ABCD, prove that ∆ACB ≅ ∆CAD.
A mason has made a concrete slab. He needs it to be rectangular. In what different ways can he make sure that it is rectangular?
If diagonal of a rectangle is 26 cm and one side is 24 cm, find the other side.
A quadrilateral whose opposite sides and all the angles are equal is a ______.
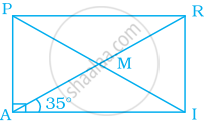
In rectangle PAIR, find ∠ARI, ∠RMI and ∠PMA.
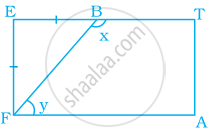
A playground is in the form of a rectangle ATEF. Two players are standing at the points F and B where EF = EB. Find the values of x and y.
Quadrilateral EFGH is a rectangle in which J is the point of intersection of the diagonals. Find the value of x if JF = 8x + 4 and EG = 24x – 8.
A line l is parallel to line m and a transversal p intersects them at X, Y respectively. Bisectors of interior angles at X and Y interesct at P and Q. Is PXQY a rectangle? Given reason.
