Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Describe completely the locus of points in the following cases:
Centre of a circle of varying radius and touching the two arms of ∠ ABC.
Solution
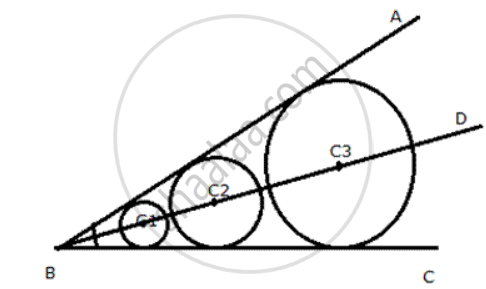
The Iocus of a cirde of varying radius and touching two arms of ∠ ABC is the bisector of that angle.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Construct a triangle ABC with AB = 5.5 cm, AC = 6 cm and ∠BAC = 105°
Hence:
1) Construct the locus of points equidistant from BA and BC
2) Construct the locus of points equidistant from B and C.
3) Mark the point which satisfies the above two loci as P. Measure and write the length of PC.
On a graph paper, draw the line x = 6. Now, on the same graph paper, draw the locus of the point which moves in such a way that its distantce from the given line is always equal to 3 units
Construct a triangle ABC, with AB = 6 cm, AC = BC = 9 cm. Find a point 4 cm from A and equidistant from B and C.
Construct a rhombus ABCD with sides of length 5 cm and diagonal AC of length 6 cm. Measure ∠ ABC. Find the point R on AD such that RB = RC. Measure the length of AR.
Draw and describe the lorus in the following cases:
The lorus of points inside a circle and equidistant from two fixed points on the circle .
Describe completely the locus of point in the following cases:
Midpoint of radii of a circle.
Describe completely the locus of points in the following cases:
Point in a plane equidistant from a given line.
Draw and describe the locus in the following cases :
The locus of a point in the rhombus ABCD which is equidistant from the point A and C
Construct a triangle BPC given BC = 5 cm, BP = 4 cm and .
i) complete the rectangle ABCD such that:
a) P is equidistant from AB and BCV
b) P is equidistant from C and D.
ii) Measure and record the length of AB.
Use ruler and compass to answer this question. Construct ∠ABC = 90°, where AB = 6 cm, BC = 8 cm.
- Construct the locus of points equidistant from B and C.
- Construct the locus of points equidistant from A and B.
- Mark the point which satisfies both the conditions (a) and (b) as 0. Construct the locus of points keeping a fixed distance OA from the fixed point 0.
- Construct the locus of points which are equidistant from BA and BC.
