Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Discuss the nature of bonding in the following coordination entity on the basis of valence bond theory:
[CoF6]3−
Solution
Co(27) = [Ar] 3d74s2
Co3+ = [Ar] 3d64s0
F− being a weak field ligand cannot pair electrons.
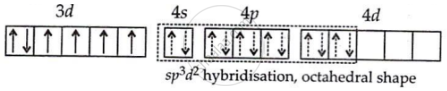
Hence, [CoF6]3− is a paramagnetic and octahedral complex.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
[NiCl4]2− is paramagnetic, while [Ni(CO)4] is diamagnetic, though both are tetrahedral. Why? (Atomic number of Ni = 28)
Explain on the basis of valence bond theory that [Ni(CN)4]2− ion with square planar structure is diamagnetic and the [NiCl4]2− ion with tetrahedral geometry is paramagnetic.
Predict the number of unpaired electrons in the square planar [Pt(CN)4]2− ion.
Write the hybridisation and number of unpaired electrons in the complex `[CoF_6]^(3-)`. (Atomic No. of Co = 27)
[NiCl4]2- is paramagnetic while [Ni(CO)4] is diamagnetic though both are tetrahedral. Why? (Atomic no. Ni = 28)
Using valence bond theory, explain the following in relation to the complexes given below:
\[\ce{[FeCl6]^{4-}}\]
(i) Type of hybridisation.
(ii) Inner or outer orbital complex.
(iii) Magnetic behaviour.
(iv) Spin only magnetic moment value.
Write the hybridization and shape of the following complexes:
[Ni(CN)4]2−
In a coordination entity, the electronic configuration of the central metal ion is t2g3 eg1
Is the coordination compound a high spin or low spin complex?
If orbital quantum number (l) has values 0, 1, 2 and 3, deduce the corresponding value of principal quantum number, n.
As the s-character of hybridised orbital increases, the bond angle
Which of the following has square planar structures?
What is the no. of possible isomers for the octahedral complex [Co(NH3)2(C2O4)2]?
Valence bond theory is based on the assumption that the bonds formed between the metal ions and ligands are ______
Using valence bond theory, predict the hybridization and magnetic character of the following:
[CoF6]3– [Atomic number of Co = 27]
According to the valence bond theory, the hybridization of central metal atom is dsp2 for which one of the following compounds?
[Ni(CO)4] has tetrahedral geometry while [Ni(CN)4]2− has square planar, yet both exhibit diamagnetism. Explain.
[Atomic number: Ni = 28]
During chemistry class, a teacher wrote \[\ce{[Ni(CN)4]^2-}\] as a coordination complex ion on the board. The students were asked to find out the magnetic behaviour and shape of the complex. Pari, a student, wrote the answer paramagnetic and tetrahedral whereas another student Suhail wrote diamagnetic and square planer.
Evaluate Pari’s and Suhail’s responses.
