Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Draw ∆PQR such that PQ = 6.8 cm, vertical angle is 50° and the bisector of the vertical angle meets the base at D where PD = 5.2 cm
Solution
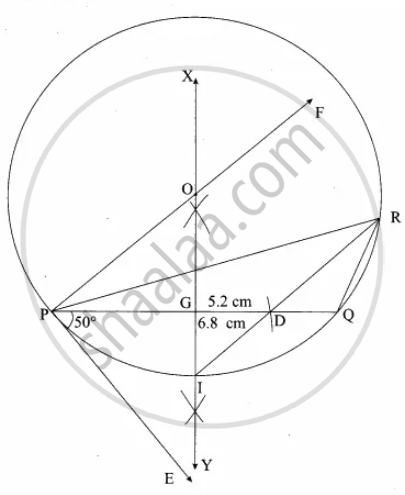
Steps of construction:
1. Draw a line segment PQ = 6.8 cm.
2. At P draw PE such that ∠QPE = 50°.
3. At P draw PF such that ∠EPF = 90°.
4. Draw the perpendicular bisector to PQ which intersects PF at O and PQ at G.
5. With O as centre and OP as radius draw a circle.
6. From P mark an arc of 5.2 cm on PQ at D.
7. The perpendicular bisector intersects the circle at I. Join ID.
8. ID produced meets the circle at A. Now Joint PR and QR. This ∆PQR is the required triangle.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
In ∆ABC, D and E are points on the sides AB and AC respectively such that DE || BC
If `"AD"/"DB" = 3/4` and AC = 15 cm find AE
ABCD is a trapezium in which AB || DC and P, Q are points on AD and BC respectively, such that PQ || DC if PD = 18 cm, BQ = 35 cm and QC = 15 cm, find AD
In ΔABC, D and E are points on the sides AB and AC respectively. For the following case show that DE || BC
AB = 12 cm, AD = 8 cm, AE = 12 cm and AC = 18 cm
If PQ || BC and PR || CD prove that `"AR"/"AD" = "AQ"/"AB"`
Check whether AD is bisector of ∠A of ∆ABC of the following
AB = 4 cm, AC = 6 cm, BD = 1.6 cm and CD = 2.4 cm.
Construct a ∆PQR in which the base PQ = 4.5 cm, ∠R = 35° and the median from R to RG is 6 cm.
Construct a ∆PQR such that QR = 6.5 cm, ∠P = 60° and the altitude from P to QR is of length 4.5 cm
Draw a triangle ABC of base BC = 5.6 cm, ∠A = 40° and the bisector of ∠A meets BC at D such that CD = 4 cm
ST || QR, PS = 2 cm and SQ = 3 cm. Then the ratio of the area of ∆PQR to the area of ∆PST is
Two circles intersect at A and B. From a point, P on one of the circles lines PAC and PBD are drawn intersecting the second circle at C and D. Prove that CD is parallel to the tangent at P.
