Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Construct a ∆PQR in which the base PQ = 4.5 cm, ∠R = 35° and the median from R to RG is 6 cm.
Solution
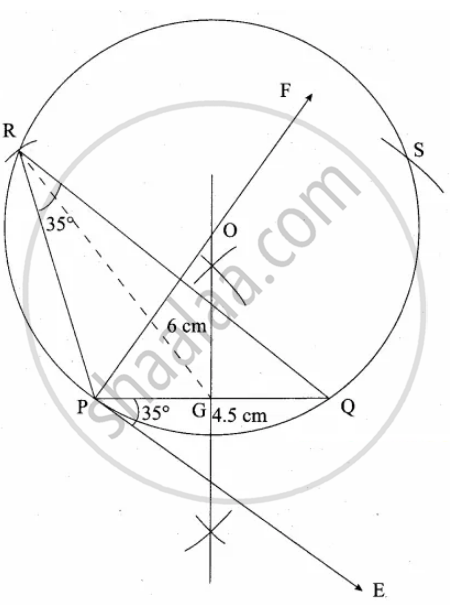
Steps of construction:
1. Draw a line segment PQ = 4.5 cm
2. At P, draw PE such that ∠QPE = 60°
3. At P, draw PF such that ∠EPF = 90°
4. Draw the perpendicular bisect to PQ, which intersects PF at O and PQ at G.
5. With O as centre and OP as radius draw a circle.
6. From G mark arcs of radius 5.8 cm on the circle. Mark them at R and S
7. Join PR and RQ.
8. PQR is the required triangle.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
In ∆ABC, D and E are points on the sides AB and AC respectively such that DE || BC
If AD = 8x – 7, DB = 5x – 3, AE = 4x – 3 and EC = 3x – 1, find the value of x
In ΔABC, D and E are points on the sides AB and AC respectively. For the following case show that DE || BC
AB = 12 cm, AD = 8 cm, AE = 12 cm and AC = 18 cm
If PQ || BC and PR || CD prove that `"AR"/"AD" = "AQ"/"AB"`
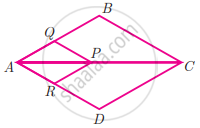
Rhombus PQRB is inscribed in ΔABC such that ∠B is one of its angle. P, Q and R lie on AB, AC and BC respectively. If AB = 12 cm and BC = 6 cm, find the sides PQ, RB of the rhombus.
∠QPR = 90°, PS is its bisector. If ST ⊥ PR, prove that ST × (PQ + PR) = PQ × PR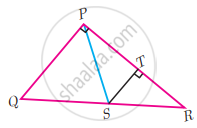
ABCD is a quadrilateral in which AB = AD, the bisector of ∠BAC and ∠CAD intersect the sides BC and CD at the points E and F respectively. Prove that EF || BD.
Construct a ∆ABC such that AB = 5.5 cm, ∠C = 25° and the altitude from C to AB is 4 cm
Draw ∆PQR such that PQ = 6.8 cm, vertical angle is 50° and the bisector of the vertical angle meets the base at D where PD = 5.2 cm
ST || QR, PS = 2 cm and SQ = 3 cm. Then the ratio of the area of ∆PQR to the area of ∆PST is
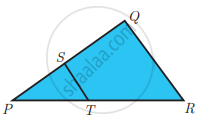
ABC is a triangle in which AB = AC. Points D and E are points on the side AB and AC respectively such that AD = AE. Show that the points B, C, E and D lie on a same circle