Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Ethylbenzene is generally prepared by acetylation of benzene followed by reduction and not by direct alkylation. Think of a possible reason.
Solution
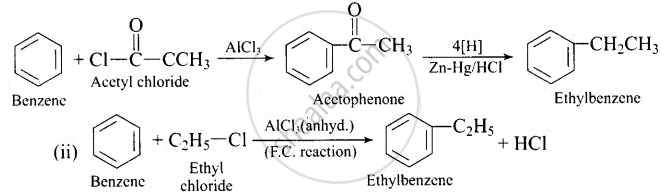
In (ii) reaction, it readily undergoes further alkylation to produce polysubs- tituted derivative.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Write the reaction involved in the Stephen reduction
When 0.4g of oxalic acid is dissolved in 40g of benzene, the freezing point of the solution is lowered by 0.45 K. Calculate the degree of association of acetic acid. Acetic acid forms dimer when dissolved in benzene.
(Kf for benzene = 5.12 K kg mol-1, at. wt. C = 12, H = 1, O = 16)
Match the common names given in Column I with the IUPAC names given in Column II.
| Column I (Common names) |
Column II (IUPAC names) |
||
| (i) | Cinnamaldehyde | (a) | Pentanal |
| (ii) | Acetophenone | (b) | Prop-2-enal |
| (iii) | Valeraldehyde | (c) | 4-Methylpent-3-en-2-one |
| (iv) | Acrolein | (d) | 3-Phenylprop-2-enal |
| (v) | Mesityl oxide | (e) | 1-Phenylethanone |
The strongest base among the following
The reagent in friedel - craft reaction is:
The oxidation of toluene to benzaldehyde by chromyl chloride is called ______.
Predict the reagent for carrying out the following transformations:
Benzoyl chloride to Benzaldehyde
The reaction of benzene with CO and HCl in the presence of anhydrous AlCl3 gives ______.
Assertion (A): Strong oxidising agents oxidise toluene and its derivatives to benzoic acids.
Reason (R): It is possible to stop the oxidation of toluene at the aldehyde stage with suitable reagents.
Select the most appropriate answer from the options given below:
Write the name of the reaction, structure and IUPAC name of the product formed when:
CH3CH2CN reacts with stannous chloride in the presence of hydrochloric acid, followed by hydrolysis.
