Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Evaluate the following limits:
`lim_(x -> pi) (sin3x)/(sin2x)`
Solution
`lim_(x -> pi) (sin3x)/(sin2x) = lim_(x -> pi) (3sin x - 4 sin^3 x)/(2sinx cos x)`
= `lim_(x -> pi) [(3sinx)/(2sinx cosx) - (4sin^3x)/(sinx cosx)]`
= `lim_(x -> pi) [3/(2cosx) - (2sin^2x)/cosx]`
= `lim_(x -> pi) 3/(2cosx) - lim_(x -> pi) (2sin^2x)/cosx`
= `3/(2cospi) - (2sin^2pi)/cospi`
=`3/(2 xx -1) - (2 xx 0)/(-1)`
`lim_(x -> pi) (sin3x)/(sin2x) = - 3/2`
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Evaluate the following limit :
`lim_(x -> 7) [(x^3 - 343)/(sqrt(x) - sqrt(7))]`
In the following example, given ∈ > 0, find a δ > 0 such that whenever, |x – a| < δ, we must have |f(x) – l| < ∈.
`lim_(x -> 2)(2x + 3)` = 7
In problems 1 – 6, using the table estimate the value of the limit.
`lim_(x -> 2) (x - 2)/(x^2 - x - 2)`
| x | 1.9 | 1.99 | 1.999 | 2.001 | 2.01 | 2.1 |
| f(x) | 0.344820 | 0.33444 | 0.33344 | 0.333222 | 0.33222 | 0.332258 |
In exercise problems 7 – 15, use the graph to find the limits (if it exists). If the limit does not exist, explain why?
`lim_(x -> 1) f(x)` where `f(x) = {{:(x^2 + 2",", x ≠ 1),(1",", x = 1):}`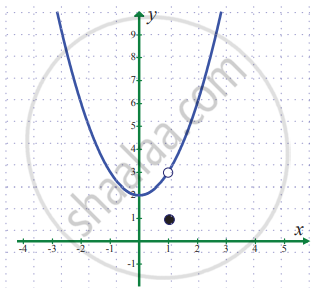
In exercise problems 7 – 15, use the graph to find the limits (if it exists). If the limit does not exist, explain why?
`lim_(x -> 0) sec x`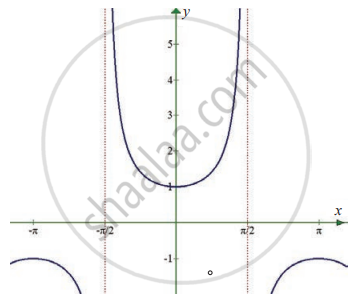
In exercise problems 7 – 15, use the graph to find the limits (if it exists). If the limit does not exist, explain why?
`lim_(x -> x/2) tan x`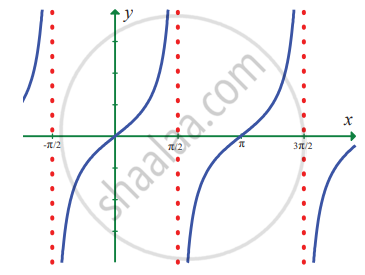
If the limit of f(x) as x approaches 2 is 4, can you conclude anything about f(2)? Explain reasoning
Evaluate the following limits:
`lim_(x ->) (x^"m" - 1)/(x^"n" - 1)`, m and n are integers
Evaluate the following limits:
`lim_(x -> 5) (sqrt(x + 4) - 3)/(x - 5)`
Find the left and right limits of f(x) = `(x^2 - 4)/((x^2 + 4x+ 4)(x + 3))` at x = – 2
Evaluate the following limits:
`lim_(x -> oo) (1 + x - 3x^3)/(1 + x^2 +3x^3)`
An important problem in fishery science is to estimate the number of fish presently spawning in streams and use this information to predict the number of mature fish or “recruits” that will return to the rivers during the reproductive period. If S is the number of spawners and R the number of recruits, “Beverton-Holt spawner recruit function” is R(S) = `"S"/((alpha"S" + beta)` where `alpha` and `beta` are positive constants. Show that this function predicts approximately constant recruitment when the number of spawners is sufficiently large
Evaluate the following limits:
`lim_(x -> 0) (tan 2x)/x`
Evaluate the following limits:
`lim_(x -> oo) x [3^(1/x) + 1 - cos(1/x) - "e"^(1/x)]`
Evaluate the following limits:
`lim_(x -> pi) (1 + sinx)^(2"cosec"x)`
Evaluate the following limits:
`lim_(x -> 0) (sqrt(2) - sqrt(1 + cosx))/(sin^2x)`
Evaluate the following limits:
`lim_(x -> 0) ("e"^x - "e"^(-x))/sinx`
Choose the correct alternative:
`lim_(x -> oo) sinx/x`
Choose the correct alternative:
`lim_(x -> 0) sqrt(1 - cos 2x)/x`
Choose the correct alternative:
The value of `lim_(x -> 0) sinx/sqrt(x^2)` is
