Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Figure shown a two slit arrangement with a source which emits unpolarised light. P is a polariser with axis whose direction is not given. If I0 is the intensity of the principal maxima when no polariser is present, calculate in the present case, the intensity of the principal maxima as well as of the first minima.
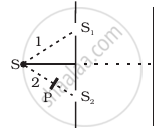
Solution
The resultant amplitude of wave reaching the screen will be the sum of amplitude of either wave in perpendicular and parallel polarisation.
Amplitude of the wave in perpendicular polarisation
`A_⊥ = A_⊥^1 + A_⊥^2 = A_⊥^0 sin (kx - ωt) + A_⊥^0 sin (kx - ωt + phi)`
⇒ `A_⊥ = A_⊥^0 (sin (kx - ωt) + sin (kx - ωt + phi)`
Amplitude of the wave in parallel polarisation
`A_(||) = A_(||)^((1)) + A_(||)^((2))`
⇒ `A_(||) = A_(||)^0 [sin (kx - ωt) + sin (kx - ωt + phi)]`
∴ Average Intensity on the screen
`I = {|A_⊥^0|^2 + |A_(||)^0|^2} [sin^2 (kx - ωt)(1 + cos^2 phi + 2 sin phi) + sin^2 (kx - ωt) sin^2 phi]_("average")`
= `{|A_⊥^0|^2 + |A_(||)^0|^2}(1/2)*2(1 + cos phi)`
⇒ `I = 2|A_⊥^0|^2 (1 + cos phi)` since, `|A_⊥^0|_("av") = |A_(||)^0|_("av")`
With polariser P,
Assume `A_⊥^2` is blocked
Intensity = `(A_(||)^1 + A_(||)^2)^2 + (A_⊥^1)^2`
= `|A_⊥^2|^2 (1 + cos phi) + |A_⊥^0|^2 * 1/2`
Given, `I_0 4|A_⊥^0|^2` = Intensity without polariser at principal maxima.
Intensity at first minima with polariser = `|A_⊥^0|^2 (1 - 1) + (|A_⊥^0|^2)/2 = I_0/8`.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Two polaroids P1 and P2 are placed with their pass axes perpendicular to each other. An unpolarised light of intensity I0 is incident on P1. A third polaroid P3 is kept in between P1 and P2 such that its pass axis makes an angle of 30° with that of P1. Determine the intensity of light transmitted through P1, P2 and P3
What is the Brewster angle for air to glass transition? (Refractive index of glass = 1.5)
Unpolarised light is passed through a polaroid P1. When this polarised beam passes through another polaroid P2 and if the pass axis of P2 makes angle θ with the pass axis of P1, then write the expression for the polarised beam passing through P2. Draw a plot showing the variation of intensity when θ varies from 0 to 2π.
A ray of light is incident on a transparent medium at a polarizing angle. What is the angle between the reflected ray and the refracted ray?
Light transmitted by Nicol prism is ______.
What is partially polarised light?
How is polarisation of light obtained by scattering of light?
The reflected light is found to be plane polarised when an unpolarized light falls on a denser medium at 60° with the normal. Find the angle of refraction and critical angle of incidence for total internal reflection in the denser to rarer medium reflection.
Can reflection result in plane polarised light if the light is incident on the interface from the side with higher refractive index?
To ensure almost 100 per cent transmissivity, photographic lenses are often coated with a thin layer of dielectric material. The refractive index of this material is intermediated between that of air and glass (which makes the optical element of the lens). A typically used dielectric film is MgF2 (n = 1.38). What should the thickness of the film be so that at the center of the visible spectrum (5500 Å) there is maximum transmission.
