Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Given the standard electrode potentials,
\[\ce{K+/K}\] = −2.93 V, \[\ce{Ag+/Ag}\] = 0.80 V,
\[\ce{Hg^{2+}/Hg}\] = 0.79 V
\[\ce{Mg^{2+}/Mg}\] = −2.37 V, \[\ce{Cr^{3+}/Cr}\] = −0.74 V
Arrange these metals in their increasing order of reducing power.
Solution
The reducing power of a metal depends on its oxidation potential. The higher the oxidation potential, the greater its tendency to be oxidized and, hence, the greater its reducing power. Hence the order of increasing of reducing the power of the given metals will be as follows:
\[\ce{Ag < Hg < Cr < Mg < K}\]
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Arrange the following reducing agents in the order of increasing strength under standard state conditions. Justify the answer
|
Element |
Al(s) |
Cu(s) |
Cl(aq) |
Ni(s) |
|
Eo |
-1.66V |
0.34V |
1.36V |
-0.26V |
Calculate Ecell and ΔG for the following at 28°C :
Mg(s) + Sn2+( 0.04M ) → Mg2+( 0.06M ) + Sn(s)
E°cell = 2.23V. Is the reaction spontaneous ?
Can copper sulphate solution be stored in an iron vessel? Explain.
The standard e.m.f of the following cell is 0.463 V
`Cu|Cu_(1m)^(++)`
What is the standard potential of Cu electrode?
(A) 1.137 V
(B) 0.337 V
(C) 0.463 V
(D) - 0.463 V
Calculate E°cell for the following reaction at 298 K:
2Al(s) + 3Cu+2(0.01M) → 2Al+3(0.01M) + 3Cu(s)
Given: Ecell = 1.98V
Calculate e.m.f of the following cell at 298 K:
2Cr(s) + 3Fe2+ (0.1M) → 2Cr3+ (0.01M) + 3 Fe(s)
Given: E°(Cr3+ | Cr) = – 0.74 VE° (Fe2+ | Fe) = – 0.44 V
Draw a neat and labelled diagram of the lead storage battery.
Calculate the emf of the following cell at 25°C :
Galvanic or a voltaic cell converts the chemical energy liberated during a redox reaction to ____________.
Standard hydrogen electrode operated under standard conditions of 1 atm H2 pressure, 298 K, and pH = 0 has a cell potential of ____________.
Which cell will measure standard electrode potential of copper electrode?
Using the data given below find out the strongest reducing agent.
`"E"_("Cr"_2"O"_7^(2-)//"Cr"^(3+))^⊖` = 1.33 V `"E"_("Cl"_2//"Cl"^-) = 1.36` V
`"E"_("MnO"_4^-//"Mn"^(2+))` = 1.51 V `"E"_("Cr"^(3+)//"Cr")` = - 0.74 V
Assertion: Cu is less reactive than hydrogen.
Reason: `E_((Cu^(2+))/(Cu))^Θ` is negative.
Consider the figure and answer the following question.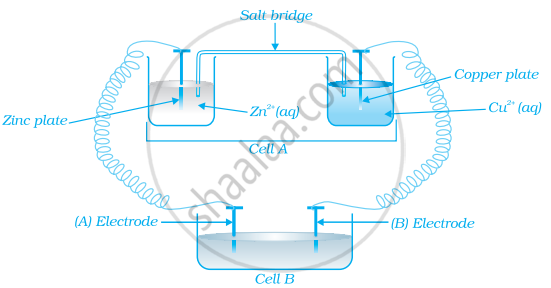
If cell ‘A’ has ECell = 0.5V and cell ‘B’ has ECell = 1.1V then what will be the reactions at anode and cathode?
Represent the cell in which the following reaction takes place.The value of E˚ for the cell is 1.260 V. What is the value of Ecell?
\[\ce{2Al (s) + 3Cd^{2+} (0.1M) -> 3Cd (s) + 2Al^{3+} (0.01M)}\]
Standard electrode potential of three metals X, Y and Z are – 1.2 V, + 0.5 V and – 3.0 V, respectively. The reducing power of these metals will be:
The potential of a hydrogen electrode at PH = 10 is
A voltaic cell is made by connecting two half cells represented by half equations below:
\[\ce{Sn^{2+}_{ (aq)} + 2e^- -> Sn_{(s)}}\], E0 = − 0.14 V
\[\ce{Fe^{3+}_{ (aq)} + e^- -> Fe^{2+}_{ (aq)}}\], E0 = + 0.77 V
Which statement is correct about this voltaic cell?
