Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
If the external force acting on a system have zero resultant, the centre of mass
(a) must not move
(b) must not accelerate
(c) may move
(d) may accelerate.
Solution
(b) must not accelerate
(c) may move
If the external force acting on a system has zero resultant,
then, acceleration of centre of mass \[= \frac{\vec{F}_{net}}{M} = 0\]
However, it may move uniformly with constant velocity.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Give the location of the centre of mass of a
- sphere,
- cylinder,
- ring, and
- cube,
each of uniform mass density. Does the centre of mass of a body necessarily lie inside the body?
If all the particles of a system lie in X-Y plane, is it necessary that the centre of mass be in X-Y plane?
If all the particle of a system lie in a cube, is it necessary that the centre of mass be in the cube?
In a head-on collision between two particles, is it necessary that the particles will acquire a common velocity at least for one instant?
A high-jumper successfully clears the bar. Is it possible that his centre of mass crossed the bar from below it? Try it with appropriate figures.
A ball kept in a closed box moves in the box making collisions with the walls. The box is kept on a smooth surface. The velocity of the centre of mass
In an elastic collision
A nonzero external force acts on a system of particles. The velocity and the acceleration of the centre of mass are found to be v0 and a0 at instant t. It is possible that
(a) v0 = 0, a0 = 0
(b) v0 = 0, a0 ≠ 0
(c) v0 ≠ 0, a0 = 0
(d) v0 ≠ 0, a0 ≠ 0
Two balls are thrown simultaneously in air. The acceleration of the centre of mass of the two balls while in air
A square plate of edge d and a circular disc of diameter d are placed touching each other at the midpoint of an edge of the plate as shown in figure. Locate the centre of mass of the combination, assuming same mass per unit area for the two plates.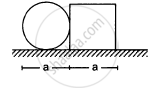
Calculate the velocity of the centre of mass of the system of particles shown in figure.

Two blocks of masses 10 kg and 30 kg are placed along a vertical line. The first block is raised through a height of 7 cm. By what distance should the second mass be moved to raise the centre of mass by 1 cm?
Mr. Verma (50 kg) and Mr. Mathur (60 kg) are sitting at the two extremes of a 4 m long boat (40 kg) standing still in water. To discuss a mechanics problem, they come to the middle of the boat. Neglecting friction with water, how far does the boat move on the water during the process?
A railroad car of mass M is at rest on frictionless rails when a man of mass m starts moving on the car towards the engine. If the car recoils with a speed v backward on the rails, with what velocity is the man approaching the engine?
Consider the situation of the previous problem. Suppose the block of mass m1 is pulled by a constant force F1 and the other block is pulled by a constant force F2. Find the maximum elongation that the spring will suffer.
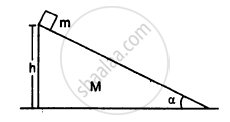
A block of mass m is placed on a triangular block of mass M which in turn is placed on a horizontal surface as shown in figure. Assuming frictionless surfaces find the velocity of the triangular block when the smaller block reaches the bottom end.
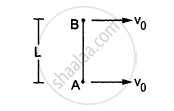
Two small balls A and B, each of mass m, are joined rigidly to the ends of a light rod of length L (see the following figure). The system translates on a frictionless horizontal surface with a velocity \[\nu_0\] in a direction perpendicular to the rod. A particle P of mass m kept at rest on the surface sticks to the ball A as the ball collides with it. Find
(a) the linear speeds of the balls A and B after the collision, (b) the velocity of the centre of mass C of the system A + B + P and (c) the angular speed of the system about C after the collision.
[Hint : The light rod will exert a force on the ball B
only along its length.]
In system of two particles of masses 'm1' and 'm2', the first particle is moved by a distance 'd' towards the centre of mass. To keep the centre of mass unchanged, the second particle will have to be moved by a distance ______.
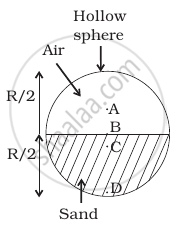
Which of the following points is the likely position of the centre of mass of the system shown in figure?