Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
If X is a random-variable with probability distribution as given below:
| X = xi : | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| P (X = xi) : | k | 3 k | 3 k | k |
The value of k and its variance are
Options
1/8, 22/27
1/8, 23/27
1/8, 24/27
1/8, 3/4
Solution
1/8, 3/4
We know that the sum of probabilities in a probability distribution is always 1.
∴ P (X = 0) + P (X = 1) + P (X = 2) + P (X = 3) = 1
\[\Rightarrow k + 3k + 3k + k = 1\]
\[ \Rightarrow 8k = 1\]
\[ \Rightarrow k = \frac{1}{8}\]
Now,
| xi | pi | pixi | pixi2 |
| 0 | k = \[\frac{1}{8}\] |
0 | 0 |
| 1 | 3k =\[\frac{3}{8}\] |
\[\frac{3}{8}\]
|
\[\frac{3}{8}\]
|
| 2 | 3k = \[\frac{3}{8}\] |
\[\frac{6}{8}\]
|
\[\frac{12}{8}\]
|
| 3 | k = \[\frac{1}{8}\] |
\[\frac{3}{8}\]
|
\[\frac{9}{8}\]
|
|
\[\sum\nolimits_{}^{}\]pixi = \[\frac{12}{8} =\frac{3}{2}\]
|
\[\sum\nolimits_{}^{}\] pixi2 = \[\frac{24}{8}\]
|
\[\text{ Mean } = \sum p_i x_i = \frac{3}{2}\]
\[\text{ Variance } = \sum p_i {x_i}2^{}_{} - \left( \text{ Mean } \right)^2 = \frac{24}{8} - \left( \frac{3}{2} \right)^2 = \frac{24}{8} - \frac{9}{4} = \frac{24 - 18}{8} = \frac{6}{8} = \frac{3}{4}\]
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
State the following are not the probability distributions of a random variable. Give reasons for your answer.
| Y | -1 | 0 | 1 |
| P(Y) | 0.6 | 0.1 | 0.2 |
An urn contains 5 red and 2 black balls. Two balls are randomly drawn. Let X represents the number of black balls. What are the possible values of X? Is X a random variable?
Find the probability distribution of number of tails in the simultaneous tosses of three coins.
An urn contains 25 balls of which 10 balls bear a mark ‘X’ and the remaining 15 bear a mark ‘Y’. A ball is drawn at random from the urn, its mark is noted down and it is replaced. If 6 balls are drawn in this way, find the probability that
(i) all will bear ‘X’ mark.
(ii) not more than 2 will bear ‘Y’ mark.
(iii) at least one ball will bear ‘Y’ mark
(iv) the number of balls with ‘X’ mark and ‘Y’ mark will be equal.
Assume that the chances of the patient having a heart attack are 40%. It is also assumed that a meditation and yoga course reduce the risk of heart attack by 30% and prescription of certain drug reduces its chances by 25%. At a time a patient can choose any one of the two options with equal probabilities. It is given that after going through one of the two options the patient selected at random suffers a heart attack. Find the probability that the patient followed a course of meditation and yoga?
A random variable X has the following probability distribution:
| Values of X : | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
| P (X) : | a | 3a | 5a | 7a | 9a | 11a | 13a | 15a | 17a |
Determine:
(i) The value of a
(ii) P (X < 3), P (X ≥ 3), P (0 < X < 5).
Find the probability distribution of the number of heads, when three coins are tossed.
Two cards are drawn successively with replacement from well shuffled pack of 52 cards. Find the probability distribution of the number of aces.
From a lot containing 25 items, 5 of which are defective, 4 are chosen at random. Let X be the number of defectives found. Obtain the probability distribution of X if the items are chosen without replacement .
Four balls are to be drawn without replacement from a box containing 8 red and 4 white balls. If X denotes the number of red balls drawn, then find the probability distribution of X.
Find the mean and standard deviation of each of the following probability distribution:
| xi : | −1 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| pi : | 0.3 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.3 | 0.2 |
Find the mean and standard deviation of each of the following probability distribution :
| xi : | -2 | -1 | 0 | 1 | 2 |
| pi : | 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.4 | 0.2 | 0.1 |
A discrete random variable X has the probability distribution given below:
| X: | 0.5 | 1 | 1.5 | 2 |
| P(X): | k | k2 | 2k2 | k |
Find the value of k.
Two cards are drawn simultaneously from a pack of 52 cards. Compute the mean and standard deviation of the number of kings.
A fair coin is tossed four times. Let X denote the longest string of heads occurring. Find the probability distribution, mean and variance of X.
Two numbers are selected at random (without replacement) from positive integers 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 and 7. Let X denote the larger of the two numbers obtained. Find the mean and variance of the probability distribution of X.
If the probability distribution of a random variable X is given by Write the value of k.
| X = xi : | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
| P (X = xi) : | 2k | 4k | 3k | k |
Find the mean of the following probability distribution:
| X= xi: | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| P(X= xi) : |
\[\frac{1}{4}\]
|
\[\frac{1}{8}\]
|
\[\frac{5}{8}\]
|
A pair of dice is thrown 4 times. If getting a doublet is considered a success, find the probability distribution of the number of successes and, hence, find its mean.
A departmental store gives trafnfng to the salesmen in service followed by a test. It is experienced that the performance regarding sales of any salesman is linearly related to the scores secured by him. The following data gives the test scores and sales made by nine (9) salesmen during a fixed period.
| Test scores (X) | 16 | 22 | 28 | 24 | 29 | 25 | 16 | 23 | 24 |
| Sales (Y) (₹ in hundreds) | 35 | 42 | 57 | 40 | 54 | 51 | 34 | 47 | 45 |
(a) Obtain the line of regression of Y on X.
(b) Estimate Y when X = 17.
Alex spends 20% of his income on food items and 12% on conveyance. If for the month of June 2010, he spent ₹900 on conveyance, find his expenditure on food items during the same month.
A card is drawn at random and replaced four times from a well shuftled pack of 52 cards. Find the probability that -
(a) Two diamond cards are drawn.
(b) At least one diamond card is drawn.
An urn contains 5 red and 2 black balls. Two balls are drawn at random. X denotes number of black balls drawn. What are possible values of X?
The probability that a bulb produced by a factory will fuse after 200 days of use is 0.2. Let X denote the number of bulbs (out of 5) that fuse after 200 days of use. Find the probability of X > 1
Find the probability of throwing at most 2 sixes in 6 throws of a single die.
Solve the following problem :
Following is the probability distribution of a r.v.X.
| x | – 3 | – 2 | –1 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| P(X = x) | 0.05 | 0.1 | 0.15 | 0.20 | 0.25 | 0.15 | 0.1 |
Find the probability that X is non-negative
Solve the following problem :
A computer installation has 3 terminals. The probability that any one terminal requires attention during a week is 0.1, independent of other terminals. Find the probabilities that 0
Solve the following problem :
It is observed that it rains on 10 days out of 30 days. Find the probability that it rains on at most 2 days of a week.
A discrete random variable X has the probability distribution given as below:
| X | 0.5 | 1 | 1.5 | 2 |
| P(X) | k | k2 | 2k2 | k |
Find the value of k
Consider the probability distribution of a random variable X:
| X | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
| P(X) | 0.1 | 0.25 | 0.3 | 0.2 | 0.15 |
Calculate `"V"("X"/2)`
The probability distribution of a random variable X is given below:
| X | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| P(X) | k | `"k"/2` | `"k"/4` | `"k"/8` |
Determine the value of k.
Let X be a discrete random variable whose probability distribution is defined as follows:
P(X = x) = `{{:("k"(x + 1), "for" x = 1"," 2"," 3"," 4),(2"k"x, "for" x = 5"," 6"," 7),(0, "Otherwise"):}`
where k is a constant. Calculate the value of k
Let X be a discrete random variable whose probability distribution is defined as follows:
P(X = x) = `{{:("k"(x + 1), "for" x = 1"," 2"," 3"," 4),(2"k"x, "for" x = 5"," 6"," 7),(0, "Otherwise"):}`
where k is a constant. Calculate Standard deviation of X.
The probability distribution of a discrete random variable X is given as under:
| X | 1 | 2 | 4 | 2A | 3A | 5A |
| P(X) | `1/2` | `1/5` | `3/25` | `1/10` | `1/25` | `1/25` |
Calculate: Variance of X
Kiran plays a game of throwing a fair die 3 times but to quit as and when she gets a six. Kiran gets +1 point for a six and –1 for any other number.
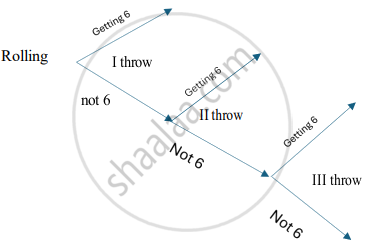
- If X denotes the random variable “points earned” then what are the possible values X can take?
- Find the probability distribution of this random variable X.
- Find the expected value of the points she gets.
