Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Two cards are drawn successively with replacement from well shuffled pack of 52 cards. Find the probability distribution of the number of aces.
Solution
Let X denote the number of aces in a sample of 2 cards drawn from a well-shuffled pack of 52 playing cards. Then, X can take the values 0, 1 and 2.
Now,
\[P\left( X = 0 \right)\]
\[ = P\left( \text{ no ace } \right)\]
\[ = \frac{48}{52} \times \frac{48}{52}\]
\[ = \frac{12 \times 12}{13 \times 13}\]
\[ = \frac{144}{169}\]
\[P\left( X = 1 \right)\]
\[ = P\left( 1 \text{ ace } \right)\]
\[ = \frac{4}{52} \times \frac{48}{52}\]
\[ = \frac{2 \times 12}{13 \times 13}\]
\[ = \frac{24}{169}\]
\[P\left( X = 2 \right)\]
\[ = P\left( 2 \text{ aces } \right)\]
\[ = \frac{4}{52} \times \frac{4}{52}\]
\[ = \frac{1 \times 1}{13 \times 13}\]
\[ = \frac{1}{169}\]
Thus, the probability distribution of X is given by
| X | P(X) |
| 0 |
\[\frac{144}{169}\]
|
| 1 |
\[\frac{24}{169}\]
|
| 2 |
\[\frac{1}{169}\]
|
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
A random variable X has the following probability distribution:
then E(X)=....................
State the following are not the probability distributions of a random variable. Give reasons for your answer.
| X | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
| P(X) | 0.1 | 0.5 | 0.2 | -0.1 | 0.3 |
Suppose that two cards are drawn at random from a deck of cards. Let X be the number of aces obtained. Then the value of E(X) is
(A) `37/221`
(B) 5/13
(C) 1/13
(D) 2/13
A random variable X has the following probability distribution:
| Values of X : | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
| P (X) : | a | 3a | 5a | 7a | 9a | 11a | 13a | 15a | 17a |
Determine:
(i) The value of a
(ii) P (X < 3), P (X ≥ 3), P (0 < X < 5).
Find the probability distribution of Y in two throws of two dice, where Y represents the number of times a total of 9 appears.
Find the mean and standard deviation of each of the following probability distribution:
| xi : | 1 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| pi: | 0.4 | 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.3 |
A discrete random variable X has the probability distribution given below:
| X: | 0.5 | 1 | 1.5 | 2 |
| P(X): | k | k2 | 2k2 | k |
Determine the mean of the distribution.
A fair coin is tossed four times. Let X denote the number of heads occurring. Find the probability distribution, mean and variance of X.
Three cards are drawn at random (without replacement) from a well shuffled pack of 52 cards. Find the probability distribution of number of red cards. Hence, find the mean of the distribution .
An urn contains 5 red and 2 black balls. Two balls are randomly drawn, without replacement. Let X represent the number of black balls drawn. What are the possible values of X ? Is X a random variable ? If yes, then find the mean and variance of X.
Two numbers are selected at random (without replacement) from positive integers 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 and 7. Let X denote the larger of the two numbers obtained. Find the mean and variance of the probability distribution of X.
If X denotes the number on the upper face of a cubical die when it is thrown, find the mean of X.
If the probability distribution of a random variable X is given by Write the value of k.
| X = xi : | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
| P (X = xi) : | 2k | 4k | 3k | k |
Mark the correct alternative in the following question:
Let X be a discrete random variable. Then the variance of X is
An urn contains 3 white and 6 red balls. Four balls are drawn one by one with replacement from the urn. Find the probability distribution of the number of red balls drawn. Also find mean and variance of the distribution.
Three fair coins are tossed simultaneously. If X denotes the number of heads, find the probability distribution of X.
If the demand function is D = 150 - p2 - 3p, find marginal revenue, average revenue and elasticity of demand for price p = 3.
The expenditure Ec of a person with income I is given by Ec = (0.000035) I2 + (0. 045) I. Find marginal propensity to consume (MPC) and average propensity to consume (APC) when I = 5000.
If p : It is a day time , q : It is warm
Give the verbal statements for the following symbolic statements :
(a) p ∧ ∼ q (b) p v q (c) p ↔ q
Alex spends 20% of his income on food items and 12% on conveyance. If for the month of June 2010, he spent ₹900 on conveyance, find his expenditure on food items during the same month.
The probability that a bomb dropped from an aeroplane will strike a target is `1/5`, If four bombs are dropped, find the probability that :
(a) exactly two will strike the target,
(b) at least one will strike the target.
Amit and Rohit started a business by investing ₹20,000 each. After 3 months Amit withdrew ₹5,000 and Rohit put in ₹5,000 additionally. How should a profit of ₹12,800 be divided between them at the end of the year?
The p.d.f. of r.v. of X is given by
f (x) = `k /sqrtx` , for 0 < x < 4 and = 0, otherwise. Determine k .
Determine c.d.f. of X and hence P (X ≤ 2) and P(X ≤ 1).
A sample of 4 bulbs is drawn at random with replacement from a lot of 30 bulbs which includes 6 defective bulbs. Find the probability distribution of the number of defective bulbs.
A die is thrown 4 times. If ‘getting an odd number’ is a success, find the probability of 2 successes
Defects on plywood sheet occur at random with the average of one defect per 50 Sq.ft. Find the probability that such a sheet has no defect
Solve the following problem :
A computer installation has 3 terminals. The probability that any one terminal requires attention during a week is 0.1, independent of other terminals. Find the probabilities that 0
Solve the following problem :
It is observed that it rains on 10 days out of 30 days. Find the probability that it rains on at most 2 days of a week.
Find the probability distribution of the number of doublets in three throws of a pair of dice
A discrete random variable X has the probability distribution given as below:
| X | 0.5 | 1 | 1.5 | 2 |
| P(X) | k | k2 | 2k2 | k |
Determine the mean of the distribution.
Let X be a discrete random variable whose probability distribution is defined as follows:
P(X = x) = `{{:("k"(x + 1), "for" x = 1"," 2"," 3"," 4),(2"k"x, "for" x = 5"," 6"," 7),(0, "Otherwise"):}`
where k is a constant. Calculate E(X)
The probability distribution of a discrete random variable X is given as under:
| X | 1 | 2 | 4 | 2A | 3A | 5A |
| P(X) | `1/2` | `1/5` | `3/25` | `1/10` | `1/25` | `1/25` |
Calculate: Variance of X
A random variable x has to following probability distribution.
| X | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
| P(x) | 0 | k | 2k | 2k | 3k | k2 | 2k2 | 7k2 + k |
Determine
Box I contains 30 cards numbered 1 to 30 and Box II contains 20 cards numbered 31 to 50. A box is selected at random and a card is drawn from it. The number on the card is found to be a nonprime number. The probability that the card was drawn from Box I is ______.
A random variable X has the following probability distribution:
| x | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
| P(x) | k | 2k | 2k | 3k | k2 | 2k2 | 7k2 + k |
Find:
- k
- P(X < 3)
- P(X > 4)
A large chain retailer purchases an electric device from the manufacturer. The manufacturer indicates that the defective rate of the device is 10%. The inspector of the retailer randomly selects 4 items from a shipment. Complete the following activity to find the probability that the inspector finds at most one defective item in the 4 selected items.
Solution:
Here, n = 4
p = probability of defective device = 10% = `10/100 = square`
∴ q = 1 - p = 1 - 0.1 = `square`
X ∼ B(4, 0.1)
`P(X=x)=""^n"C"_x p^x q^(n-x)= ""^4"C"_x (0.1)^x (0.9)^(4 - x)`
P[At most one defective device] = P[X ≤ 1]
= P[X=0] + P[X=1]
= `square+square`
∴ P[X ≤ 1] = `square`
A primary school teacher wants to teach the concept of 'larger number' to the students of Class II.
To teach this concept, he conducts an activity in his class. He asks the children to select two numbers from a set of numbers given as 2, 3, 4, 5 one after the other without replacement.
All the outcomes of this activity are tabulated in the form of ordered pairs given below:
| 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | |
| 2 | (2, 2) | (2, 3) | (2, 4) | |
| 3 | (3, 2) | (3, 3) | (3, 5) | |
| 4 | (4, 2) | (4, 4) | (4, 5) | |
| 5 | (5, 3) | (5, 4) | (5, 5) |
- Complete the table given above.
- Find the total number of ordered pairs having one larger number.
- Let the random variable X denote the larger of two numbers in the ordered pair.
Now, complete the probability distribution table for X given below.
X 3 4 5 P(X = x) - Find the value of P(X < 5)
- Calculate the expected value of the probability distribution.
Kiran plays a game of throwing a fair die 3 times but to quit as and when she gets a six. Kiran gets +1 point for a six and –1 for any other number.
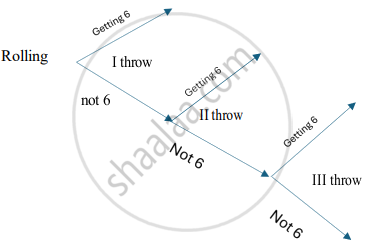
- If X denotes the random variable “points earned” then what are the possible values X can take?
- Find the probability distribution of this random variable X.
- Find the expected value of the points she gets.
