Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
If the demand function is D = 150 - p2 - 3p, find marginal revenue, average revenue and elasticity of demand for price p = 3.
Solution
Demand function D = 150 -p2 - 3p
∴ Revenue = D × P
R = 150p - p3 - 3p2
∴ Marginal revenue Rm = `(dR)/(dP)`
Rm = 150 - 3p2- 6p
where p = 3
Rm = 150 - 3(32) - 6(3)
Rm = 105
Average revenue RA = `R/P`
RA = 150 - p2 - 3p
When p = 3
RA = 150-32 -3(3)
∴ RA = 132
Elasticity of demand
η = `(-p)/D xx (dD)/(dp)`
= `(-p)/(150 - p^2 - 3p) xx (-2p - 3)`
= `(-3)/(150 - 3^2 - 3(3)) xx (-2(3) - 3)`
= `27/132`
= `9/44`
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
From a lot of 30 bulbs which include 6 defectives, a sample of 4 bulbs is drawn at random with replacement. Find the probability distribution of the number of defective bulbs.
The random variable X has probability distribution P(X) of the following form, where k is some number:
`P(X = x) {(k, if x = 0),(2k, if x = 1),(3k, if x = 2),(0, "otherwise"):}`
- Determine the value of 'k'.
- Find P(X < 2), P(X ≥ 2), P(X ≤ 2).
Two numbers are selected at random (without replacement) from the first six positive integers. Let X denotes the larger of the two numbers obtained. Find E(X).
Three persons A, B and C shoot to hit a target. If A hits the target four times in five trials, B hits it three times in four trials and C hits it two times in three trials, find the probability that:
1) Exactly two persons hit the target.
2) At least two persons hit the target.
3) None hit the target.
Let, X denote the number of colleges where you will apply after your results and P(X = x) denotes your probability of getting admission in x number of colleges. It is given that
where k is a positive constant. Find the value of k. Also find the probability that you will get admission in (i) exactly one college (ii) at most 2 colleges (iii) at least 2 colleges.
The probability distribution function of a random variable X is given by
| xi : | 0 | 1 | 2 |
| pi : | 3c3 | 4c − 10c2 | 5c-1 |
where c > 0 Find: P (1 < X ≤ 2)
A class has 15 students whose ages are 14, 17, 15, 14, 21, 19, 20, 16, 18, 17, 20, 17, 16, 19 and 20 years respectively. One student is selected in such a manner that each has the same chance of being selected and the age X of the selected student is recorded. What is the probability distribution of the random variable X?
Five defective bolts are accidently mixed with twenty good ones. If four bolts are drawn at random from this lot, find the probability distribution of the number of defective bolts.
Find the probability distribution of Y in two throws of two dice, where Y represents the number of times a total of 9 appears.
From a lot containing 25 items, 5 of which are defective, 4 are chosen at random. Let X be the number of defectives found. Obtain the probability distribution of X if the items are chosen without replacement .
Let X represent the difference between the number of heads and the number of tails when a coin is tossed 6 times. What are the possible values of X?
Let, X denote the number of colleges where you will apply after your results and P(X = x) denotes your probability of getting admission in x number of colleges. It is given that
where k is a positive constant. Find the value of k. Also find the probability that you will get admission in (i) exactly one college (ii) at most 2 colleges (iii) at least 2 colleges.
Find the mean and standard deviation of each of the following probability distribution:
| xi : | 1 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| pi: | 0.4 | 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.3 |
Find the mean and standard deviation of each of the following probability distribution :
| xi : | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
| pi : | 0.4 | 0.3 | 0.2 | 0.1 |
Find the mean and standard deviation of each of the following probability distribution :
| xi : | -3 | -1 | 0 | 1 | 3 |
| pi : | 0.05 | 0.45 | 0.20 | 0.25 | 0.05 |
A fair die is tossed. Let X denote 1 or 3 according as an odd or an even number appears. Find the probability distribution, mean and variance of X.
Three cards are drawn at random (without replacement) from a well shuffled pack of 52 cards. Find the probability distribution of number of red cards. Hence, find the mean of the distribution .
If the probability distribution of a random variable X is as given below:
Write the value of P (X ≤ 2).
| X = xi : | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
| P (X = xi) : | c | 2c | 4c | 4c |
Three fair coins are tossed simultaneously. If X denotes the number of heads, find the probability distribution of X.
The probability that a bomb dropped from an aeroplane will strike a target is `1/5`, If four bombs are dropped, find the probability that :
(a) exactly two will strike the target,
(b) at least one will strike the target.
An urn contains 5 red and 2 black balls. Two balls are drawn at random. X denotes number of black balls drawn. What are possible values of X?
Solve the following:
Identify the random variable as either discrete or continuous in each of the following. Write down the range of it.
A highway safety group is interested in studying the speed (km/hrs) of a car at a check point.
Determine whether each of the following is a probability distribution. Give reasons for your answer.
| z | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 | -1 |
| P(z) | 0.3 | 0.2 | 0.4. | 0.05 | 0.05 |
A coin is biased so that the head is 3 times as likely to occur as tail. Find the probability distribution of number of tails in two tosses.
Solve the following problem :
Following is the probability distribution of a r.v.X.
| X | – 3 | – 2 | –1 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| P(X = x) | 0.05 | 0.1 | 0.15 | 0.20 | 0.25 | 0.15 | 0.1 |
Find the probability that X is positive.
Solve the following problem :
If a fair coin is tossed 4 times, find the probability that it shows 3 heads
Solve the following problem :
The probability that a machine will produce all bolts in a production run within the specification is 0.9. A sample of 3 machines is taken at random. Calculate the probability that all machines will produce all bolts in a production run within the specification.
Find the probability distribution of the number of successes in two tosses of a die, where a success is defined as six appears on at least one die
Let X be a discrete random variable. The probability distribution of X is given below:
| X | 30 | 10 | – 10 |
| P(X) | `1/5` | `3/10` | `1/2` |
Then E(X) is equal to ______.
The probability distribution of a random variable X is given below:
| X | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| P(X) | k | `"k"/2` | `"k"/4` | `"k"/8` |
Determine P(X ≤ 2) and P(X > 2)
Find the probability distribution of the maximum of the two scores obtained when a die is thrown twice. Determine also the mean of the distribution.
The probability distribution of a random variable x is given as under:
P(X = x) = `{{:("k"x^2, "for" x = 1"," 2"," 3),(2"k"x, "for" x = 4"," 5"," 6),(0, "otherwise"):}`
where k is a constant. Calculate E(X)
The probability distribution of a random variable x is given as under:
P(X = x) = `{{:("k"x^2, "for" x = 1"," 2"," 3),(2"k"x, "for" x = 4"," 5"," 6),(0, "otherwise"):}`
where k is a constant. Calculate P(X ≥ 4)
If the p.m.f of a r. v. X is
P(x) = `c/x^3`, for x = 1, 2, 3
= 0, otherwise
then E(X) = ______.
Find the mean number of defective items in a sample of two items drawn one-by-one without replacement from an urn containing 6 items, which include 2 defective items. Assume that the items are identical in shape and size.
Two numbers are selected from first six even natural numbers at random without replacement. If X denotes the greater of two numbers selected, find the probability distribution of X.
Five numbers x1, x2, x3, x4, x5 are randomly selected from the numbers 1, 2, 3, ......., 18 and are arranged in the increasing order such that x1 < x2 < x3 < x4 < x5. What is the probability that x2 = 7 and x4 = 11?
Kiran plays a game of throwing a fair die 3 times but to quit as and when she gets a six. Kiran gets +1 point for a six and –1 for any other number.
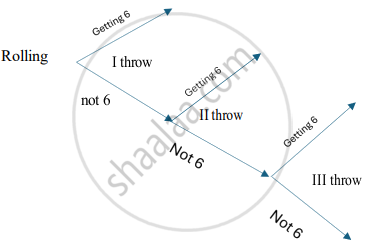
- If X denotes the random variable “points earned” then what are the possible values X can take?
- Find the probability distribution of this random variable X.
- Find the expected value of the points she gets.
