Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Let \[f : \left( - \frac{\pi}{2}, \frac{\pi}{2} \right) \to R\] be a function defined by f(x) = cos [x]. Write range (f).
Solution
\[\text{Domain} =\left( \frac{- \pi}{2}, \frac{\pi}{2} \right)=\left( - 1 . 57, 1 . 57 \right)(\text{ as } \pi=\frac{22}{7})\]
\[So, \cos \left[ x \right] = \cos \left( - 2 \right) = \cos 2 \forall x \in \left( - 1 . 57, 0 \right)\]
\[\text{Also}, \cos 0 = 1 for x = 0\]
\[\text{And }\cos \left[ x \right] = \cos 1 \forall x \in \left( 0, 1 . 57 \right)\]
\[ \therefore \text{Range}=\left\{ 1, \cos 1, \cos 2 \right\}\]
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Show that the function f in `A=R-{2/3} ` defined as `f(x)=(4x+3)/(6x-4)` is one-one and onto hence find f-1
Show that the function f: R* → R* defined by `f(x) = 1/x` is one-one and onto, where R* is the set of all non-zero real numbers. Is the result true if the domain R* is replaced by N, with co-domain being same as R?
Prove that the greatest integer function f: R → R, given by f(x) = [x], is neither one-one nor onto, where [x] denotes the greatest integer less than or equal to x.
Give examples of two functions f: N → Z and g: Z → Z such that g o f is injective but gis not injective.
(Hint: Consider f(x) = x and g(x) =|x|)
If the function `f(x) = sqrt(2x - 3)` is invertible then find its inverse. Hence prove that `(fof^(-1))(x) = x`
Which of the following functions from A to B are one-one and onto ?
f3 = {(a, x), (b, x), (c, z), (d, z)} ; A = {a, b, c, d,}, B = {x, y, z}.
Classify the following function as injection, surjection or bijection : f : Z → Z given by f(x) = x2
If f : R → R be the function defined by f(x) = 4x3 + 7, show that f is a bijection.
If A = {1, 2, 3}, show that a one-one function f : A → A must be onto.
Find gof and fog when f : R → R and g : R → R is defined by f(x) = 2x + 3 and g(x) = x2 + 5 .
Find gof and fog when f : R → R and g : R → R is defined by f(x) = x and g(x) = |x| .
Let f : R → R and g : R → R be defined by f(x) = x2 and g(x) = x + 1. Show that fog ≠ gof.
Give examples of two functions f : N → N and g : N → N, such that gof is onto but f is not onto.
Find fog and gof if : f (x) = x+1, g (x) = sin x .
Find fog and gof if : f(x) = `x^2` + 2 , g (x) = 1 − `1/ (1-x)`.
` if f : (-π/2 , π/2)` → R and g : [−1, 1]→ R be defined as f(x) = tan x and g(x) = `sqrt(1 - x^2)` respectively, describe fog and gof.
Let C denote the set of all complex numbers. A function f : C → C is defined by f(x) = x3. Write f−1(1).
If f : C → C is defined by f(x) = x4, write f−1 (1).
Let `f : R - {- 3/5}` → R be a function defined as `f (x) = (2x)/(5x +3).`
f-1 : Range of f → `R -{-3/5}`.
Let f : R → R, g : R → R be two functions defined by f(x) = x2 + x + 1 and g(x) = 1 − x2. Write fog (−2).
Write the domain of the real function
`f (x) = 1/(sqrt([x] - x)`.
Write the domain of the real function f defined by f(x) = `sqrt (25 -x^2)` [NCERT EXEMPLAR]
Let A = {a, b, c, d} and f : A → A be given by f = {( a,b ),( b , d ),( c , a ) , ( d , c )} write `f^-1`. [NCERT EXEMPLAR]
Let
\[A = \left\{ x \in R : - 1 \leq x \leq 1 \right\} = B\] Then, the mapping\[f : A \to \text{B given by} f\left( x \right) = x\left| x \right|\] is
Let
f : R → R be given by
\[f\left( x \right) = \left[ x^2 \right] + \left[ x + 1 \right] - 3\]
where [x] denotes the greatest integer less than or equal to x. Then, f(x) is
(d) one-one and onto
The function \[f : [0, \infty ) \to \text {R given by } f\left( x \right) = \frac{x}{x + 1} is\]
Let
\[A = \left\{ x : - 1 \leq x \leq 1 \right\} \text{and} f : A \to \text{A such that f}\left( x \right) = x|x|\]
Let
\[f : R - \left\{ n \right\} \to R\]
The function
If \[f\left( x \right) = \sin^2 x\] and the composite function \[g\left( f\left( x \right) \right) = \left| \sin x \right|\] then g(x) is equal to
Let f: R – `{3/5}` → R be defined by f(x) = `(3x + 2)/(5x - 3)`. Then ______.
Let f: R → R be given by f(x) = tan x. Then f–1(1) is ______.
If f(x) = (4 – (x – 7)3}, then f–1(x) = ______.
Which of the following functions from Z into Z is bijective?
The mapping f : N → N is given by f(n) = 1 + n2, n ∈ N when N is the set of natural numbers is ____________.
Let f: R → R defined by f(x) = 3x. Choose the correct answer
A function f: x → y is said to be one – one (or injective) if:
The graph of the function y = f(x) is symmetrical about the line x = 2, then ______.
Which one of the following graphs is a function of x?
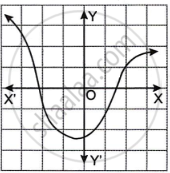 |
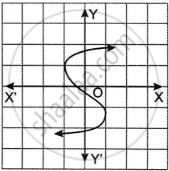 |
| Graph A | Graph B |
