Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Let IA and IB be moments of inertia of a body about two axes A and B respectively. The axis A passes through the centre of mass of the body but B does not.
Options
IA < IB
If IA < IB, the axes are parallel
If the axes are parallel, IA < IB
If the axes are not parallel, IA ≥ IB
Solution
If the axes are parallel, IA < IB
If axes A and B are parallel, we get
\[I_B = I_A + m r^2\]
Here, r is the distance between two axes and m is the mass of the body.
\[\therefore l_A<l_B\]
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Find the moment of inertia of a sphere about a tangent to the sphere, given the moment of inertia of the sphere about any of its diameters to be 2MR2/5, where M is the mass of the sphere and R is the radius of the sphere.
Given the moment of inertia of a disc of mass M and radius R about any of its diameters to be MR2/4, find its moment of inertia about an axis normal to the disc and passing through a point on its edge
A child stands at the centre of a turntable with his two arms outstretched. The turntable is set rotating with an angular speed of 40 rev/min. How much is the angular speed of the child if he folds his hands back and thereby reduces his moment of inertia to 2/5 times the initial value? Assume that the turntable rotates without friction.
Show that the child’s new kinetic energy of rotation is more than the initial kinetic energy of rotation. How do you account for this increase in kinetic energy?
A rope of negligible mass is wound round a hollow cylinder of mass 3 kg and radius 40 cm. What is the angular acceleration of the cylinder if the rope is pulled with a force of 30 N? What is the linear acceleration of the rope? Assume that there is no slipping.
A hoop of radius 2 m weighs 100 kg. It rolls along a horizontal floor so that its centre of mass has a speed of 20 cm/s. How much work has to be done to stop it?
A cylinder of mass 10 kg and radius 15 cm is rolling perfectly on a plane of inclination 30°. The coefficient of static friction µs = 0.25.
(a) How much is the force of friction acting on the cylinder?
(b) What is the work done against friction during rolling?
(c) If the inclination θ of the plane is increased, at what value of θ does the cylinder begin to skid, and not roll perfectly?
A body having its centre of mass at the origin has three of its particles at (a,0,0), (0,a,0), (0,0,a). The moments of inertia of the body about the X and Y axes are 0⋅20 kg-m2 each. The moment of inertia about the Z-axis
The pulley shown in the following figure has a radius 10 cm and moment of inertia 0⋅5 kg-m2about its axis. Assuming the inclined planes to be frictionless, calculate the acceleration of the 4⋅0 kg block.
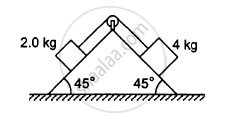
Solve the previous problem if the friction coefficient between the 2⋅0 kg block and the plane below it is 0⋅5 and the plane below the 4⋅0 kg block is frictionless.
A uniform metre stick of mass 200 g is suspended from the ceiling thorough two vertical strings of equal lengths fixed at the ends. A small object of mass 20 g is placed on the stick at a distance of 70 cm from the left end. Find the tensions in the two strings.
A wheel of moment of inertia 0⋅500 kg-m2 and radius 20⋅0 cm is rotating about its axis at an angular speed of 20⋅0 rad/s. It picks up a stationary particle of mass 200 g at its edge. Find the new angular speed of the wheel.
A diver having a moment of inertia of 6⋅0 kg-m2 about an axis thorough its centre of mass rotates at an angular speed of 2 rad/s about this axis. If he folds his hands and feet to decrease the moment of inertia to 5⋅0 kg-m2, what will be the new angular speed?
Two blocks of masses 400 g and 200 g are connected through a light string going over a pulley which is free to rotate about its axis. The pulley has a moment of inertia \[1 \cdot 6 \times {10}^{- 4} kg - m^2\] and a radius 2⋅0 cm, Find (a) the kinetic energy of the system as the 400 g block falls through 50 cm, (b) the speed of the blocks at this instant.
Why does a solid sphere have smaller moment of inertia than a hollow cylinder of same mass and radius, about an axis passing through their axes of symmetry?
A thin circular plate of mass M and radius R has its density varying as ρ(r) = ρ0r with ρ0 as constant and r is the distance from its center. The moment of Inertia of the circular plate about an axis perpendicular to the plate and passing through its edge is I = a MR2. The value of the coefficient a is ______.
A cubical block of mass 6 kg and side 16.1 cm is placed on a frictionless horizontal surface. It is hit by a cue at the top to impart impulse in the horizontal direction. The minimum impulse imparted to topple the block must be greater than ______ kg m/s.
