Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
State Gauss's law in electrostatics. Show, with the help of a suitable example along with the figure, that the outward flux due to a point charge 'q'. in vacuum within a closed surface, is independent of its size or shape and is given by `q/ε_0`
Solution
Statement: The electric flux linked with a closed surface is equal to `(1)/ε_0` times the net charge enclosed by a closed surface.
Mathematical expression :
`Ø_"E" = oint vec"E".dvec"s" = (1)/(ε_0) (q_"net")`
Consider two spherical surfaces of radius r and 2r respectively and a charge 1 is enclosed in it. According to gauss theorem, the total electric flux linked with a closed surface depends on the charge enclosed in it so
(a)
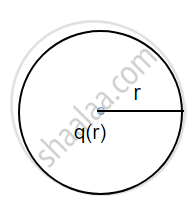
(b)
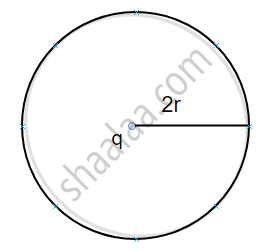
`Ø_E = q/ε_0 "and for fig"("b")`
`Ø_E = q/ε_0`.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
State and explain Gauss’s law.
A thin conducting spherical shell of radius R has charge Q spread uniformly over its surface. Using Gauss’s law, derive an expression for an electric field at a point outside the shell.
A charge Q is placed at the centre of a cube. Find the flux of the electric field through the six surfaces of the cube.
Answer the following question.
State Gauss's law for magnetism. Explain its significance.
Gaussian surface cannot pass through discrete charge because ____________.
The surface considered for Gauss’s law is called ______.
If there were only one type of charge in the universe, then ______.
- `oint_s` E.dS ≠ 0 on any surface.
- `oint_s` E.dS = 0 if the charge is outside the surface.
- `oint_s` E.dS could not be defined.
- `oint_s` E.dS = `q/ε_0` if charges of magnitude q were inside the surface.
If the total charge enclosed by a surface is zero, does it imply that the elecric field everywhere on the surface is zero? Conversely, if the electric field everywhere on a surface is zero, does it imply that net charge inside is zero.
The region between two concentric spheres of radii a < b contain volume charge density ρ(r) = `"c"/"r"`, where c is constant and r is radial- distanct from centre no figure needed. A point charge q is placed at the origin, r = 0. Value of c is in such a way for which the electric field in the region between the spheres is constant (i.e. independent of r). Find the value of c:
A charge Q is placed at the centre of a cube. The electric flux through one of its faces is ______.
