Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
The electric force experienced by a charge of 1.0 × 10−6 C is 1.5 × 10−3 N. Find the magnitude of the electric field at the position of the charge.
Solution
Given:
Magnitude of the charges, q = 1.0 × 10−6 C
Electric force, F = 1.5 × 10−3 N
We know that F = qE
\[\Rightarrow E = \frac{F}{q} = \frac{1 . 5 \times {10}^{- 3}}{1 . 0 \times {10}^{- 6}} \]
\[ = 1 . 5 \times {10}^3\]N/C
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
How does Ampere-Maxwell law explain the flow of current through a capacitor when it is being charged by a battery?
Mark out the correct options.
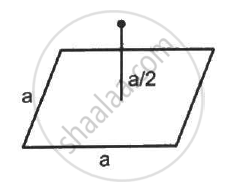
A charge Q is placed at a distance a/2 above the centre of a horizontal, square surface of edge a as shown in the following figure . Find the flux of the electric field through the square surface.
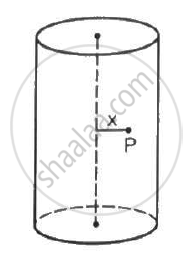
A long cylindrical volume contains a uniformly distributed charge of density ρ. Find the electric field at a point P inside the cylindrical volume at a distance x from its axis (see the figure).
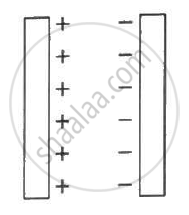
Two large conducting plates are placed parallel to each other and they carry equal and opposite charges with surface density σ as shown in the figure. Find the electric field (a) at the left of the plates (b) in between the plates and (c) at the right of the plates.
A positive charge q is placed in front of a conducting solid cube at a distance d from its centre. Find the electric field at the centre of the cube to the charges appearing on its surface.
When 1019 electrons are removed from a neutral metal plate through some process, the electric charge on it is ______
A conducting sphere of radius 0.104 m has an unknown charge. If the electric field at 0.20 m from the centre of the sphere is 1.5 x 103 NC-1 and points radially inward, what is the electric flux?
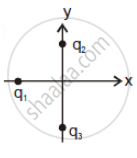
In figure two positive charges q2 and q3 fixed along the y-axis, exert a net electric force in the + x-direction on a charge q1 fixed along the x-axis. If a positive charge Q is added at (x, 0), the force on q1 ______.
(1) |
(2)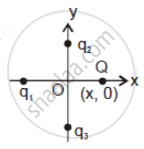 |
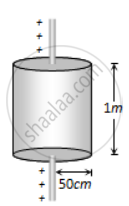
Electric charge is uniformly distributed along a long straight wire of radius 1 mm. The charge per cm length of the wire is Q coulomb. Another cylindrical surface of radius 50 cm and length 1 m symmetrically enclose the wire as shown in the figure. The total electric flux passing through the cylindrical surface is ______.
Two charges q1 and q2 are placed in vacuum at a distance d and the force acting between them is F. If a medium of dielectric constant 4 is introduced around them, the force now will be ______.
Total charge –Q is uniformly spread along length of a ring of radius R. A small test charge +q of mass m is kept at the centre of the ring and is given a gentle push along the axis of the ring.
- Show that the particle executes a simple harmonic oscillation.
- Obtain its time period.
Two identical metallic spheres A and B when placed at certain distance in air repel each other with a force of F. Another identical uncharged sphere C is first placed in contact with A and then in contact with B and finally placed at midpoint between spheres A and B. The force experienced by sphere C will be:
A charge of 4 µC is to be divided into two. The distance between the two divided charges is constant. The magnitude of the divided charges so that the force between them is maximum, will be:
A particle of mass m and charge q is placed at rest in a uniform electric field E and then released. The kinetic energy gained by the particle after moving a distance of y will be ______.
Two particles A and B having the same mass have charges +q and +4q, respectively. When they are allowed to fall from rest through the same electric potential difference the ratio of their speeds vA to vB will become ______.
The potential at a point x (measured in µm) due to some charges situated on the X-axis is given by v(x) = `20/((x^2 - 4)` V. The electric field E at x = 4 µm is given by ______.
