Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Through the mid-point M of the side CD of a parallelogram ABCD, the line BM is drawn intersecting diagonal AC in L and AD produced in E. Prove that: EL = 2BL.
Solution
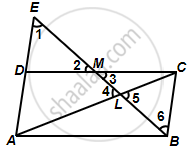
∠1 = ∠6 ...(Alternate interior angles)
∠2 = ∠3 ...(Vertically opposite angles)
DM = MC ...(M is the mid-point of CD)
∴ ∆DEM ≅ ∆CBM ...(AAS congruence criterion)
So, DE = BC ...(Corresponding parts of congruent triangles)
Also, AD = BC ...(Opposite sides of a parallelogram)
`=>` AE = AD + DE = 2BC
Now, ∠1 = ∠6 and ∠4 = ∠5
∴ ∆ELA ~ ∆BLC ...(AA similarity)
`=> (EL)/(BL) = (EA)/(BC)`
`=> (EL)/(BL) = (2BC)/(BC) = 2`
`=>` EL = 2BL
RELATED QUESTIONS
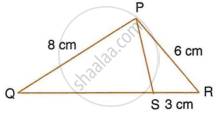
PQR is a triangle. S is a point on the side QR of ΔPQR such that ∠PSR = ∠QPR. Given QP = 8 cm, PR = 6 cm and SR = 3 cm.
- Prove ΔPQR ∼ ΔSPR.
- Find the length of QR and PS.
- `"area of ΔPQR"/"area of ΔSPR"`
In ∆PQR, ∠Q = 90° and QM is perpendicular to PR. Prove that:
- PQ2 = PM × PR
- QR2 = PR × MR
- PQ2 + QR2 = PR2
In ∆ABC, right – angled at C, CD ⊥ AB.
Prove:
`"CD"^2 = "AD"xx "DB"`
Given : AB || DE and BC || EF. Prove that :
- `(AD)/(DG) = (CF)/(FG)`
- ∆DFG ∼ ∆ACG
In the given figure, P is a point on AB such that AP : PB = 4 : 3. PQ is parallel to AC.
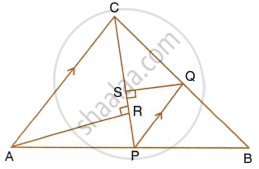
- Calculate the ratio PQ : AC, giving reason for your answer.
- In triangle ARC, ∠ARC = 90° and in triangle PQS, ∠PSQ = 90°. Given QS = 6 cm, calculate the length of AR.
In the figure, given below, ABCD is a parallelogram. P is a point on BC such that BP : PC = 1 : 2. DP produced meets AB produces at Q. Given the area of triangle CPQ = 20 cm2.

Calculate:
- area of triangle CDP,
- area of parallelogram ABCD.
In the given figure, ABC is a triangle. DE is parallel to BC and `(AD)/(DB)=3/2`
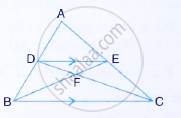
(1) Determine the ratios `(AD)/(AB) and (DE)/(BC)`
(2 ) Prove that ∆DEF is similar to ∆CBF Hence, find `(EF)/(FB)`.
(3) What is the ratio of the areas of ∆DEF and ∆BFC.
An aeroplane is 30 m long and its model is 15 cm long. If the total outer surface area of the model is 150 cm2, find the cost of painting the outer surface of the aeroplane at the rate of Rs.120 per sq. m. Given that 50 sq. m of the surface of the aeroplane is left for windows.
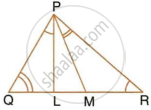
In a triangle PQR, L and M are two points on the base QR, such that ∠LPQ = ∠QRP and ∠RPM = ∠RQP. Prove that:
- ΔPQL ∼ ΔRPM
- QL × RM = PL × PM
- PQ2 = QR × QL
In the give figure, ABC is a triangle with ∠EDB = ∠ACB. Prove that ΔABC ∼ ΔEBD. If BE = 6 cm, EC = 4 cm, BD = 5 cm and area of ΔBED = 9 cm2. Calculate the:
- length of AB
- area of ΔABC

