Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Two waves of equal amplitude A, and equal frequency travel in the same direction in a medium. The amplitude of the resultant wave is
Options
0
A
2A
between 0 and 2A.
Solution
between 0 and 2A
The amplitude of the resultant wave depends on the way two waves superimpose, i.e., the phase angle (φ). So, the resultant amplitude lies between the maximum resultant amplitude (Amax) and the minimum resultant amplitude (Amin).
Amax = A + A = 2A
Amin = A − A = 0
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Use the formula `v = sqrt((gamma P)/rho)` to explain why the speed of sound in air increases with humidity.
For the wave described in Exercise 15.8, plot the displacement (y) versus (t) graphs for x = 0, 2 and 4 cm. What are the shapes of these graphs? In which aspects does the oscillatory motion in travelling wave differ from one point to another: amplitude, frequency or phase?
A steel rod 100 cm long is clamped at its middle. The fundamental frequency of longitudinal vibrations of the rod is given to be 2.53 kHz. What is the speed of sound in steel?
A train, standing at the outer signal of a railway station blows a whistle of frequency 400 Hz in still air. (i) What is the frequency of the whistle for a platform observer when the train (a) approaches the platform with a speed of 10 m s–1, (b) recedes from the platform with a speed of 10 m s–1? (ii) What is the speed of sound in each case? The speed of sound in still air can be taken as 340 m s–1.
A SONAR system fixed in a submarine operates at a frequency 40.0 kHz. An enemy submarine moves towards the SONAR with a speed of 360 km h–1. What is the frequency of sound reflected by the submarine? Take the speed of sound in water to be 1450 m s–1.
The radio and TV programmes, telecast at the studio, reach our antenna by wave motion. Is it a mechanical wave or nonmechanical?
Velocity of sound in air is 332 m s−1. Its velocity in vacuum will be
A wave pulse, travelling on a two-piece string, gets partially reflected and partially transmitted at the junction. The reflected wave is inverted in shape as compared to the incident one. If the incident wave has wavelength λ and the transmitted wave λ'
The displacement of the particle at x = 0 of a stretched string carrying a wave in the positive x-direction is given f(t) = A sin (t/T). The wave speed is v. Write the wave equation.
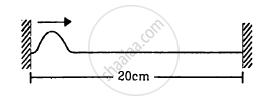
A string of length 20 cm and linear mass density 0⋅40 g cm−1 is fixed at both ends and is kept under a tension of 16 N. A wave pulse is produced at t = 0 near an ends as shown in the figure, which travels towards the other end. (a) When will the string have the shape shown in the figure again? (b) Sketch the shape of the string at a time half of that found in part (a).
A 200 Hz wave with amplitude 1 mm travels on a long string of linear mass density 6 g m−1 kept under a tension of 60 N. (a) Find the average power transmitted across a given point on the string. (b) Find the total energy associated with the wave in a 2⋅0 m long portion of the string.
The string of a guitar is 80 cm long and has a fundamental frequency of 112 Hz. If a guitarist wishes to produce a frequency of 160 Hz, where should the person press the string?
An organ pipe of length 0.4 m is open at both ends. The speed of sound in the air is 340 m/s. The fundamental frequency is ______
A string 1 m long is fixed at one end. The other end is moved up and down with a frequency of 20 Hz. Due to this, a stationary wave with four complete loops gets produced on the string. Find the speed of the progressive wave which produces the stationary wave.
Use the formula `v = sqrt((gamma P)/rho)` to explain why the speed of sound in air is independent of pressure.
Use the formula `v = sqrt((gamma P)/rho)` to explain why the speed of sound in air increases with temperature.
For the travelling harmonic wave
y (x, t) = 2.0 cos 2π (10t – 0.0080x + 0.35)
Where x and y are in cm and t in s. Calculate the phase difference between oscillatory motion of two points separated by a distance of `λ/2`.
A string of mass 2.5 kg is under a tension of 200 N. The length of the stretched string is 20.0 m. If the transverse jerk is struck at one end of the string, the disturbance will reach the other end in ______.
Given below are some functions of x and t to represent the displacement of an elastic wave.
- y = 5 cos (4x) sin (20t)
- y = 4 sin (5x – t/2) + 3 cos (5x – t/2)
- y = 10 cos [(252 – 250) πt] cos [(252 + 250)πt]
- y = 100 cos (100πt + 0.5x)
State which of these represent
- a travelling wave along –x direction
- a stationary wave
- beats
- a travelling wave along +x direction.
Given reasons for your answers.
An engine is approaching a cliff at a constant speed. When it is at a distance of 0.9 km from cliff it sounds a whistle. The echo of the sound is heard by the driver after 5 seconds. Velocity of sound in air is equal to 330 ms-1. The speed of the engine is ______ km/h.
