Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
A string of length 20 cm and linear mass density 0⋅40 g cm−1 is fixed at both ends and is kept under a tension of 16 N. A wave pulse is produced at t = 0 near an ends as shown in the figure, which travels towards the other end. (a) When will the string have the shape shown in the figure again? (b) Sketch the shape of the string at a time half of that found in part (a).
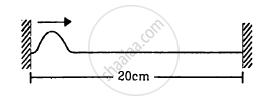
Solution
Given,
Length of the string = 20 cm
Linear mass density of the string = 0.40 g cm−1
Applied tension = 16 N = \[16 \times {10}^5 dyn\]
Velocity of the wave:
\[\nu = \sqrt{\left( \frac{T}{m} \right)}\]
\[ = \sqrt{\frac{\left( 16 \times {10}^5 \right)}{0 . 4}}\]
\[ = 2000 \text{ cm }/s\]
∴ Time taken to reach the other end
\[= \frac{20}{2000} = 0 . 01 s\]
Time taken to see the pulse again in the original position
\[= 0 . 01 \times 2 = 0 . 02 s\]
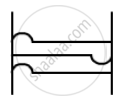
(b) At t = 0.01 s, there will be a trough at the right end as it is reflected.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
For the wave described in Exercise 15.8, plot the displacement (y) versus (t) graphs for x = 0, 2 and 4 cm. What are the shapes of these graphs? In which aspects does the oscillatory motion in travelling wave differ from one point to another: amplitude, frequency or phase?
A SONAR system fixed in a submarine operates at a frequency 40.0 kHz. An enemy submarine moves towards the SONAR with a speed of 360 km h–1. What is the frequency of sound reflected by the submarine? Take the speed of sound in water to be 1450 m s–1.
The radio and TV programmes, telecast at the studio, reach our antenna by wave motion. Is it a mechanical wave or nonmechanical?
Show that the particle speed can never be equal to the wave speed in a sine wave if the amplitude is less than wavelength divided by 2π.
Velocity of sound in air is 332 m s−1. Its velocity in vacuum will be
Two wave pulses travel in opposite directions on a string and approach each other. The shape of one pulse is inverted with respect to the other.
A wave propagates on a string in the positive x-direction at a velocity \[\nu\] \[t = t_0\] is given by \[g\left( x, t_0 \right) = A \sin \left( x/a \right)\]. Write the wave equation for a general time t.
The equation of a wave travelling on a string is \[y = \left( 0 \cdot 10 \text{ mm } \right) \sin\left[ \left( 31 \cdot 4 m^{- 1} \right)x + \left( 314 s^{- 1} \right)t \right]\]
(a) In which direction does the wave travel? (b) Find the wave speed, the wavelength and the frequency of the wave. (c) What is the maximum displacement and the maximum speed of a portion of the string?
A wave travels along the positive x-direction with a speed of 20 m s−1. The amplitude of the wave is 0⋅20 cm and the wavelength 2⋅0 cm. (a) Write the suitable wave equation which describes this wave. (b) What is the displacement and velocity of the particle at x= 2⋅0 cm at time t = 0 according to the wave equation written? Can you get different values of this quantity if the wave equation is written in a different fashion?
A travelling wave is produced on a long horizontal string by vibrating an end up and down sinusoidally. The amplitude of vibration is 1⋅0 and the displacement becomes zero 200 times per second. The linear mass density of the string is 0⋅10 kg m−1 and it is kept under a tension of 90 N. (a) Find the speed and the wavelength of the wave. (b) Assume that the wave moves in the positive x-direction and at t = 0, the end x = 0 is at its positive extreme position. Write the wave equation. (c) Find the velocity and acceleration of the particle at x = 50 cm at time t = 10 ms.
A 200 Hz wave with amplitude 1 mm travels on a long string of linear mass density 6 g m−1 kept under a tension of 60 N. (a) Find the average power transmitted across a given point on the string. (b) Find the total energy associated with the wave in a 2⋅0 m long portion of the string.
The equation for the vibration of a string, fixed at both ends vibrating in its third harmonic, is given by
\[y = \left( 0 \cdot 4 cm \right) \sin\left[ \left( 0 \cdot 314 {cm}^{- 1} \right) x \right] \cos \left[ \left( 600\pi s^{- 1} \right) t \right]\]
(a) What is the frequency of vibration? (b) What are the positions of the nodes? (c) What is the length of the string? (d) What is the wavelength and the speed of two travelling waves that can interfere to give this vibration?
A man standing unsymmetrical position between two mountains and fires a gun. He hears the first echo after 1.5 s and the second echo after 2.5 s. If the speed of sound in air is 340 m/s, then the distance between the mountains will be ______
What is the interference of sound waves?
A bat emits an ultrasonic sound of frequency 1000 kHz in the air. If the sound meets a water surface, what is the wavelength of the the reflected sound? The speed of sound in air is 340 m s–1 and in water 1486 m s–1.
For the travelling harmonic wave
y (x, t) = 2.0 cos 2π (10t – 0.0080x + 0.35)
Where x and y are in cm and t in s. Calculate the phase difference between oscillatory motion of two points separated by a distance of `λ/2`.
Sound waves of wavelength λ travelling in a medium with a speed of v m/s enter into another medium where its speed is 2v m/s. Wavelength of sound waves in the second medium is ______.
Speed of sound waves in a fluid depends upon ______.
- directty on density of the medium.
- square of Bulk modulus of the medium.
- inversly on the square root of density.
- directly on the square root of bulk modulus of the medium.
At what temperatures (in °C) will the speed of sound in air be 3 times its value at O°C?
The amplitude of wave disturbance propagating in the positive x-direction given is by `1/(1 + x)^2` at time t = 0 and `1/(1 + (x - 2)^2)` at t = 1 s, where x and y are in 2 metres. The shape of wave does not change during the propagation. The velocity of the wave will be ______ m/s.
