Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Two wave pulses travel in opposite directions on a string and approach each other. The shape of one pulse is inverted with respect to the other.
Options
The pulses will collide with each other and vanish after collision.
The pulses will reflect from each other, i.e., the pulse going towards right will finally move towards left and vice versa.
The pulses will pass through each other but their shapes will be modified.
The pulses will pass through each other without any change in their shapes.
Solution
The pulses will pass through each other without any change in their shapes.
The pulses continue to retain their identity after they meet, but the moment they meet their wave profile differs from the individual pulse.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Use the formula `v = sqrt((gamma P)/rho)` to explain why the speed of sound in air increases with humidity.
A bat emits an ultrasonic sound of frequency 1000 kHz in the air. If the sound meets a water surface, what is the wavelength of the transmitted sound? The speed of sound in air is 340 m s–1 and in water 1486 m s–1.
A hospital uses an ultrasonic scanner to locate tumours in a tissue. What is the wavelength of sound in the tissue in which the speed of sound is 1.7 km s–1? The operating frequency of the scanner is 4.2 MHz.
A steel rod 100 cm long is clamped at its middle. The fundamental frequency of longitudinal vibrations of the rod is given to be 2.53 kHz. What is the speed of sound in steel?
The radio and TV programmes, telecast at the studio, reach our antenna by wave motion. Is it a mechanical wave or nonmechanical?
Show that the particle speed can never be equal to the wave speed in a sine wave if the amplitude is less than wavelength divided by 2π.
Two strings A and B, made of same material, are stretched by same tension. The radius of string A is double of the radius of B. A transverse wave travels on A with speed `v_A` and on B with speed `v_B`. The ratio `v_A/v_B` is ______.
Velocity of sound in air is 332 m s−1. Its velocity in vacuum will be
A wave pulse, travelling on a two-piece string, gets partially reflected and partially transmitted at the junction. The reflected wave is inverted in shape as compared to the incident one. If the incident wave has wavelength λ and the transmitted wave λ'
Two wires A and B, having identical geometrical construction, are stretched from their natural length by small but equal amount. The Young modules of the wires are YA and YB whereas the densities are \[\rho_A \text{ and } \rho_B\]. It is given that YA > YB and \[\rho_A > \rho_B\]. A transverse signal started at one end takes a time t1 to reach the other end for A and t2 for B.
The equation of a wave travelling on a string stretched along the X-axis is given by
\[y = A e {}^- \left( \frac{x}{a} + \frac{t}{T} \right)^2 .\]
(a) Write the dimensions of A, a and T. (b) Find the wave speed. (c) In which direction is the wave travelling? (d) Where is the maximum of the pulse located at t = T? At t = 2 T?
A sonometer wire of length l vibrates in fundamental mode when excited by a tuning fork of frequency 416. Hz. If the length is doubled keeping other things same, the string will ______.
A string of length 40 cm and weighing 10 g is attached to a spring at one end and to a fixed wall at the other end. The spring has a spring constant of 160 N m−1 and is stretched by 1⋅0 cm. If a wave pulse is produced on the string near the wall, how much time will it take to reach the spring?
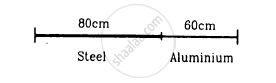
Figure shows an aluminium wire of length 60 cm joined to a steel wire of length 80 cm and stretched between two fixed supports. The tension produced is 40 N. The cross-sectional area of the steel wire is 1⋅0 mm2 and that of the aluminium wire is 3⋅0 mm2. What could be the minimum frequency of a tuning fork which can produce standing waves in the system with the joint as a node? The density of aluminium is 2⋅6 g cm−3 and that of steel is 7⋅8 g cm−3.
Use the formula `v = sqrt((gamma P)/rho)` to explain why the speed of sound in air increases with temperature.
A sound wave is passing through air column in the form of compression and rarefaction. In consecutive compressions and rarefactions ______.
If c is r.m.s. speed of molecules in a gas and v is the speed of sound waves in the gas, show that c/v is constant and independent of temperature for all diatomic gases.
The displacement y of a particle in a medium can be expressed as, y = `10^-6sin(100t + 20x + pi/4)` m where t is in second and x in meter. The speed of the wave is ______.
