Advertisements
Advertisements
Questions
What is ferromagnetism?
Explain the following with suitable examples:
Ferromagnetism
Solution 1
The substances that can be permanently magnetised even in the absence of a magnetic field are called ferromagnetic substances, and the mechanism is called ferromagnetism.
Solution 2
The substances that are strongly attracted by a magnetic field are called ferromagnetic substances. Ferromagnetic substances can be permanently magnetised even in the absence of a magnetic field. Some examples of ferromagnetic substances are iron, cobalt, nickel, gadolinium, and CrO2.
In solid state, the metal ions of ferromagnetic substances are grouped together into small regions called domains, and each domain acts as a tiny magnet. In an unmagnetized piece of a ferromagnetic substance, the domains are randomly oriented, and so their magnetic moments get cancelled. However, when the substance is placed in a magnetic field, all the domains get oriented in the direction of the magnetic field. As a result, a strong magnetic effect is produced. This ordering of domains persists even after the removal of the magnetic field. Thus the ferromagnetic substance becomes a permanent magnet.
Schematic alignment of magnetic moments in ferromagnetic substances
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Iron (z=26) is highly ferromagnetic. Explain.
What type of magnetism is shown in the following alignment of magnetic moments?

Define the following term: Ferromagnetism
Write the type of magnetism observed when the magnetic moments are aligned in parallel and anti-parallel directions in unequal numbers.
What type of substances would make better permanent magnets, ferromagnetic or ferrimagnetic. Justify your answer.
Analysis shows that nickel oxide has the formula Ni0.98O1.00. What fractions of nickel exist as Ni2+ and Ni3+ ions?
Explain the following with suitable examples: Paramagnetism
Explain the following with suitable examples: Antiferromagnetism
Give reasons:Ferrimagnetic substances show better magnetism than antiferromagnetic substances.
The complexion [Ni(CN)4]2- is:
Explain why:
(i) Transition elements form coloured compounds.
(ii) Interhalogen compounds are more reactive than their constituent elements.
(iii) Cu+ is diamagnetic but Cu2+ is paramagnetic. (Z = 29)
Pyrolusite ore is _______.
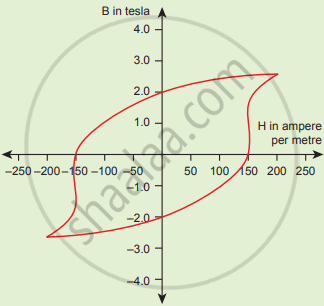
The BH curve for a ferromagnetic material is shown in the figure. The material is placed inside a long solenoid which contains 1000 turns/cm. The current that should be passed in the solenonid to demagnetize the ferromagnet completely is
What is magnetic susceptibility?
Give the properties of dia/para/ferromagnetic materials.
All those atoms or molecules which have an odd number of electrons are
Substances that are strongly attracted by the applied magnetic field and can be permanently magnetized are ____________.
When heated to high temperature, ferromagnetic substance changes to ____________.
Fe3O4 is ____________.
Which type of substances would make better permanent magnets?
Assertion: On heating ferromagnetic or ferrimagnetic substances, they become paramagnetic.
Reason: The electrons change their spin on heating.
Fe3O4 (magnetite) is an example of ___________.
A ferromagnetic substance becomes a permanent magnet when it is placed in a magnetic field becuase ______.
The value of magnetic moment is zero in the case of antiferromagnetic substances because the domains:
(i) get oriented in the direction of the applied magnetic field.
(ii) get oriented opposite to the direction of the applied magnetic field.
(iii) are oppositely oriented with respect to each other without the application of magnetic field.
(iv) cancel out each other’s magnetic moment.
Which of the following statements are correct?
(i) Ferrimagnetic substances lose ferrimagnetism on heating and become paramagnetic.
(ii) Ferrimagnetic substances do not lose ferrimagnetism on heating and remain ferrimagnetic.
(iii) Antiferromagnetic substances have domain structures similar to ferromagnetic substances and their magnetic moments are not cancelled by each other.
(iv) In ferromagnetic substances all the domains get oriented in the direction of magnetic field and remain as such even after removing magnetic field.
Which one of the following homo-diatomic molecule is paramagnetic?
The heat of combustion of a substance is:
Given below are two statements labelled as Assertion (A) and Reason (R).
Assertion: Magnetic moment values of actinides are lesser than the theoretically predicted values.
Reason: Actinide elements are strongly paramagnetic.
Select the most appropriate answer from the options given below:
The correct order of bond strength is ______.
The susceptibility of a paramagnetic material is 99. The permeability of the material in Wb/A-m is ______.
[permeability of the free space μ0 = 4π × 10-7 Wb/A - m]
Among the following ions, which one has the highest paramagnetism?
Match items of List - I with those of List - II:
| List - I | List - II | ||
| (Property) | (Example) | ||
| (A) | Diamagnetism | (i) | MnO |
| (B) | Ferrimagnetism | (ii) | O2 |
| (C) | Paramagnetism | (iii) | NaCl |
| (D) | Antiferromagnetism | (iv) | Fe3O4 |
Choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below:
Which one of the following compounds is diamagnetic and colourless?
The metal complex ion that is paramagnetic is ______.
(Atomic number of Fe = 26, Cu = 29, Co = 27 and Ni = 28)
