Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
What is lanthanoid contraction?
Solution 1
The atomic and ionic radii of lanthanoids gradually decrease with an increase in atomic number. This process is known as lanthanoid contraction.
Solution 2
In the lanthanoid series, as the atomic number increases, the atomic and ionic radii decrease from one element to the next, but this decrease is very small. For example – on going from Ce to Lu the atomic radius decreases from 183 pm to 173 pm and this decrease is only 10 pm. Similarly, on going from Ce3+ to Lu3+ ion the ionic radius decreases from 103 pm to 85 pm, which is only 18 pm. Hence, for an increase of 14 in atomic number, the decrease in atomic and ionic radii is much less. This decrease is much less than the elements of other groups and periods.
Table - Variation in atomic and ionic radii of lanthanum and lanthanoids (pm)
| Element | La | Ce | Pr | Nd | Pm | Sm | Eu | Gd | Tb | Dy | Ho | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu |
| Radius (Ln) | 187 | 183 | 182 | 181 | 181 | 180 | 199 | 180 | 178 | 177 | 176 | 175 | 174 | 173 | - |
| Radius (Ln3+) | 106 | 103 | 101 | 99 | 98 | 96 | 95 | 94 | 92 | 91 | 89 | 88 | 87 | 85 | - |
The steady decrease in atomic and ionic sizes of lanthanoid elements with an increase in atomic number is called 'lanthanoid contraction'.
The decrease in ionic radii of trivalent lanthanoids (Ln3+) is shown in.
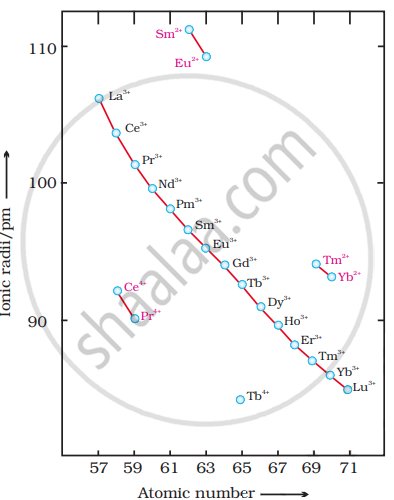
Causes of Lanthanide Contraction: In the lanthanoid series, on going from one element to the next, the nuclear charge increases by one unit and an electron is added. These new electrons are added to the parallel 4f-subshells. However, the shielding effect of one 4f-electron on the other 4f-electron (from the nuclear charge) is less due to the very large size of the f-orbitals. Although the nuclear charge increases by one unit at each step, the effective nuclear charge experienced by each 4f-electron increases with the increase in atomic number and nuclear charge. As a result, the entire 4f-electron shell contracts with the addition of each element, although this reduction is minimal. As a result, a regular decrease in the size of lanthanoids is observed with increasing atomic number. The sum of successive reductions gives the total lanthanoid contraction.
Notes
Students can refer to the provided solutions based on their preferred marks.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Account for the following :
Zr and Hf have almost similar atomic radii.
What are the different oxidation states exhibited by the lanthanoids?
Compare the chemistry of actinoids with that of lanthanoids with special reference to electronic configuration.
Name the members of the lanthanoid series which exhibit +4 oxidation state and those which exhibit +2 oxidation state. Try to correlate this type of behavior with the electronic configurations of these elements.
Write the electronic configurations of the elements with the atomic numbers 61, 91, 101 and 109.
What are the consequences of lanthanoid contraction?
Explain the cause of lanthanoid contraction?
Account for the following:
Zn, Cd and Hg are soft metals.
What is Lanthanoid contraction?
Answer the followiiig questions:
Which trivalent ion has maximum size in the Lanthanoid series i.e. Lanthanum ion (La3+) to Luteium ion (Lu3+)?
(at. no. of Lanthanum = 57 and Lutetium = 71)
Name an element of lanthanoid series which is well knwon to shown +4 oxidation state. Is it a strong oxidising agent or reducing agent?
What is meant by Lanthanide contraction? Write the general electronic configuration of inner transition elements.
What is the action of the following on lanthanoids?
a. water
b. Sulphur, heat
c. nitrogen, heat
The f-block elements are known as ____________.
Gadolinium belongs to 4f series. It’s atomic number is 64. Which of the following is the correct electronic configuration of gadolinium?
Although +3 oxidation states is the characteristic oxidation state of lanthanoids but cerium shows +4 oxidation state also. Why?
Match the compounds/elements given in Column I with uses given in Column II.
| Column I (Compound/element) | Column II (Use) | |
| (i) | Lanthanoid oxide | (a) Production of iron alloy |
| (ii) | Lanthanoid | (b) Television screen |
| (iii) | Misch metal | (c) Petroleum cracking |
| (iv) | Magnesium based alloy is constituent of | (d) Lanthanoid metal + iron |
| (v) | Mixed oxides of lanthanoids are employed | (e) Bullets |
| (f) In X-ray screen |
On the basis of Lanthanoid contraction, explain the following:
Trends in the stability of oxo salts of lanthanoids from \[\ce{La}\] to \[\ce{Lu}\].
On the basis of Lanthanoid contraction, explain the following:
Radii of 4d and 5d block elements.
Which of the following pairs has the same ionic size?
The titanium (Z = 22) compound that does not exist is:-
Zr(Z = 40) and Hf(Z = 72) have similar atomic and ionic radii because of ______
Zr (Z = 40) and Hf (Z = 72) have similar atomic and ionic radii because of _______.
Write any two consequences of Lanthanoid Contraction.
Mischmetal is an alloy consisting mainly of ______.
Cerium (Z = S8) is an important member of lanthanoids. Which of the following statements about cerium is incorrect?
State a reason for the following:
La(OH)3 is more basic than Lu(OH)3.
Why is Mn2+ ion more stable than Fe2+ ion?
(Atomic numbers of Mn = 25 and Fe = 26)
Assertion: There is a continuous increase in size among Lanthanoids with an increase in atomic number.
Reason: Lanthanoids do not show Lanthanoid contraction.
Mention alloy uses.
