Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Which sample, A or B shown in figure has shorter mean-life?
Solution
Mean (or average) life (ґ): The time for which a radioactive material remains active is defined as the mean (average) life of that material.
• It is defined as the sum of lives of all atoms divided by the total number of atoms.
i.e., `r = "Sum of the lives of all the atoms"/"Total number of atoms" = 1/λ`
• From `N = N_0e^(-λt)` ⇒ In `(N/N_0)/t = - λ`, the slope of the line shown in the graph, i.e., the magnitude of the inverse of slope of `N/N_0` vs t curve is known as mean life (τ).

• From `N = N_0e^(-λt)`, if `t = 1/λ = τ`
⇒ `N = N_0e^(-t) = N_0(1/e)` = 0.37 N0
= 37% of N0
i.e., mean life is the time interval in which the number of undecayed atoms (N) becomes `1/e` times or 0.37 times or 37% of the original number of atoms
• It is the time in which the number of decayed atoms (N0 – N) becomes `(1 - 1/e)` times or 0.63 times or 63% of the original number of atoms.
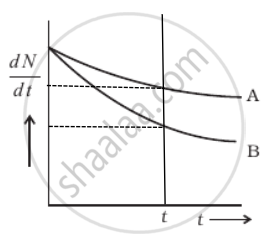
From the given figure, we can say that
At t = 0, `((dN)/(dt))_A = ((dN)/(dt))_B`
As `(dN)/(dt) = - λN`
⇒ (N0)A = (N0)B
Now considering any instant t by drawing a line perpendicular to the time axis, we find that `((dN)/(dt))_A > ((dN)/(dt))_B`
Hence, λANA = λBNB
∴ NA > NB ⇒ λB > λB ......[Rate of decay of B is slower]
But average life `τ = 1/λ` ⇒ τA > τB
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
A radioactive isotope has a half-life of T years. How long will it take the activity to reduce to a) 3.125%, b) 1% of its original value?
Under certain circumstances, a nucleus can decay by emitting a particle more massive than an α-particle. Consider the following decay processes:
\[\ce{^223_88Ra -> ^209_82Pb + ^14_6C}\]
\[\ce{^223_88 Ra -> ^219_86 Rn + ^4_2He}\]
Calculate the Q-values for these decays and determine that both are energetically allowed.
Two different radioactive elements with half lives T1 and T2 have N1 and N2 undecayed atoms respectively present at a given instant. Derive an expression for the ratio of their activities at this instant in terms of N1 and N2 ?
Define the activity of a given radioactive substance. Write its S.I. unit.
A freshly prepared radioactive source of half-life 2 h emits radiation of intensity which is 64 times the permissible safe level. The minimum time after which it would be possible to work safely with this source is
The decay constant of 238U is 4.9 × 10−18 S−1. (a) What is the average-life of 238U? (b) What is the half-life of 238U? (c) By what factor does the activity of a 238U sample decrease in 9 × 109 years?
Disintegration rate of a sample is 1010 per hour at 20 hours from the start. It reduces to 6.3 x 109 per hour after 30 hours. Calculate its half-life and the initial number of radioactive atoms in the sample.
The half-life of the radioactive substance is 40 days. The substance will disintegrate completely in
Suppose we consider a large number of containers each containing initially 10000 atoms of a radioactive material with a half life of 1 year. After 1 year ______.
A piece of wood from the ruins of an ancient building was found to have a 14C activity of 12 disintegrations per minute per gram of its carbon content. The 14C activity of the living wood is 16 disintegrations per minute per gram. How long ago did the tree, from which the wooden sample came, die? Given half-life of 14C is 5760 years.
