Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Solution
What is perfect competition? Explain price determination under perfect competition.
Perfect competition is a market situation where there are large number of buyers and seller. Buying and selling homogenous products at a single uniform price.
Conditions of perfect competition are
(a) Large number of buyers and sellers
(b) Homogeneous product
(c) Uniform price
(d) Free entry and Exist
(e) Perfect Knowledge
(f) Perfect mobility of production factors.
(g) Absence if transport cost
(h) Absence of Government interference
Price Determination under Perfect Competition
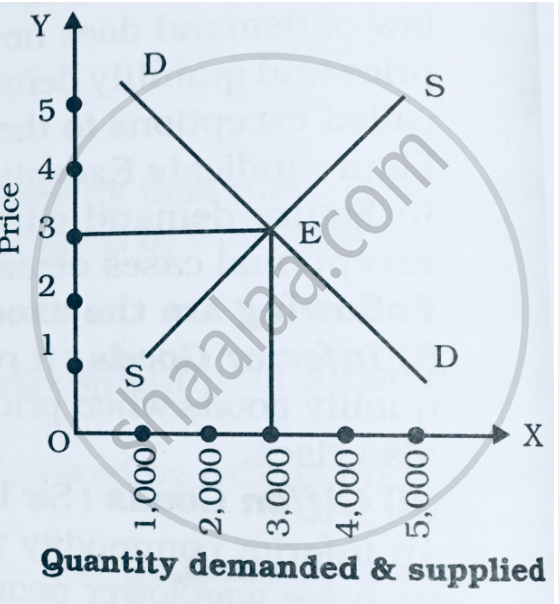
Equilibrium price: Equilibrium price is the price at which quantity demanded is equal to quantity supplied. The price of the product under perfect competition, is influenced by both buyers and sellers and equilibrium price is determined by the interaction of demand and supply forces. According to Marshall, demand and supply are like two blades of a pair of scissors. Just as cutting of cloth is not possible with the use of one blade, the equilibrium price of a commodity cannot be determined, either by the forces of demand or by supply alone. Both together determine the price.
We can study this with the help of the following table and graph.
|
Price (Rs)
Per Unit
|
Quantity Demanded (Units)
|
Quantity Supplied (Units)
|
|
5
|
100
|
500
|
|
4
|
200
|
400
|
|
3
|
300
|
300
|
|
2
|
400
|
200
|
|
1
|
500
|
100
|
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
State whether the following statement is True or False
Product differentiation is the most distinguishing feature of monopolistic competition.
What are the features of perfect competition.
The objective of a seller in monopoly market is...............................
(loss \ profit \ negative profit \ zero profit)
The seller is a price maker in the perfect competition.
Explain the features of monopoly.
Homogenous product’ is a characteristic of : (choose the correct alternative)
(a) Perfect competition only
(b) Perfect oligopoly only
(c) Both (a) and (b)
(d) None of the above
There is inverse relation between price and demand for the product of a firm under:
(choose the correct alternative)
(a) Monopoly only
(b) Monopolistic competition only
(c) Both under monopoly and monopolistic competition
(d) Perfect competition only
Explain the implications of the following in a perfectly competitive market:
Large number of buyers
Explain the implications of the following in an oligopoly market:
Inter- dependence between firms
Giving reason, state whether the following statement is true or false.
A Monopolist can sell any quantity he likes at a price.
Differentiated products is a characteristic of: (Choose the correct alternative):
(a) Monopolistic competition only
(b) Oligopoly only
(c) Both monopolistic competition and oligopoly
(d) Monopoly
Demand curve of a firm is perfectly elastic under: (Choose the correct alternative)
(a) Perfect competition
(b) Monopoly
(c) Monopolistic competition
(d) Oligopoly
Explain the implications of the following in an oligopoly market: Barriers to entry of new firms
Explain the implications of the following in an oligopoly market: A few or a few big sellers
Explain the implications of the following : Product differentiation in monopolistic competition.
What is price-maker firm?
Explain the implications of the following in a perfectly competitive market:
Freedom of entry and exit to firms
Explain the implications of the following in an oligopoly market:
Non-price competition
Average revenue and Price are always equal under:(choose the correct alternative)
(a) Perfect competition only
b) Monopolistic competition only
(c) Monopoly only
(d) All market forms
Explain the 'free entry and exit of firms' feature of monopolistic competition.
A seller cannot influence the market price under (choose the correct alternative)
a) Perfect competition
b) Monopoly
c) Monopolistic competition
d) All of the above
Distinguish between perfect oligopoly and imperfect oligopoly. Also, explain the interdependence between the firms' feature of oligopoly.
What is meant by collusive oligopoly?
Price discrimination is possible under monopoly.
In monopolistic completion, goods have no close substitutes.
Define or Explain the following concepts
Monopoly
Explain the significance of the feature 'product differentiation' in monopolistic competition.
Give reason or explain the following.
Price discrimination is possbile under monopoly.
Fill in the blank with proper alternatives given in the bracket:
Under monopoly there is existence of ______________ .
State whether the following statement is true or false.
There is no product differentiation under monopolistic competition.
Define or Explain :
Average revenue.
State whether the following statement is True or False with reason:
Perfect competition means pure competition.
Distinguish between :
Output method and Expenditure method.
Distinguish between Any FOUR of the following :
Consumption expenditure and Investment expenditure.
State with reasons, whether you Agree or Disagree with the following statements.
Perfect competition is an imaginary concept.
Give reasons or explain the following statements
There is single price in perfect competition.
Answer the following question
What are the features of Perfect Competition?
Answer the following question
What are the features of monopoly?
Answer the following question
What are the features of monopolistic competition?
State with reason whether you agree or disagree with the following statement
Perfect Competition means Monopolistic Competition.
Answer in detail
What is Perfect Competition? Explain price determination under Perfect Competition.
Answer in detail
What is monopoly? Explain in detail the features of monopoly?
Distinguish between the following:
Perfect competition and Pure competition
Distinguish between the following:
Perfect competition and Monopoly
Distinguish between the following:
Natural monopoly and legal monopoly
Distinguish between the following:
Perfect competition and Monopolistic competition
Distinguish between the following:
Natural monopoly and Social monopoly
Define or explain the following concept:
Monopolistic Competition
Define or explain the following concept:
Selling cost
Give reason or explain:
Single price prevails in perfect competition.
Give reason or explain:
Price discrimination is possible under monopoly.
Give reason or explain:
Selling cost is incurred by a firm in Monopolistic competition.
Give reason or explain:
A monopolist can control the supply of goods.
Give reason or explain:
Sellers and the buyers are price takers in perfect competition.
State whether the following statement is TRUE and FALSE.
There is no price discrimination under Monopolistic competition.
State whether the following statement is TRUE and FALSE.
In a monopoly market, firm and industry are the same.
State whether the following statement is TRUE and FALSE.
Product differentiation is not possible under perfect competition.
Match the following:
|
Group A
|
Group B
|
|
Monopoly
|
Public monopoly
|
|
Product differentiation
|
Abnormal profit
|
|
Railway
|
Monopolistic Competition
|
|
Perfect Competition
|
Prof. Chamberlin
|
|
Pure Competition
|
Homogenous product
|
|
|
Cartel
|
|
|
Selling cost
|
Fill in the blank with appropriate alternative given below
Under perfect competition commodities are ________________ in nature.
Fill in the blank with appropriate alternative given below
_____________ appears in a monopoly market.
Fill in the blank with appropriate alternative given below
Monopolist means __________ competitive.
Define 'or' explain the following concept.
Product Differentiation:
Answer the following question.
What is the reason for an indeterminate demand curve under Oligopoly?
Answer the following question.
Elaborate three main features of a monopoly form of market.
Distinguish between perfect competition and monopolistic competition on the basis of the following:
(a) Number of sellers
(b) Nature of product
(c) Selling cost
Observe the table and answer the question:
| Price of banana (per dozen) in ₹ | Demand (in dozen) | Supply (in dozen) | Relation between DD and SS |
| 10 | 500 | 100 | DD > SS |
| 20 | 400 | _____ | DD > SS |
| 30 | _____ | 300 | DD = SS |
| 40 | 200 | _____ | DD < SS |
| 50 | ______ | 500 | DD < SS |
Fill in the blanks in the above schedule.
Features of oligopoly market:
- There are few firms or sellers.
- Sellers sell differentiated product.
- There is free entry and exit of firms.
- There is considerable element of uncertainty in this type of market.
Find the odd word
Selling cost -
PASSAGE
In India, markets for automobiles, cement, steel, aluminium, etc, are the examples of oligopolistic market. In all these markets, there are few firms for each particular product. Duopoly is a special case of oligopoly, in which there are exactly two sellers. Under duopoly, it is assumed that the product sold by the two firms is homogeneous and there is no substitute for it. Examples where two companies control a large proportion of a market are: (i) Pepsi and Coca-Cola in the soft drink market; (ii) Airbus and Boeing in the commercial large jet aircraft market.
Operating systems for smart phones and computers provide excellent examples of oligopolies in big tech. Apple iOS and Google Android dominate smart phone operating systems. Computer operating systems are overshadowed by Apple and Microsoft Windows.
- Give examples of oligopolistic market in India (1 mark)
- Explain the concept of duopoly with a suitable example from the passage (1 mark)
- Express your personal opinion based on the above information (2 marks)
In which one of the following types of markets are Average Revenue curve and Market Demand curve the same?
